 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koeh-246.jpg |
 |
| USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database |
Translate this page:
Summary
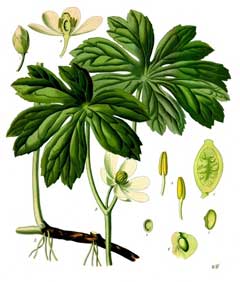
Bloom Color: White. Main Bloom Time: Early spring, Mid spring. Form: Upright or erect.
Physical Characteristics

 Podophyllum peltatum is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft) by 0.3 m (1ft in) at a medium rate.
Podophyllum peltatum is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft) by 0.3 m (1ft in) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 4 and is not frost tender. It is in leaf from April to October, in flower from May to June, and the seeds ripen from July to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs). The plant is not self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid and neutral soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) or semi-shade (light woodland). It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Dappled Shade; Shady Edge; not Deep Shade;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Fruit
Edible Uses:
Fruit - raw, cooked or made into jams, jellies, marmalades, pies etc[1, 2, 4, 43, 101, 183]. The fruit can also be dried for later use[257]. The fruit should only be eaten when it is fully ripe[55, 62, 95], the unripe fruit is strongly laxative[183]. Remove the rind[95]. The fruit is very aromatic[95], and has a peculiar though agreeable flavour[183]. Sweet and acid. Do not eat the seeds[62]. In excess the fruit can cause colic[22, 65, 159]. The fruit is about 5cm long[200].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antibilious Cancer Cathartic Cytostatic Homeopathy Hydrogogue Purgative Warts
Women's complaints
American mandrake is a most powerful and useful herbal medicine, exercising an influence on every part of the system and stimulating the glands to healthy action[4]. Its greatest power lies in its action on the liver and bowels[4]. It is a gastro-intestinal irritant, a powerful hepatic and intestinal stimulant[4]. Although often used internally in the past, the plant's cytotoxic action makes it an unsafe remedy for internal use[254]. The root is antibilious, cathartic, cytostatic, hydrogogue and purgative[4, 19, 46, 57, 64, 124, 222]. The plant contains podophyllin, which has an antimiotic effect (it interferes with cell division and can thus prevent the growth of cells). It is, therefore, a possible treatment for cancer, and has been used especially in the treatment of ovarian cancer[46, 51, 57, 64, 65, 124, 244]. However, alopecia is said to be a common side-effect of this treatment[244]. The root is most active medicinally in early spring when it is beginning to shoot[4]. The resin, which is obtained from the root[207], is used in the treatment of warts and has been found to be effective against uterine warts that are sometimes experienced in pregnancy[200, 222]. It is also used in the treatment of small-cell carcinoma[207]. The root is harvested in the autumn and either dried for later use or the resin is extracted[238]. The whole plant, apart from the ripe fruit, is highly poisonous and should only be used under the supervision of a qualified practitioner[238]. It should not be prescribed for pregnant women[238]. Large doses have been used to commit suicide[213]. A homeopathic remedy is obtained from the fresh root, harvested before the fruit is ripe[232]. This is used particularly in the treatment of diarrhoea[232].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Insecticide
An infusion of the boiled leaves has been sprayed on potato plants to protect them from insects[213]. Other reports suggest that it is insecticidal rather than repellent[238, 257]. The root ooze has been used to soak corn seed prior to planting it out in order to prevent it being eaten by crows or insects[257].
Special Uses
Food Forest Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Ground cover, Woodland garden. Prefers a moist peaty soil and filtered light or shade[4, 111]. Grows well in a moist open woodland[28, 31] and also succeeds under beech trees in a deep moist leafy soil[130]. Succeeds in a pH ranging from 4 to 7[238]. A very hardy plant[4], tolerating temperatures down to -15°c or lower when dormant[187], though the young leaves in spring can be damaged by late frosts[233]. Plants in this genus have excited quite a lot of interest for the compounds found in their roots which have been shown to have anti-cancer activity[124]. There are various research projects under way (as of 1990)[124]. The flower has a foul smell[232]. The plant takes some years to become established[124] but is very long lived in a suitable habitat[130] and can become a vigorous colonizer[233]. Special Features:
North American native, Naturalizing. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 8 through 2. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is a runner spreading indefinitely by rhizomes or stolons [1-2]. The root pattern is fibrous dividing into a large number of fine roots [1-2]. The root pattern is rhizomatous with underground stems sending roots and shoots along their length [1-2].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame. Sow stored seed in a cold frame in early spring. The seed germinates in 1 - 4 months at 15°c. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when they are large enough to handle and grow on in a shady part of the greenhouse for at least 2 growing seasons. Plant them out into their permanent positions in the winter when the plants are dormant. Division in March/April[111].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: Canada, Québec, Nova Scotia, Ontario, United States, Connecticut, Indiana, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Wisconsin, Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Texas,
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
43200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Podophyllum peltatum
|
|
|
|