 |
|
http://www.edibleplants.org |
 |
| cookislands.bishopmuseum.org |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

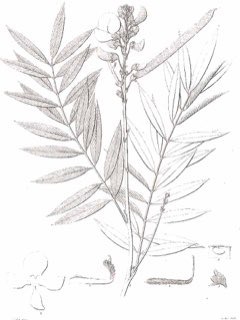
 Tephrosia candida is a deciduous Shrub growing to 3 m (9ft) by 3 m (9ft) at a medium rate.
Tephrosia candida is a deciduous Shrub growing to 3 m (9ft) by 3 m (9ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10. The flowers are pollinated by Insects.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Cracca candida (DC.) Kuntze Kiesera sericea Reinw. Robinia candida Roxb. Xiphocarpus candidus (DC.)
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Biomass Fuel Green manure Hedge Insecticide Soil conditioner Soil reclamation Soil stabilization
Agroforestry Uses: With its ability to fix large amounts of atmospheric nitrogen and produce a good bulk of biomass, white tephrosia is widely used in agroforestry as a green manure crop, to restore degraded land etc[303 ]. Not only does it provide nitrogen, the plant also raises soil phosphorus and potassium levels in proportion to increased levels of organic matter[303 ]. Soil structure improves, water-holding capacity and permeability increase, and soil losses caused by water erosion decrease[303 ]. It can yield well on acid soils; for example, in Vietnam, green-matter content of the soil increased from 1.7 to 4%[303 ]. White tephrosia is widely grown in mixed cultivation, for example with pineapple, maize and other annual crops, and it is said to improve the quality of tobacco. Cassava is a shade-sensitive species and needs regular lopped hedgerows, for which T. Candida is a very suitable species. It has been tried as an alley crop with cassava planted in 7-m-wide inter-rows. Preliminary results indicate a greatly increased yield of cassava and a considerable reduction of erosion[303 ]. It is grown as a temporary shade crop in newly planted perennial crops such as citrus, coconut, coffee, rubber and tea[303 ]. It has been used for rehabilitating degraded land[303 ]. Suitable for making hedges along contours, around fields and home gardens, as it is not eaten by domestic animals such as buffaloes and goats[303 ]. It is commonly used for hedgerows, providing mulch for different upland crops[303 ]. Other Uses Powdered leaves are used as an insecticide[303 ]. When the species becomes woody with age, it provides suitable fuel wood[303 ].
Special Uses
Food Forest Hedge Nitrogen Fixer
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
A plant of the seasonally dry tropics, where it is found at elevations up to 1,650 metres. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 20 - 30°c, but can tolerate 14 - 34°c[418 ]. It does not tolerate frost[303 ]. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 1,400 - 1,800mm, but tolerates 700 - 2,700mm[418 ]. Prefers a sunny position, tolerating light shade[418 ]. Grows well on sandy soils in coastal areas and on very poor, eroded upland soils and mine spoils where few other crops can grow[303 ]. Plants are intolerant of waterlogged soils[303 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 4.5 - 6.5, tolerating 3.5 - 7.5[418 ]. The more acidic soils seem to be more suitable[303 ]. White tephrosia is a deep rooting and can be slow to establish, but it grows steadily once established[303 ]. Maximum growth normally takes place in the 2nd year after planting, but with regular pruning a dense cover can be maintained for many years[303 ]. Annual biomass yields of about 12 - 18 tonnes per hectare can be obtained when the plant is grown with cassava, whilst 20 - 40 tonnes or more can be obtained when grown on its own[303 ]. Flowering times vary considerably - in Malaysia it flowers all year round, but it only flowers for 2 months of the year in Vietnam[303 ]. Over-mature pods will shatter and lose their seeds[303 ]. This species has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria, these bacteria form nodules on the roots and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Some of this nitrogen is utilized by the growing plant but some can also be used by other plants growing nearby[200 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - soak the seed for 4 - 5 hours in warm water prior to sowing[303 ]. It should be sown just before or during the rainy season. The germination rate of fresh seed is 95 - 100%, but viability decreases rapidly unless seeds are stored in a cool, dry place[303 ]. When broadcasting, a planting density of 50 000-60 000/ha is aimed at, requiring 15-20 kg seed[303 ]. Seed storage behaviour is orthodox. No loss in viability following 3 years in either open storage or hermetic storage at room temperature with 13% ? 2% mc. There are between 300 and 500 seeds/kg[303 ].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TROPICAL ASIA: Bhutan (natzd.?), India, Nepal (natzd.?)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
DC.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Tephrosia candida
|
|
|
|