 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Psophocarpus_tetragonolobus_Blanco2.293-cropped.jpg |
 |
| http://www.hear.org/starr/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

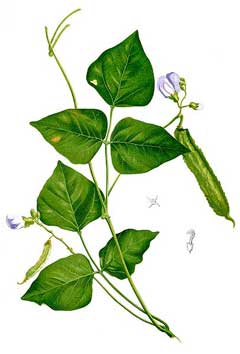
 Psophocarpus tetragonolobus is a PERENNIAL growing to 2 m (6ft 7in).
Psophocarpus tetragonolobus is a PERENNIAL growing to 2 m (6ft 7in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10 and is frost tender. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in heavy clay soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Flowers Leaves Oil Oil Root Seed Seedpod Shoots Stem
Edible Uses: Coffee Colouring Oil Oil
Young seedpods - cooked for a few minutes[2, 46, 61, 116]. They tastes like French beans (Phaseolus vulgaris)[183]. The pods are harvested when about 15 - 20 cm long and 2cm wide[200]. They will store for up to 21 days at 10°c with a relative humidity of 90%[200]. The yields of pods average 250 - 500g per m²[200]. Immature seeds are used in soups etc[183]. Mature seeds are eaten cooked[2, 46, 61, 116]. They are very nutritious, being rich in oil (up to 17%)[160], protein, vitamin E and calcium. The seed can also be roasted and eaten like peanuts or fermented and used as tempeh[183]. An edible oil is obtained from the seed[183]. Root - raw or cooked like potatoes[160, 183]. Slightly sweet, it contains 20% or more protein, which is about 12 times that of potatoes[116, 183]. Leaves and young shoots - cooked. They are used like spinach[61, 116, 183]. Flowers and flower buds - raw or cooked[183]. They have a flavour similar to mushrooms when sautéed[116]. The light blue flowers are also used as a colouring in foods[183]. The roasted seed is a coffee substitute[183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Agroforestry Services: Nitrogen Management: Standard Minor Global Crop Staple Crop: Protein-oil
Prefers a loamy slightly acidic soil, but there are cultivars suitable for many soil types[200]. Tolerates heavy soils[116] but dislikes wet soils[200]. Dislikes drought[200]. Very widely cultivated as a food plant in the tropics and sub-tropics, there are many named varieties[183]. It is usually treated as an annual. In temperate zones it has to be grown as an annual crop. Most varieties will only flower when daylight hours are around 12 per day[116] but day-neutral varieties are being developed that will flower in the summer in northerly and southerly latitudes[200]. Temperatures in the range of 25 - 30°c are necessary for optimum growth[200]. Plants take 60 - 80 days from sowing to the first harvest of seedpods[200]. Mature tubers can be harvested 120 - 240 days from sowing[200]. The plant is very disease resistant[160]. This species has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria, these bacteria form nodules on the roots and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Some of this nitrogen is utilized by the growing plant but some can also be used by other plants growing nearby[200].
Carbon Farming
-
Agroforestry Services: Nitrogen
Plants that contribute to nitrogen fixation include the legume family – Fabaceae.
-
Management: Standard
Plants grow to their standard height. Harvest fruit, seeds, or other products. Non-Destructive management systems.
-
Minor Global Crop
These crops are already grown or traded around the world, but on a smaller scale than the global perennial staple and industrial crops, The annual value of a minor global crop is under $1 billion US. Examples include shea, carob, Brazil nuts and fibers such as ramie and sisal.
-
Staple Crop: Protein-oil
(16+ percent protein, 16+ percent oil). Annuals include soybeans, peanuts, sunflower seeds. Perennials include seeds, beans, nuts, and fruits such as almond, Brazil nut, pistachio, walnut, hazel, and safou.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Pre-soak the seed for 12 hours in warm water and sow in early spring in a warm greenhouse. Place two or three seeds in each pot, thinning to the strongest plant. Plant them out in late spring or early summer, after the last expected frosts and give them the protection of a cloche or cold frame until they are growing away strongly[240].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Betlanei, Charfakia, Chipir, Dambala, Dara-dhambala, Fava de cavalo, Fogiolo quadrato, Four angled bean, Goa bean, Goabohne, Kacang botor, Kachang belimbing, Kachang botol, Kachang botor, Kechipir, Kecipir, Manilla bean, Pois asperge, Prapiey chrung, Samporong, Sbai daograng, Sem, Shikakumame, Si jiang dou, Sigarilyas, Sikaku mame, Su-ling dou, Sz kok tau, Thua phuu, Thua pu, Tua pu, asparagus bean|dara dambala, asparagus-pea, calamismis, four-angle-bean, goa bean, goa-bean, goabohne, goaböna, hane-mi-sasage, pois carré, princess-pea, shikaku-mame, winged bean, winged pea, winged-bean.
Native Range
Coming Soon
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(L.)DC.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment