 |
|
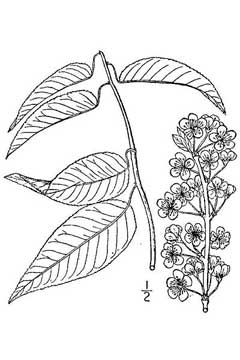
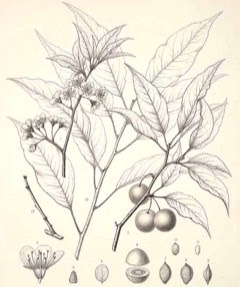
USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913. An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. Vol. 2: 323. |
 |
|
Translate this page:
Summary
Hog Plum (P. hortulana) is a small to medium-sized tree with thin-skinned tasty fruit about 12mm (0.5in) in diameter. This tree is of very little value in colder temperate areas, requiring hotter summers to fruit well. The genus Prunus includes deciduous or evergreen shrubs and trees with showy spring flowers and good autumn leaf colour; some have attractive ornamental bark. Prunus includes several species developed for fruit and nut production, such as apricots, cherries, peaches, nectarines, almonds, and plums. Other species are useful in food forests for their seed and fruit. Most edible fruit from this genus is eaten raw, cooked or dried for later use. Seeds are edible, but if they are bitter, eat them in strict moderation. Several Prunus species will succeed in light shade but fruit better in a sunny position. The seeds of all members of this genus could be used for oil extraction. The extracted oil is semi-drying. Consume in small quantities if it tastes strongly of bitter almonds. Most genus members are shallow-rooted, forming a plate near the soil surface, and will produce suckers if the roots are damaged.
Physical Characteristics

 Prunus hortulana is a deciduous Tree growing to 9 m (29ft 6in) at a medium rate.
Prunus hortulana is a deciduous Tree growing to 9 m (29ft 6in) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6. It is in flower from April to May, and the seeds ripen from September to October. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects. The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Canopy; Secondary; Sunny Edge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Flowers Fruit Seed
Edible Uses:
Fruit - raw or cooked. Thin-skinned[227] with an agreeable flavour, it can be eaten out of hand or be made into pies, preserves etc[183]. Another report says that it is small and not very palatable, and is only used in preserves[171]. The fruit is about 12mm in diameter and contains one large seed[200]. The fruit is up to 25mm long according to other reports[227, 229]. Flower buds[46]. No more details are given. Seed - raw or cooked. Do not eat the seed if it is too bitter - see the notes above on toxicity.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Although no specific mention has been seen for this species, all members of the genus contain amygdalin and prunasin, substances which break down in water to form hydrocyanic acid (cyanide or prussic acid). In small amounts this exceedingly poisonous compound stimulates respiration, improves digestion and gives a sense of well-being[238].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Dye Wood
Agroforestry uses:
Prunus species can be used as windbreaks and in alley cropping systems. They also improve biodiversity by providing habitats for pollinators and other wildlife. Some varieties can fix nitrogen in the soil, contributing to soil health.
A green dye can be obtained from the leaves[168]. A dark grey to green dye can be obtained from the fruit[168]. Wood - heavy, hard, strong. Used for turnery[46]. 1. Nectary - Flowers rich in nectar and pollen:
Yes – Prunus species are known for their showy flowers that produce both nectar and pollen, attracting bees, butterflies, and other pollinators.
2. Wildlife - Food (Fruit, Seeds, Leaf litter, Shelter, Nesting, Roosting):
Yes – The fruits are an important food source for birds and mammals, and the trees provide shelter through their dense foliage. Some species, especially cherries and plums, are known to support wildlife with both food and roosting/nesting sites.
3. Invertebrate Shelter (Overwintering sites, Leaf litter, Groundcover):
Yes – Prunus species offer shelter for invertebrates, particularly in their rough bark and leaf litter. They also support beneficial insects by providing overwintering sites.
4. Pest Confuser (Smell):
No – While Prunus species are fragrant when blooming, they are not known for emitting strong pest-repelling scents.
Special Uses
Food Forest
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Thrives in a well-drained moisture-retentive loamy soil[11, 200]. Prefers some lime in the soil but is likely to become chlorotic if too much lime is present[1]. Succeeds in sun or partial shade though it fruits better in a sunny position[11, 200]. Sometimes cultivated for its edible fruit in Southern N. America, there are some named varieties[43, 183]. This tree is of very little value for its fruit in Britain, requiring hotter summers than are usually experienced here if it is to fruit well[1]. Most members of this genus are shallow-rooted and will produce suckers if the roots are damaged[238]. Plants in this genus are notably susceptible to honey fungus[200]. For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. A sprouting standard sending up shoots from the base [1-2]. The root pattern is flat with shallow roots forming a plate near the soil surface [1-2]. Harvesting typically occurs in late summer to early autumn, with specific timing varying by species. For instance, plums and peaches are usually harvested from July to September (Northern Hemisphere), while almonds are harvested in August to September (Northern Hemisphere).
Prunus species usually flower in early spring, often between March and April (Northern Hemisphere), depending on the species and local climate. Growth rates vary among species, but generally, Prunus trees can grow moderately fast, often reaching full height in 3 to 5 years. However, they may take several years to bear fruit, depending on the species and growing conditions. Some Prunus species (like many plums and almonds) are self-fertile, while others (like sweet cherries and certain apricots) require cross-pollination with another compatible variety for optimal fruit set. While Prunus hortulana (Hog Plum or Hortulan Plum) is self-compatible and can produce fruit on its own, a second plant nearby can lead to a better crop.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - requires 2 - 3 months cold stratification and is best sown in a cold frame as soon as it is ripe[200]. Sow stored seed in a cold frame as early in the year as possible[200]. Protect the seed from mice etc. The seed can be rather slow, sometimes taking 18 months to germinate[113]. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when they are large enough to handle. Grow them on in a greenhouse or cold frame for their first winter and plant them out in late spring or early summer of the following year. Cuttings of half-ripe wood with a heel, July/August in a frame[11, 200]. Softwood cuttings from strongly growing plants in spring to early summer in a frame[200]. Layering in spring.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: United States, Indiana (south), Ohio (southwest), Illinois, Iowa (southeast), Kansas (east), Missouri, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Kentucky (north), Tennessee, Virginia,
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Prunus africana | Pygeum | Tree | 18.0 |
10-12
| F | LM | N | M | 0 | 5 | 2 |
| Prunus alabamensis | Alabama Cherry | Tree | 8.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus alleghaniensis | Allegheny Plum, Davis' plum | Tree | 3.5 |
4-8
| F | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus americana | American Plum, American Wild Plum, Wild Plum | Tree | 6.0 |
3-8
| M | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Prunus americana lanata | | Tree | 10.0 |
3-7
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus andersonii | Desert Peach | Shrub | 1.8 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Prunus angustifolia | Chickasaw Plum, Watson's plum, Hally Jolivette Cherry | Tree | 3.0 |
5-9
| M | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Prunus angustifolia watsonii | Sand Plum | Shrub | 3.0 |
5-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus apetala | Clove Cherry | Shrub | 7.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus arabica | | Shrub | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | DM | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus armeniaca | Apricot | Tree | 9.0 |
5-7
| M | LM | SN | M | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Prunus armeniaca mandschurica | Manchurian apricot | Tree | 6.0 |
3-9
| M | LM | SN | M | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Prunus avium | Wild Cherry, Sweet cherry | Tree | 18.0 |
3-7
| F | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| Prunus besseriana | Dwarf Almond | Tree | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus besseyi | Western Sand Cherry | Shrub | 1.2 |
3-6
| M | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus bifrons | | Shrub | 1.8 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus bokharensis | Bokhara Plum | Tree | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus brigantina | Briançon Apricot | Tree | 6.0 |
6-9
| M | LMH | SN | DM | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Prunus buergeriana | | Tree | 9.0 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus campanulata | Taiwan Cherry | Tree | 7.0 |
7-9
| M | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus canescens | Greyleaf Cherry | Shrub | 3.0 |
5-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Prunus capsica | | Tree | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus caroliniana | American Cherry Laurel, Carolina laurelcherry, Laurel Cherry, | Shrub | 12.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | SN | DM | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Prunus cerasifera | Cherry Plum, Myrobalan Plum, Newport Cherry Plum, Pissard Plum | Tree | 9.0 |
5-8
| M | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Prunus cerasifera divaricata | | Tree | 10.0 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Prunus cerasoides | Wild Himalayan Cherry | Tree | 30.0 |
7-10
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Prunus cerasus | Sour Cherry | Tree | 6.0 |
3-7
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Prunus cerasus austera | Morello Cherry | Tree | 9.0 |
3-7
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Prunus cerasus caproniana | Kentish Red Cherry | Tree | 9.0 |
3-7
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| Prunus cerasus frutescens | Bush Sour Cherry | Tree | 1.0 |
3-7
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 1 | 3 |
|
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.H.Bailey.
Botanical References
1143200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Prunus hortulana
|
|
|
|