 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Justicia_gendarussa_Blanco1.80-cropped.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:J.M.Garg |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

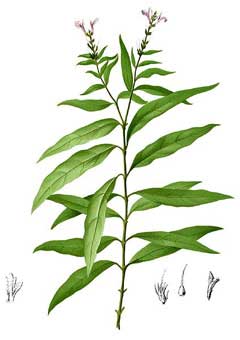
 Justicia gendarussa is a deciduous Shrub growing to 1 m (3ft 3in). The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs).
Justicia gendarussa is a deciduous Shrub growing to 1 m (3ft 3in). The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs).
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Gendarussa vulgaris. Nees.
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anodyne Antiperiodic Antiphlogistic Antispasmodic Carminative Diaphoretic Diuretic Emetic
Febrifuge Laxative
The leaf is antispasmodic, carminative[147] and has antiperiodic properties[218]. The leaves and tender young shoots are diaphoretic[240]. A decoction is used in the treatment of chronic rheumatism[240]. An infusion of the leaves is taken internally in the treatment of pains in the head, paralysis of one side of the body and facial paralysis[240]. The leaf juice is used in the treatment of earache[240]. The bitter root is anodyne, diaphoretic, diuretic and laxative[218]. The root bark is emetic[218]. The whole plant is emetic and febrifuge[240]. A decoction is used to treat bruises[218].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Insecticide
The dried leaves are used to repel insects from clothing[218].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
We have very little information on this species, it is probably not hardy in this country but might succeed outdoors in the mildest areas. One report says that it should be grown in a warm greenhouse and treated like a Fuchsia[1].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow spring in a greenhouse. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when large enough to handle and grow on in the greenhouse for at least the first winter. Plant out in late spring or early summer after the last expected frosts and give some protection over the winter.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: China (Fujian Sheng, Guangdong Sheng, Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu, Hainan Sheng, Yunnan Sheng)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
1146
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment