 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koeh-198.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Sanjay_ach |
Translate this page:
Summary
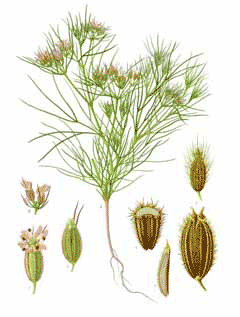
Cumin or Cuminum cyminum is a flowering plant native to Pakistan and India. It is a well-branched, erect, annual plant that usually grows up to 30 cm in height. The leaves are long. The flowers are small and white or pink in color. Cumin seed is well-known food flavouring especially in tropical Asia. It has a hot and aromatic flavour and is often used in curries. The essential oil obtained from the seed is used as flavouring as well. Cumin is also used medicinally. In particular, it is used to stimulate the sexual organs and to treat minor digestive conditions, coughs, pain, and rotten teeth.
Physical Characteristics

 Cuminum is a ANNUAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft) by 0.2 m (0ft 8in) at a fast rate.
Cuminum is a ANNUAL growing to 0.3 m (1ft) by 0.2 m (0ft 8in) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 9 and is frost tender. It is in leaf from May to October, in flower from June to July, and the seeds ripen from August to September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects. The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid and very alkaline soils.
It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry or moist soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Cuminia cyminum. Cuminum aegyptiacum. Cuminum hispanicum. Cuminum sativum
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Seed - cooked as a flavouring. Cumin seed was once widely used as a food flavouring in Europe, the Romans ground it into a powder and used it like pepper[ 268 ]. It is little used at present in Western cooking, though it is very commonly employed in India[ 268 ]. A hot and aromatic flavour, it is an important ingredient in curries, is used as a seasoning in soups and stews, and is also often used as a flavouring in biscuits, cakes and bread where it also helps in improving the digestion[ 1 , 4 , 14 , 21 , 27 , 46 , 132 , 171 , 244 , 418 ]. The seed is harvested when fully ripe and is then dried and stored in airtight jars[ 244 ]. An essential oil from the seed is used as a food flavouring[ 46 , 61 , 171 ]. According to the USDA, one tablespoon of cumin spice contains: 22 kcal (92 kJ) of food energy, 1.34 g (0.047 oz) of fat, 2.63 g (0.093 oz) of carbohydrates, 0.6 g (0.021 oz) of fibre and 1.07 g (0.038 oz) of protein.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Cumin is an aromatic, astringent herb that benefits the digestive system and acts as a stimulant to the sexual organs[ 238 ]. It has been used in the treatment of minor digestive complaints, chest conditions and coughs, as a pain killer and to treat rotten teeth[ 238 , 254 ]. Cumin is seldom used in Western herbal medicine, having been superseded by caraway which has similar properties but a more pleasant flavour[ 4 ]. It is still widely used in India, however[ 4 ] where it is said to promote the assimilation of other herbs and to improve liver function[ 238 ]. The seed is antispasmodic, carminative, galactagogue, stimulant and stomachic[ 4 , 46 , 240 , 254 ]. A general tonic to the whole digestive system, it is used in the treatment of flatulence and bloating, reducing intestinal gas and relaxing the gut as a whole[ 254 ]. In India it is also used in the treatment of insomnia, colds and fevers and to improve milk production in nursing mothers[ 254 ]. Ground into a powder and mixed into a paste with onion juice, it has been applied to scorpion stings[ 254 ]. The herb has been used externally as a poultice to relieve stitch and pains in the side[ 244 ]. The essential oil obtained from the seed is antibacterial and larvicidal[ 238 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
The seed contains about 2.5% essential oil[ 240 ]. It is used in perfumery and for flavouring beverages[ 46 , 61 , 177 , 272 ].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
An annual plant, it is cultivated from low elevations in the warm temperate to higher elevations in tropical zones. It does not do well in lowland areas of the tropics, but is successful at higher elevations, being grown up to 2,200 metres. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 17 - 26°c, but can tolerate 9 - 30°c[ 418 ]. The plant is intolerant of frost. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 1,200 - 1,800mm, but tolerates 800 - 2,700mm[ 418 ]. Tolerant of most well-drained soils[ 268 ], though it prefers a warm fertile well-drained sandy loam in a sheltered sunny position[ 14 , 200 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5 - 6.5, tolerating 4.5 - 8.3[ 418 ]. The plant can be harvested for its seed about 60 - 110 days after sowing[ 418 ]. Seed yields can be 500 - 1,200 kilos per hectare[ 418 ]. When bruised, the plant has a pungent aroma[ 245 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow early spring in individual pots in a greenhouse. Grow the plants on fast, and plant them out after the last expected frosts[ 200 ]. Give the plants some temporary protection such as a cloche for their first few weeks in the open ground to make sure that they keep on growing in the cooler weather of early summer[ K ].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Also known as: Comino, Jeera, Jeerige, Jilakara, Jintan puteh, Jinten bodas, Jinten, Jira zeera, Jira, Jiraka jira, Jiraka, Jiregire, Jorekam, Kumin, Safed jeera, Siragam, Sududuru, Sulpha phul, Yeera, Zira-sufed.
Native Range
Coming Soon
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed.

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
|