 |
|
https://edibleplants.org/ |
 |
| wikimedia.org |
Translate this page:
Summary
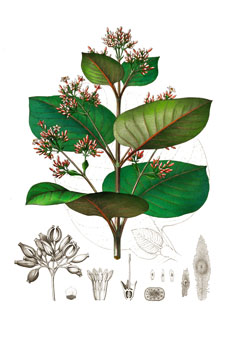
A native species to Central and South America, Red Bark or Red Cinchona (Cinchona pubescens) is a usually 10 m tall deciduous tree with small, thick, and hairy branches known as an effective medicinal plant for malaria due to the quinine content of its bark. It is fast-growing and flowering starts 2 - 3 years after planting. The bark is a bitter, astringent, tonic herb and made into powder, tablets, liquid extracts and tinctures. It should be noted however that excessive use of such has various side effects like headache, rash, abdominal pain, deafness, and blindness. The quinine is also used in making hair oils, shampoo, and insecticide, and as a vulcanizing agent, and in the preparation of certain metals.
Physical Characteristics

 Cinchona pubescens is an evergreen Tree growing to 15 m (49ft) by 15 m (49ft) at a fast rate.
Cinchona pubescens is an evergreen Tree growing to 15 m (49ft) by 15 m (49ft) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10. The flowers are pollinated by Bees, Butterflies.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Cinchona caloptera Miq. Cinchona chomeliana Wedd. Cinchona colorata Laubert ex B.D.Jacks. Cinchona c
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Inner bark
Edible Uses: Drink
Quinine, extracted from the bark of the tree, is used as a bitter flavouring in tonic waters, some liqueurs, carbonated drinks, baked goods, candy etc[ 238 , 301 ].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antispasmodic Astringent Bitter Cardiac Febrifuge Malaria Tonic
Red bark has a long history of native use, especially as a treatment for fevers and malaria. Modern research has shown it to be a very effective treatment for fevers, and especially as a treatment and preventative of malaria. The bark contains various alkaloids, particularly quinine and quinidine. Up to 70 - 80% of the total alkaloids contained in the bark are quinine[ 418 ]. The bark is a bitter, astringent, tonic herb that lowers fevers, relaxes spasms, is antimalarial (the alkaloid quinine) and slows the heart (the alkaloid quinidine)[ 238 ]. The bark is made into various preparations, such as tablets, liquid extracts, tinctures and powders[ 238 ]. It is used internally in the treatment of malaria, neuralgia, muscle cramps and cardiac fibrillation[ 238 ]. It is an ingredient in various proprietary cold and influenza remedies[ 238 ]. The liquid extract is useful as a cure for drunkenness[ 418 ]. It is also used as a gargle to treat sore throats[ 238 ]. Care must be taken in the use of this herb since excess can cause a number of side effects including cinchonism, headache, rash, abdominal pain, deafness and blindness[ 238 ]. The herb, especially in the form of the extracted alkaloid quinine, is subject to legal restrictions in some countries[ 238 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Hair Insecticide Teeth
Other uses rating: Low (2/5). The alkaloid quinine, extracted from the bark, is used in products like hair oils and shampoo, sun-tan oil, insecticides, as a vulcanizing agent in the rubber industry, and in the preparation of certain metals[ 418 ].
Special Uses
Carbon Farming Coppice
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Industrial Crop: Medicinal Management: Coppice Minor Global Crop
A plant of moderate elevations in the moist tropics, where it is found at elevations from 800 - 3,500 metres. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 17 - 25°c, but can tolerate 9 - 28°c[ 418 ]. It can be killed by temperatures of 5°c or lower[ 418 ]. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 2,500 - 3,500mm, but tolerates 1,400 - 4,000mm[ 418 ]. Requires a well-drained, moist soil and a position in full sun or partial shade[ 238 , 418 ]. It grows very poorly or not at all on soils that have been exposed to fire[ 418 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5 - 6, tolerating 4.5 - 6.5[ 418 ]. A fast-growing tree, the plants start flowering after 2 - 3 years, and are uprooted and harvested after 8 - 12 years[ 418 ]. In commercial plantations, the trees are coppiced when about 6 years old[ 238 ].
Carbon Farming
-
Industrial Crop: Medicinal
Most pharmaceuticals are synthesized from petroleum but 25% of modern medicines are based on plants.
-
Management: Coppice
Cut to the ground repeatedly - resprouting vigorously. Non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Minor Global Crop
These crops are already grown or traded around the world, but on a smaller scale than the global perennial staple and industrial crops, The annual value of a minor global crop is under $1 billion US. Examples include shea, carob, Brazil nuts and fibers such as ramie and sisal.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Red Bark or Red Cinchona (Cinchona pubescens). Other Names: Jesuits' Peruvian-bark; red Cinchona; red Peruvian-bark; sacred Peruvian-bark. Spanish: cascarilla amarga; cascarilla gallinazo; varona. French: quinquina rouge. Brazil: quina-do-Amazonas. Ecuador: cascarilla; roja-roja.
Native Range
SOUTHERN AMERICA: Costa Rica, Panama (Chiriquí), Venezuela, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Widely introduced throughout the tropics over the past 150 years because of its medicinal properties. However, it is only in small island systems, notably the Galapagos and Hawaii, that it has become invasive [1d].
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Vahl
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Cinchona pubescens
|
|
|
|