 |
|
http://www.edibleplants.org |
 |
| http://www.edibleplants.org |
Translate this page:
Summary
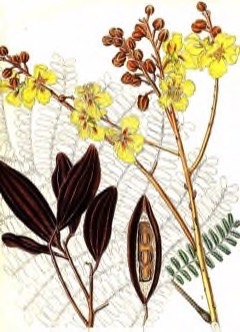
pterocarpum is a fast-growing species with a deep root system and a dense spreading crown. It is often planted as a shade tree in plantations in East Asia. Also, it has symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria that form nodules in the root and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Flowering commence at four years. It grows up to 24m in height and up to 100cm in trunk diameter. The leaves are bipinnate and each leaf is comprised of about 20-40 oval leaflets. The flowers are yellow. There is no known edible part of this plant but it is used in traditional medicine. In particular, the bark is used as treatment for sprains, bruises, swelling, eye problems, body sore, and intestinal disorders. Leaflets and buds are found to have antifungal properties while an alcoholic extract from the flowers has anti inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Moreover, the bark produces a yellowish brown dye which is used in the textile industry particularly for dyeing batik products and fishing nets. The wood is used as fuel and as material for constructions, boat building, cabinet making, etc. Other common names include poinciana, yellow, yellow flamboyant, and yellow flame. Copperpod or Peltophorum.
Physical Characteristics

 Peltophorum pterocarpum is an evergreen Tree growing to 20 m (65ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a fast rate.
Peltophorum pterocarpum is an evergreen Tree growing to 20 m (65ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10 and is frost tender. The flowers are pollinated by Bees, Insects.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in heavy clay and nutritionally poor soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid, very alkaline and saline soils.
It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil and can tolerate drought. The plant can tolerates strong winds but not maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Baryxylum inerme (Roxb.) Pierre Caesalpinia ferruginea Decne. Caesalpinia inermis Roxb. Inga pteroca
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antibacterial Antifungal Antiinflammatory Astringent Mouthwash Ophthalmic
The bark contains tannins[317 ]. In traditional medicine it is used as an astringent to cure or relieve intestinal disorders after pain at childbirth, sprains, bruises and swelling or as a lotion for eye troubles, muscular pains and sores[303 ]. It is also used for gargles and tooth powders[303 ]. An antifungal principle is present in the leaflets and buds[303 ]. The flowers contain a flavanone glycoside pigment, naringenin 7-glucoside[310 ]. An alcoholic extract from the flowers has an anti-inflammatory effect and an antibacterial activity[310 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Containers Dye Fuel Furniture Green manure Hedge Preservative Shelterbelt Tannin Teeth Wood
Seaside. Large flowering tree. Street tree. Specimen, Xerophytic. Agroforestry Uses: The tree has a dense, spreading crown and so is widely appreciated for providing shade[303 ]. It is planted as a shade tree in coffee and cacao plantations[317 ] and is used in shelterbelts because it is wind firm[303 ]. It has been tested in rotational alley-cropping/fallow systems in Sumatra, where it shows promise[303 ]. Young trees are often planted in an intercropping system with mahogany or Tectona grandis303, 317 ]. A fast-growing tree that fixes atmospheric nitrogen, it has potential use for reforestation and is used as a source of green manure[303 ]. It can be used for the reforestation of wastelands that are heavily infested with the grass Imperata cylindrica[418 ]. The tree can be used as a hedge[303 ]. Other Uses The bark furnishes a yellowish brown dye, which serves the dyeing of cotton and batik products[317 ]. The bark has been an important component of the dark or black 'soga' dye in Java (where it is mixed with the bark of Ceriops tagal, the wood of Maclura cochinchinensis and other ingredients), which is used for batik work[303 , 310 ]. The dye, derived from the heart wood, is applied in the textile industry[317 ]. The bark contains 11 - 21% tannin, which is of the proanthocyanidin type[310 ]. It is used for preserving and dyeing fishing nets[303 ]. The wood and leaves contain smaller amounts of tannin[310 ]. The sapwood is greyish-white, turning grey-brown on aging, the heartwood is light reddish-brown or black[303 ]. The wood is moderately hard, moderately heavy, and somewhat lustrous, with a straight to interlocking grain[303 ]. It is easily worked and is used locally for light construction purposes, boat building, cabinet making, sawn or hewn building timbers, wood ware, woodcarving and marquetry[303 , 317 ]. The tree is used as fuel wood[303 ].
Special Uses
Food Forest Hedge Nitrogen Fixer
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
A plant of the moist to wet tropics, where it is usually found at elevations below 100 metres but can occasionally be found up to 1,600 metres[303 ]. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 27 - 36°c, but can tolerate 10 - 40°c[418 ]. Plants have been known to survive occasional low temperatures down to -5°c[200 ]. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 1,200 - 1,800mm, but tolerates 1,000 - 4,000mm[418 ]. It thrives best under more or less seasonal conditions with a dry season of 1 - 3 months[303 ]. Grows best in a sunny position[418 ]. The tree prefers light to medium free draining alkaline soils although it also tolerates clay soils[303 ]. Plants can tolerate moderate levels of salt in the soil[418 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5 - 6.5, tolerating 4.3 - 7.3[418 ]. A fast-growing tree, attaining a height of 9 metres in 3 years and flowering when around 4 years old[303 ]. Agroforestry trials in south Sumatra with hedgerows spaced at 4 metre intervals and cut 2 - 4 times a year indicated that, over a 3-year period, an average pruning yield of 8 tons/ha was possible[303 ]. The umbrella-shaped crowns which developed following cutting allowed little light to reach the ground[303 ]. After the first year of establishment, little effort is needed to maintain plantations[303 ]. Stands will usually survive, even with thick ground cover, such as Imperata or other tall grasses[303 ]. The tree has a deep root system[303 ]. This species has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria, these bacteria form nodules on the roots and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Some of this nitrogen is utilized by the growing plant but some can also be used by other plants growing nearby[200 ]. Flowering Time: Early summer, Mid summer. Bloom Color: Yellow.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed. Untreated seeds need several months to germinate[310 ] - germination is hastened by scarifying one end of the hard seed coat, softening the seed coat in dilute acid, or immersing the seed in boiling water for 2 minutes followed by soaking it in cold water for one night[303 ]. Germination has been recorded at 78%[303 ]. Seedlings are best raised in the nursery for one year before transplanting to the field[303 ]. Grafts or cuttings may be used to obtain better uniformity for roadside trees. Wildings have also been successfully used for planting[303 ].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Copperpod, Yellow Poinciana, Yellow Flamboyant, Yellow Flame
Native Range
TROPICAL ASIA: Sri Lanka, Papua New Guinea, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines AUSTRALASIA: Australia (Northern Territory (n. (islands)))
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(DC.) Backer ex K.Heyne
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Peltophorum pterocarpum
|
|
|
|