 |
|
|
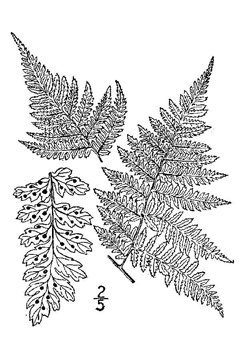 |
| USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913. An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. Vol. 1: 21. |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

 Dryopteris expansa is a FERN growing to 0.4 m (1ft 4in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in).
Dryopteris expansa is a FERN growing to 0.4 m (1ft 4in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 3. The seeds ripen from July to September.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid and neutral soils. It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) or semi-shade (light woodland). It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Dappled Shade; Shady Edge; not Deep Shade;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Leaves Root Shoots
Edible Uses:
Root - raw or cooked[256]. Baked and then peeled before being eaten[257]. The raw root is rather bitter but they develop a sweet taste when cooked and are said by some people to develop a flavour rather like sweet potatoes[256]. The root is best harvested in early autumn. At this time the rhizomes are surrounded by scaly, finger-like projections - if the projections are flat and dark inside then the rhizomes are not good to eat but if they are round, fleshy and light-coloured then they can be eaten[256]. The young shoots, harvested in spring before they have fully unfurled, can be cooked and eaten[257]. They can be added to soups[257].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anthelmintic Poultice
A poultice of the pounded roots has been applied to cuts[257]. We have no other reports for this species, but the following uses apply to many members of this genus and quite probably also to this species[K]. The root contains ‘filicin’, a substance that paralyses tapeworms and other internal parasites and has been used as a worm expellent[4, 172, 238]. It is one of the most effective treatments known for tapeworms - its use should be immediately followed by a non-oily purgative such as magnesium sulphate in order to expel the worms from the body[238]. An oily purge, such as caster oil, increases the absorption of the fern root and can be dangerous[238]. The root is harvested in the autumn and can be dried for later use, it should not be stored for longer than 12 months[238]. This remedy should be used with caution and only under the supervision of a qualified practitioner[238]. The root is toxic and the dosage is critical[238]. See also the notes above on toxicity. The root is also used in the treatment of dandruff[4, 172].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Hair
An infusion of the leaves has been used as a hair wash[257].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
An easily grown plant[233], it prefers an acid to neutral soil, succeeding in ordinary fertile soil in a shady position[175, 200]. Prefers a moist soil[188]. Closely related to D. dilatata and hybridising where their ranges meet to produce D. x ambroseae. Members of this genus are rarely if ever troubled by browsing deer[233].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Spores - can be sown at any time of the year in a greenhouse. Surface sow on a sterilised compost and keep moist, possibly by placing the pot in a plastic bag. Germinates in 1 - 3 months at 20°c. Pot up small clumps of the plants when they are large enough to handle and grow on in a shady part of the greenhouse until large enough to plant out. Division in spring. Larger clumps can be replanted direct into their permanent positions, though it is best to pot up smaller clumps and grow them on in a cold frame until they are rooting well. Plant them out in the spring.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Turkey NORTHERN AMERICA: Canada (Northwest Territories, Yukon, Québec, Ontario, Newfoundland and Labrador, Alberta, British Columbia), Greenland, United States (Alaska, Michigan, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington, Wyoming, California) EUROPE: Denmark, Finland, United Kingdom, Iceland, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France, Portugal
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(C.Presl.)Fraser-Jenkins&Jermy.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Dryopteris expansa
|
|
|
|