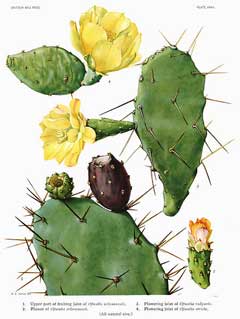
 |
|
(c) 2010 Ken Fern & Plants For A Future |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Opuntia16_filtered.jpg |
Translate this page:
Summary
Opuntia species,
Prickly Pear are native to desert environments, where they thrive under extreme heat and minimal water availability. They are used for their edible fruits and pads and make a stock-proof barrier. Eat the sweet and gelatinous fruit raw, cooked or dried for later use. The unripe fruits can be added to soups, imparting an okra-like mucilaginous quality. The fruit can hang on the plant all year round. Eat the watery and very mucilaginous pads cooked or raw. Try Barbary fig (O. ficus-indica), Eastern Prickly Pear (O. compressa), Dillen Prickly Pear (O.dillenii), Engelmann’s Prickly Pear (O. engelmannii), Eastern Prickly Pear (O. humifusa), Wheel Cactus (O. robusta), and Velvet Prickly Pear (O. tomentosa). Cholla (Cylindropuntia spp.) was formerly treated as a subgenus of Opuntia. However, it has now been separated based on its cylindrical stems (Opuntia species have flattened stems) and the presence of papery epidermal sheaths on the spines. All the buds and the fruits of the cholla are edible. O. ficus-indica is native to Mexico but widely grown in Mediterranean regions, North Africa, and Southwestern U.S..
Harvesting: The fruits (tunas) are harvested in late summer to autumn.
Physical Characteristics

 Opuntia ficus-indica is an evergreen Perennial growing to 5 m (16ft) by 5 m (16ft) at a medium rate.
Opuntia ficus-indica is an evergreen Perennial growing to 5 m (16ft) by 5 m (16ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 9 and is not frost tender. It is in leaf all year, in flower from June to September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects. The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry soil and can tolerate drought. The plant can tolerates strong winds but not maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds; East Wall. By. South Wall. By.
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Flowers Fruit Leaves Seed
Edible Uses: Gum Gum
Fruit - raw, cooked or dried for later use[3, 7, 20, 46, 61, 89]. Sweet and gelatinous[85]. Very refreshing, they are somewhat like a watermelon in flavour[183]. The fruits are up to 10cm long and 9cm wide[200]. Be careful of the plants irritant hairs, see the notes above on toxicity. Pads - cooked and used like French beans[20, 183]. Watery and very mucilaginous[85]. Flowers - raw[20]. Seed - ground into a meal[20, 92]. An edible gum is obtained from the stem[64].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antispasmodic Diuretic Emollient
The flowers and stems are antispasmodic, diuretic and emollient[7]. The split stems have been bound around injured limbs as a first aid measure[254]. The flowers are astringent and are used to reduce bleeding and treat problems of the gastro-intestinal tract, especially diarrhoea, colitis and irritable bowel syndrome[254]. The flowers are also used in the treatment of an enlarged prostate gland[254].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Fodder Gum Gum
Agroforestry uses: Prickly pear can be used as a natural fence or barrier, provides habitat for wildlife, and its pads can be used as forage for livestock. A gum is obtained from the stem. It is used as a masticatory or mixed with oil to make candles[64]. The juice of the boiled stem segments is very sticky. It is added to plaster, whitewash etc to make it adhere better to walls[92]. 1. Nectary - Flowers rich in nectar and pollen:
Yes – Prickly pear flowers are known for being rich in nectar and attract a variety of pollinators, including bees and butterflies.
2. Wildlife - Food (Fruit, Seeds, Leaf litter, Shelter, Nesting, Roosting):
Yes – The fruit (tunas) and pads (nopales) of prickly pear are edible and provide food for various wildlife, including birds and mammals. The pads can also offer some shelter for small animals.
3. Invertebrate Shelter (Overwintering sites, Leaf litter, Groundcover):
Yes – The pads and spines can provide shelter for invertebrates, and the leaf litter around the base can serve as habitat for beneficial insects.
4. Pest Confuser (Smell):
No – While prickly pear may have some aromatic qualities, they are not specifically recognized for confusing or deterring pests.
Special Uses
Carbon Farming
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Agroforestry Services: Living fence Fodder: Bank Minor Global Crop
Requires a sandy or very well-drained soil[1, 3]. Prefers a pH in the range 6 to 7.5[200]. Plants must be kept fairly dry in the winter but they like a reasonable supply of water in the growing season. A position at the base of a south-facing wall or somewhere that can be protected from winter rain is best for this plant. Requires warmth and plenty of sun[3]. Plants tolerate considerable neglect[3]. Cultivated in many warm temperate and subtropical areas for its edible fruits[89,183] and its use as a stock-proof barrier, it is not very cold-tolerant and is unlikely to survive the winter outdoors in Britain. There are some named varieties[183], one at least of which is free from spines and irritant hairs. Many Opuntia species are self-fertile, though cross-pollination can improve fruit set and quality. The fruits (tunas) are typically harvested in late summer to autumn, around late summer to early fall, depending on the species and climate.
Opuntia species usually flower in late spring to early summer. Opuntia species generally grow moderately fast, with many species capable of producing new pads and fruit within the first year of planting, especially in favorable conditions.
Carbon Farming
-
Agroforestry Services: Living fence
Simply managed rows of shrubs and trees.
-
Fodder: Bank
Fodder banks are plantings of high-quality fodder species. Their goal is to maintain healthy productive animals. They can be utilized all year, but are designed to bridge the forage scarcity of annual dry seasons. Fodder bank plants are usually trees or shrubs, and often legumes. The relatively deep roots of these woody perennials allow them to reach soil nutrients and moisture not available to grasses and herbaceous plants.
-
Minor Global Crop
These crops are already grown or traded around the world, but on a smaller scale than the global perennial staple and industrial crops, The annual value of a minor global crop is under $1 billion US. Examples include shea, carob, Brazil nuts and fibers such as ramie and sisal.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow early spring in a very well-drained compost in a greenhouse. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on in the greenhouse for at least their first two winters. Plant them out into their permanent positions in late spring or early summer, after the last expected frosts. Give the plants some protection from winter wet. Make sure you have some reserve plants in case those outdoors do not overwinter. Cuttings of leaf pads at any time in the growing season. Remove a pad from the plant and then leave it in a dry sunny place for a couple of days to ensure that the base is thoroughly dry and has begun to callous. Pot up into a sandy compost. Very easy, rooting quickly.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
Mexico Southwest.
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Cylindropuntia spp. | Cholla | Perennial | 2.0 |
8-12
| S | LMH | SN | D | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| Opuntia compressa | Eastern Prickly Pear, Prickly Pear Cactus | Perennial | 0.2 |
8-10
| F | LM | N | D | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Opuntia dillenii | Dillen prickly pear, | Perennial | 1.0 |
10-12
| M | LM | N | DM | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Opuntia engelmannii | Engelmann’s Prickly Pear | Shrub | 2.5 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Opuntia erinacea | Mojave Prickly Pear | Perennial | 0.5 |
8-11
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia fragilis | Prickly Pear, Brittle pricklypear | Perennial | 0.1 |
7-10
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Opuntia howeyi | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia humifusa | Eastern Prickly Pear | Shrub | 0.2 |
4-10
| M | LM | N | DM | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Opuntia imbricata | Tree Chola | Perennial | 3.0 |
8-11
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia littoralis | Western Prickly Pear | Perennial | 0.6 |
-
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia macrorhiza | Twist-Spine Prickly Pear | Perennial | 0.1 |
8-11
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia microdasys | Bunny Ears, Angel's-wings | Perennial | 0.6 |
7-10
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia phaeacantha | Bastard Fig, Tulip pricklypear | Perennial | 0.5 |
8-11
| | LM | N | D | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Opuntia polyacantha | Plains Prickly Pear, El Paso pricklypear, Grizzlybear pricklypear, Navajo Bridge pricklypear, Hairsp | Perennial | 0.2 |
3-7
| | LM | N | D | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Opuntia ramosissima | Branched Pencil Cholla | Perennial | 0.6 |
7-10
| | LM | N | D | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia robusta | Wheel Cactus | Shrub | 2.0 |
9-11
| M | LM | N | DM | 4 | 0 | 2 |
| Opuntia tomentosa | Velvet prickly pear, Woollyjoint Pricklypear | Perennial | 4.5 |
9-12
| M | LM | N | DM | 3 | 0 | 3 |
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(L.)Mill.
Botanical References
89200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment