 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koeh-078.jpg |
 |
| http://www.flickr.com/photos/versicolor/442527595/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
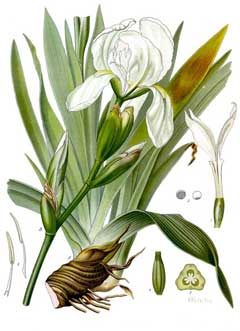
Bloom Color: White. Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Mid summer. Form: Upright or erect.
Physical Characteristics

 Iris germanica florentina is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.9 m (3ft) by 0.6 m (2ft in) at a medium rate.
Iris germanica florentina is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.9 m (3ft) by 0.6 m (2ft in) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 5 and is not frost tender. It is in flower in May, and the seeds ripen from July to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects. The plant is self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
I. florentina. L.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Dappled Shade; Shady Edge; Ground Cover;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts:
Edible Uses: Condiment
The root can be dried, ground into a powder and used as a food flavouring[105]. The root may take several years of drying to develop its full fragrance[168].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Diuretic Purgative Stomachic
The dried root is diuretic, expectorant and stomachic[21, 238]. It is taken internally in the treatment of coughs, catarrh and diarrhoea[238]. Externally it is applied to deep wounds[238]. The root is harvested in late summer and early autumn and dried for later use[238]. The juice of the fresh root is a strong purge of great efficiency in the treatment of dropsy[4].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Beads Cosmetic Dye Essential Incense
The root is a source of Orris powder which has the scent of violets[238]. It is obtained by grinding up the dried root[4, 7, 46]. It is much used as a fixative in perfumery and pot-pourri, as an ingredient of toothpastes, breath fresheners etc and as a food flavouring. The root can take several years of drying to fully develop its violet-like fragrance, when fresh it has an acrid flavour and almost no smell[4, 168]. An essential oil is obtained from the fresh root, this has the same uses as the root[57, 61]. The root has been burnt in open fires in order to sweeten the smell of a room[245]. The juice of the root is sometimes used as a cosmetic and also for the removal of freckles from the skin[4]. A black dye is obtained from the root[168]. A blue dye is obtained from the flowers[168]. The seeds are used as rosary beads[61]. Plants can be grown for ground cover, the dense mat of roots excluding all weeds[208].
Special Uses
Ground cover Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Border, Massing, Specimen. Prefers a sunny position in a well-drained soil that contains some lime[1, 79]. Grows well in dry soils in light deciduous shade[187]. Succeeds in full sun or partial shade[79]. Prefers a pH in the range 6 to 7.5 or higher[200]. The plant is sometimes cultivated for the essential oil in its root[9, 46]. Members of this genus are rarely if ever troubled by browsing deer or rabbits[233]. Special Features:
Attracts birds, Not North American native, Naturalizing, All or parts of this plant are poisonous, Attracts butterflies, Suitable for cut flowers, Fragrant flowers.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame. Stored seed should be sown as early in the year as possible in a cold frame. A sterile plant, it does not produce seed[233]. Division, best done after flowering though it is usually successful at most times of the year. Very easy, larger clumps can be replanted direct into their permanent positions, though it is best to pot up smaller clumps and grow them on in a cold frame until they are rooting well. Plant them out in the spring.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
Coming Soon
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Albizia lebbeck | Siris Tree, Woman's Tongue, East Indian Walnut | Tree | 15.0 |
10-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Albizia lucidior | Potka siris tree | Tree | 15.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | SN | M | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Albizia procera | White Siris, Tall Albizia, Forest Siris | Tree | 25.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Bobartia indica | Rush Iris | Perennial | 0.6 |
7-10
| S | L | N | DM | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Gynandriris sisyrinchium | Spanish Nut | Perennial | 0.2 |
7-10
| | MH | SN | DM | 1 | 0 | |
| Iris cristata | Crested Iris, Dwarf crested iris | Perennial | 0.2 |
5-9
| M | LM | SN | M | 1 | 1 | |
| Iris decora | | Perennial | 0.3 |
-
| | LM | N | DM | 0 | 1 | |
| Iris douglasiana | Mountain Iris, Douglas iris | Perennial | 0.3 |
6-9
| | LM | SN | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Iris ensata | Japanese Water Iris | Perennial | 0.6 |
5-8
| M | LM | N | MWe | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Iris filifolia | | Bulb | 0.5 |
-
| | LM | N | DM | 1 | 0 | |
| Iris foetidissima | Stinking Gladwin, Stinking iris, Gladwin Iris | Perennial | 1.0 |
7-10
| M | LMH | FSN | DMWe | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Iris germanica | Purple Flag, German iris, Orris-root, Tall Bearded German Iris, Bearded Iris | Perennial | 1.0 |
4-10
| M | LM | SN | DM | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Iris japonica | | Perennial | 0.6 |
-
| | LM | SN | DM | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Iris kemaonensis | | Perennial | 0.5 |
-
| | LM | SN | DM | 0 | 2 | |
| Iris macrosiphon | Bowltube Iris | Perennial | 0.2 |
-
| | LM | SN | M | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Iris missouriensis | Rocky Mountain Iris | Perennial | 0.8 |
0-0
| | LM | SN | MWe | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Iris pallida | Dalmation Iris, Sweet iris, Fragrant Iris, Zebra Iris | Perennial | 1.0 |
4-10
| M | LM | SN | DM | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Iris pseudacorus | Yellow Flag, Paleyellow iris | Perennial | 1.5 |
5-8
| M | LM | SN | MWeWa | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Iris purdyi | Purdy's Iris | Perennial | 0.4 |
-
| | LM | SN | DM | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Iris sanguinea | Blood iris | Perennial | 0.8 |
5-9
| | LM | SN | MWe | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Iris setosa | Beachhead Iris, Canada beachhead iris, Wild flag | Perennial | 0.6 |
4-8
| M | LM | SN | MWe | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Iris sibirica | Siberian Iris | Perennial | 0.6 |
4-9
| F | LM | SN | MWe | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Iris tectorum | Roof Iris, Wall iris, Japanese Roof, White Root Iris | Perennial | 0.3 |
5-9
| M | LM | SN | DM | 1 | 0 | |
| Iris tenax | Tough-Leaf Iris, Klamath iris | Perennial | 0.3 |
0-0
| | LM | SN | DM | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Iris versicolor | Blue Flag, Harlequin blueflag | Perennial | 0.6 |
4-8
| | LM | SN | MWe | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| Solanum tuberosum | Potato, Irish potato | Perennial | 1.0 |
7-10
| | LMH | N | M | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Tagetes filifolia | Irish Lace | Annual | 0.4 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 1 | 0 | 2 |
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(L.)Dykes.
Botanical References
89200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment