 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koeh-194.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Lin%C3%A91 |
Translate this page:
Summary
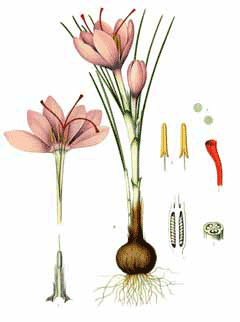
Crocus sativus,
Saffron is prized worldwide as a spice, derived from the dried styles and stigmas of the saffron crocus flower. The styles impart a distinctive flavour and vibrant yellow colour to various foods, including bread, soups, sauces, rice, and desserts. Saffron is essential in many traditional dishes such as Spanish paella, French bouillabaisse, and Italian risotto Milanese. The styles are extremely rich in riboflavin (vitamin B2). The flavour of saffron is aromatic and slightly bitter, with a unique taste that enhances both savoury and sweet dishes. However, because saffron is labour-intensive to harvest, it is one of the most expensive spices in the world. Due to its strong flavour, only a tiny amount of saffron is needed. It is often soaked in water or warm milk before being added to dishes to fully release its flavour and colour.
Saffron crocus is a hardy plant that needs well-drained soil with plenty of sunlight. It is planted in the fall, and the delicate purple flowers bloom in late autumn. Once established, the saffron crocus requires very little water.
Harvesting: autumn when the flowers bloom.
Physical Characteristics

 Crocus sativus is a CORM growing to 0.1 m (0ft 4in) by 0.1 m (0ft 4in) at a medium rate.
Crocus sativus is a CORM growing to 0.1 m (0ft 4in) by 0.1 m (0ft 4in) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6 and is not frost tender. It is in leaf from October to May, in flower in October. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees, butterflies. The plant is self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very alkaline soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers dry or moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Lawn; Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Root
Edible Uses: Colouring Condiment Tea
The flower styles are commonly used as a flavouring and yellow colouring for various foods such as bread, soups, sauces, rice and puddings[2, 4, 7, 14, 21, 27, 34, 183]. They are an essential ingredient of many traditional dishes such as paella, bouillabaisse, risotto milanese and various other Italian dishes[244]. The styles are extremely rich in riboflavin[137]. Water soluble[171]. Yields per plant are extremely low, about 4000 stigmas yield 25g of saffron[89]. Saffron is the world's most expensive spice, it takes 150,000 flowers and 400 hours work to produce 1 kilo of dried saffron[238]. About 25 kilos of styles can be harvested from a hectare of the plant[4]. Fortunately, only very small quantities of the herb are required to impart their colour and flavour to dishes[244]. Because of the cost, saffron is frequently adulterated with cheaper substitutes such as marigold flowers and safflower[244]. The flower styles are used as a tea substitute[183]. Root - cooked[183]. The corms are toxic to young animals[218] so this report of edibility should be treated with some caution[K].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Abortifacient Anodyne Antispasmodic Aphrodisiac Appetizer Carminative Diaphoretic Emmenagogue
Expectorant Narcotic Sedative Stimulant
Saffron is a famous medicinal herb with a long history of effective use, though it is little used at present because cheaper and more effective herbs are available[4, 7, 254]. The flower styles and stigmas are the parts used, but since these are very small and fiddly to harvest they are very expensive and consequently often adulterated by lesser products[7]. The styles and stigmas are anodyne, antispasmodic, aphrodisiac, appetizer, carminative, diaphoretic, emmenagogue, expectorant, sedative and stimulant[4, 7, 21, 174, 176, 218]. They are used as a diaphoretic for children, to treat chronic haemorrhages in the uterus of adults, to induce menstruation, treat period pains and calm indigestion and colic[4, 254]. A dental analgesic is obtained from the stigmas[7]. The styles are harvested in the autumn when the plant is in flower and are dried for later use[4], they do not store well and should be used within 12 months[238]. This remedy should be used with caution[21], large doses can be narcotic[240] and quantities of 10g or more can cause an abortion[218].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Dye
Saffron can be used in agroforestry systems as a companion plant to enhance biodiversity and attract pollinators. It is also beneficial for soil health due to its deep root system. The yellow dye obtained from the stigmas has been used for many centuries to colour cloth[4, 7, 14, 21]. It is the favoured colouring for the cloth of Indian swamis who have renounced the material world. A blue or green dye is obtained from the petals[168]. 1. Nectary - Flowers rich in nectar and pollen:
Yes – Saffron flowers are attractive to pollinators and produce nectar, which can attract bees and other beneficial insects.
2. Wildlife - Food (Fruit, Seeds, Leaf litter, Shelter, Nesting, Roosting):
No – While the flowers are beautiful, Crocus sativus does not produce edible fruit or seeds. It does not provide significant habitat for nesting or shelter.
3. Invertebrate Shelter (Overwintering sites, Leaf litter, Groundcover):
No – Saffron does not provide substantial shelter or overwintering sites for invertebrates. The plant is primarily grown for its flowers and the harvested saffron threads.
4. Pest Confuser (Smell):
No – Saffron does not have a strong smell that would deter pests or confuse them in the way that some other plants do.
Special Uses
Food Forest Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a well-drained sandy or loamy soil that is free from clay[137]. Prefers a sunny position[238]. Grows well on calcareous soils[27] and on hot sheltered stony banks[42]. Plants are very frost hardy[137]. They also thrive in areas with poor summers, though they usually fail to flower in such conditions[238]. Plants produce less saffron when grown on rich soils[137]. They do not flower very freely in Britain[90]. Saffron has been cultivated for over 4,000 years for the edible dye obtained from the flower stigmas[1]. It was at one time commercially grown in Britain and the town Saffron Walden obtained its name because of this. There is at least one named form. 'Cashmirianus' comes from Kashmir and has large high quality corms. It yields about 27 kilos of rich orange stigmas per hectare[183]. When inhaled near to, the flowers have a delicate perfume[245]. Unlike most members of this genus, the flowers do not close of a night time or in dull weather[245]. The flowers are only produced after hot, dry summers[245]. Plants tend to move considerably from their original planting place because of their means of vegetative reproduction, it is therefore wise not to grow different species in close proximity[1]. Any planting out is best done in late spring or early summer[245]. Plants take 4 - 5 years to come into flowering from seed. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 8 through 1. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is a runner spreading indefinitely by rhizomes or stolons [1-2]. The root pattern is a corm swelling at the stem base [1-2]. Crocus sativus is self-fertile and can produce seeds without cross-pollination. Saffron is typically harvested in autumn when the flowers bloom.
Crocus sativus flowers in the autumn, producing blooms shortly after the corms have been planted. Saffron has a moderate growth rate. The corms take about 6 to 8 weeks to establish before flowering, with full growth from planting to harvest generally taking around 6 months.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - according to some reports this species is a sterile triploid and so does not produce fertile seed[90, 238]. However, if seed is obtained then it is best sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame[1]. Stored seed can be sown in the spring in a cold frame[1]. Germination can take 1 - 6 months at 18°c[164]. Unless the seed has been sown too thickly, do not transplant the seedlings in their first year of growth, but give them regular liquid feeds to make sure they do not become deficient. Divide the small bulbs once the plants have died down, planting 2 - 3 bulbs per 8cm pot. Grow them on for another 2 years in a greenhouse or frame and plant them out into their permanent positions when dormant in late summer[K]. It takes 3 years for plants to flower from seed[244]. Division of the clumps in late summer after the plant has died down[1, 4, 14]. The bulbs can be planted out direct into their permanent positions.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
EUROPE: Greece,
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment