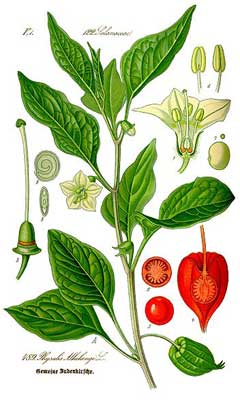
 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illustration_Physalis_alkekengi0_clean.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Llez |
Translate this page:
Summary
Bloom Color: Orange. Main Bloom Time: Early fall, Late summer. Form: Irregular or sprawling.
Physical Characteristics

 physalis alkekengi is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft) by 0.6 m (2ft in) at a fast rate.
physalis alkekengi is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft) by 0.6 m (2ft in) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6 and is not frost tender. It is in flower in July. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
P. francheti. P. latifolia.
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Fruit Leaves
Edible Uses:
Fruit - raw or cooked[1, 2, 105]. Rich in vitamins[100], with twice the vitamin C of lemons[179], but not much taste[178]. Another report says that they are juicy but with a bitter acrid flavour[4], whilst another says that they add a delicious flavour to salads[7]. We have found them to be bitter and rather unpleasant[K]. The fruit is a berry about 17mm in diameter[200]. The plant conveniently wraps up each fruit in its own 'paper bag' (botanically, the calyx) to protect it from pests and the elements. This calyx is toxic and should not be eaten[34, 65]. Young leaves - cooked[105, 170, 179]. Caution is advised, the leaves are almost certainly poisonous, at least when raw.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antiphlogistic Antirheumatic Antitussive Aperient Diuretic Expectorant Febrifuge Homeopathy
Lithontripic Malaria Urinary Vitamin C
The plant has a long history of herbal use, and an interesting chemistry, but it is seldom used in modern practice[238]. The whole plant is antiphlogistic, antipyretic, antitussive and expectorant[9, 61, 147, 178, 218]. It has been used in the treatment of urinary and skin diseases[240]. Some caution is recommended since an overdose of the plant is said to easily precipitate an abortion[218]. The fruit is aperient, strongly diuretic and lithontripic[4, 7, 9, 218]. It is used internally in the treatment of gravel, suppression of urine etc and is highly recommended in fevers and in gout[4, 238]. The fruit is harvested when fully ripe and can be used fresh, juiced or dried[238]. The calyx should be removed[238]. The leaves and stems are febrifuge and slightly tonic[4]. They are used in the treatment of the malaise that follows malaria, and for weak or anaemic people[4]. The fresh leaves have been used externally to make soothing poultices in the treatment of skin inflammations[238, 244]. The seed is used to promote early labour[218]. A homeopathic remedy is made from the fruit. It is used in the treatment of kidney and bladder disorders[9].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Border, Container. Succeeds in any well-drained soil in full sun or light shade[111, 200]. The fully dormant plant is hardy in most of Britain, though the young growth in spring can be damaged by late frosts. A very ornamental plant[1] though it can be invasive[200]. The sub-species P. alkekengi francheti. Mak. (sometimes treated as a separate species) is a more vigorous form of the species with larger fruits[200]. Slugs are very fond of the new growth in spring and can destroy even quite large clumps[K]. Special Features:
Naturalizing, Suitable for dried flowers.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow March/April in a greenhouse only just covering the seed. Germination usually takes place quickly and freely. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots of fairly rich soil when they are large enough to handle and plant them out in early summer. Diurnal temperature fluctuations assist germination[170]. Division in spring[111]. Very easy, larger divisions can be planted out direct into their permanent positions. We have found that it is better to pot up the smaller divisions and grow them on in light shade in a cold frame until they are well established before planting them out in late spring or early summer. Basal cuttings in early summer[111]. Harvest the shoots with plenty of underground stem when they are about 8 - 10cm above the ground. Pot them up into individual pots and keep them in light shade in a cold frame or greenhouse until they are rooting well. Plant them out in the summer.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Iran (n. & w.), Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia (Ciscaucasia), Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, China TROPICAL ASIA: India (Jammu and Kashmir) EUROPE: Austria, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, Belarus, Moldova, Ukraine (incl. Krym), Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Croatia, Italy, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Physalis acutifolia | Sharp-Leaf Ground Cherry | Annual | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Physalis alkekengi | Winter Cherry, Strawberry groundcherry,Ground Cherry, Chinese Lantern | Perennial | 0.3 |
6-9
| F | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 2 | |
| Physalis alkekengi franchetii | Winter Cherry | Perennial | 0.5 |
5-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Physalis angulata | Cutleaf Ground Cherry | Annual | 0.8 |
0-0
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Physalis angustifolia | Coastal groundcherry | Perennial | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis arenicola | Cypresshead groundcherry | Perennial | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis carpenteri | Carpenter's groundcherry | Annual | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis caudella | Southwestern groundcherry | Perennial | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis crassifolia | Yellow nightshade groundcherry | Perennial | 0.3 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | DM | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis foetens | | Annual | 0.6 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis foetens neomexicana | | Annual | 0.6 |
-
| | LMH | N | DM | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis greenei | | Annual | 0.3 |
-
| | LMH | N | DM | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis hederaefolia cordifolia | Ground Cherry | Perennial | 0.3 |
-
| | LMH | SN | DM | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis heterophylla | Clammy Ground Cherry, Rowell's groundcherry | Perennial | 0.9 |
7-10
| | LMH | SN | DM | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Physalis ixocarpa | Tomatillo | Annual | 1.2 |
7-10
| | LMH | SN | DM | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| Physalis lanceolata | Ground Cherry, Sword groundcherry | Perennial | 0.4 |
0-0
| | LMH | SN | DM | 2 | 1 | |
| Physalis latiphysa | Broadleaf groundcherry | | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis macrophysa | Bladder Ground Cherry, Longleaf groundcherry | Perennial | 1.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis minima | Sunberry, Pygmy groundcherry | Annual | 0.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | SN | DM | 3 | 1 | |
| Physalis missouriensis | Missouri groundcherry | Annual | 1.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis obscura | | Annual | 1.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis peruviana | Goldenberry, Peruvian groundcherry | Perennial | 1.2 |
10-12
| M | LMH | SN | M | 5 | 1 | 3 |
| Physalis philadelphica | Wild Tomatillo, Mexican groundcherry | Annual | 0.6 |
6-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Physalis pruinosa | Strawberry Tomato | Annual | 0.6 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | DM | 3 | 0 | |
| Physalis pubescens | Ground Cherry, Husk tomato | Annual | 0.5 |
10-12
| | LMH | SN | DM | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Physalis pumila | Prairie Ground Cherry, Dwarf groundcherry | Perennial | 0.3 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis subglabrata | Longleaf groundcherry | Perennial | 1.5 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | DM | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis variovestita | Field groundcherry | | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Physalis virginiana | Virginia Ground Cherry | Perennial | 0.6 |
6-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Physalis virginiana sonorae | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | DM | 2 | 0 | |
|
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment