 |
|
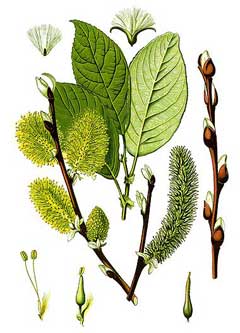
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cleaned-Illustration_Salix_caprea.jpg |
 |
|
Translate this page:
Summary
Bloom Color: Yellow. Main Bloom Time: Early spring, Late spring, Mid spring. Form: Rounded.
Physical Characteristics

 Salix caprea is a deciduous Tree growing to 10 m (32ft) by 8 m (26ft) at a fast rate.
Salix caprea is a deciduous Tree growing to 10 m (32ft) by 8 m (26ft) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 5 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from March to April, and the seeds ripen in May. The species is dioecious (individual flowers are either male or female, but only one sex is to be found on any one plant so both male and female plants must be grown if seed is required). and is pollinated by Bees. The plant is not self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and can grow in heavy clay soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers dry moist or wet soil. The plant can tolerate maritime exposure.
It can tolerate atmospheric pollution.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Canopy; Secondary; Ground Cover; Hedge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Inner bark Leaves Manna Shoots
Edible Uses:
Inner bark - raw or cooked. It can be dried, ground into a powder and then added to cereal flour for use in making bread etc. A very bitter flavour, it is a famine food that is only used when all else fails[172]. Young shoots - raw or cooked. They are not very palatable[172]. The source of an edible manna[183]. No further details.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anodyne Aphrodisiac Astringent Febrifuge Ophthalmic Stimulant
The fresh bark of all members of this genus contains salicin[226], which probably decomposes into salicylic acid (closely related to aspirin) in the human body[213]. This is used as an anodyne and febrifuge[226]. A decoction of the leaves is used in the treatment of fevers[240]. A distilled water from the flowers is aphrodisiac, cordial and stimulant[240]. It is used externally in the treatment of headaches and ophthalmia[240]. The ashes of the wood are useful in the treatment of haemoptysis[240]. The stems and the leaves are astringent[240]. A gum and the juice of the trees are used to increase visual powers[240].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Basketry Charcoal Hedge Hedge Leather Pioneer Shelterbelt Tannin Wood
Landscape Uses: Border, Massing, Pollard, Standard, Specimen. The stems are very flexible and are used in basket making[61]. The plant is usually coppiced annually when grown for basket making, though it is possible to coppice it every two years if thick poles are required as uprights. The bark is tough and flexible, it is used as a substitute for leather[115]. The bark contains around 10% tannin[223]. The plant is fast growing and tolerant of maritime exposure, it can be used as a windbreak hedge and shelterbelt though it is of untidy habit[75]. The seeds are very light and so can travel some distance in the wind. The plant is therefore able to find its way to areas such as cleared woodland where the soil has been disturbed. Seedlings will grow away quickly, even in exposed conditions and the plant will provide good shelter for the establishment of woodland plants. Thus it makes a good pioneer species and, except in wetter and moorland-type soils, will eventually be largely out-competed by the other woodland trees. Its main disadvantage as a pioneer plant is that it has an extensive root system and is quite a greedy plant, thus it will not help as much in enriching the soil for the other woodland plants as other pioneer species such as the alders, Alnus species[K]. Some cultivars can be grown as ground cover[208]. 'Pendula' is female whilst 'Kilmarnock' is a male, they should be spaced about 1.5 metres apart each way[208]. Wood - soft, elastic, easily split. Used for baskets, rugs etc[46, 61]. A good quality charcoal is made from the wood[46, 61]. Dynamic accumulator.
Special Uses
Ground cover Hedge Hedge
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Succeeds in most soils, including wet, ill-drained or intermittently flooded soils[1], but prefers a damp, heavy soil in a sunny position. Grows in drier soils than any other British species of Salix[186]. Rarely thrives on chalk[200]. Plants are found most frequently on basic soils in the wild[17]. Tolerates atmospheric pollution and exposed positions, including maritime exposure[75, 186]. A fast growing tree, it establishes well[75]. The tree has an untidy habit[75]. A light demanding tree, it becomes tall and drawn when grown in woodland, though it grows well along the sunnier edges[186]. Hybridizes freely with other members of this genus[200]. Although the flowers are produced in catkins early in the year, they are pollinated by bees and other insects rather than by the wind[11]. Trees are very tolerant of cutting, they coppice well[186]. Plants in this genus are notably susceptible to honey fungus[200]. Dioecious. Male and female plants must be grown if seed is required. Special Features:Not North American native, Wetlands plant, Attractive flowers or blooms.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - must be surface sown as soon as it is ripe in late spring. It has a very short viability, perhaps as little as a few days. Cuttings of mature wood of the current year's growth, November to February in a sheltered outdoor bed or planted straight into their permanent position and given a good weed-suppressing mulch. Cuttings of this species do not root well[200]. Plant into their permanent positions in the autumn. Cuttings of half-ripe wood, June to August in a frame. Cuttings of this species do not root well[200].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Turkey, Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia (Ciscaucasia), Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russian Federation (Dagestan), Russian Federation-Western Siberia (Western Siberia), Russian Federation-Eastern Siberia (Eastern Siberia), Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Russian Federation-Far East (Far East), China (Heilongjiang Sheng, Jilin Sheng, Liaoning Sheng, Nei Mongol Zizhiqu) EUROPE: Denmark, Finland, United Kingdom, Ireland, Norway, Sweden, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Russian Federation (European part), Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Ukraine (incl. Krym), Albania, Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece, Croatia, Italy, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France (incl. Corsica)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
1117200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment