 |
|
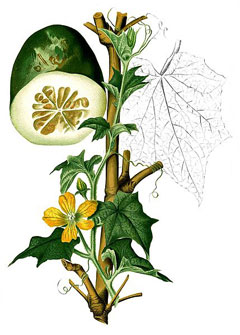
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Benincasa_hispida_Blanco2.323-cropped.jpg |
 |
|
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

 Benincasa hispida is a ANNUAL growing to 6 m (19ft 8in).
Benincasa hispida is a ANNUAL growing to 6 m (19ft 8in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10 and is frost tender. It is in leaf from June to October, in flower from July to September, and the seeds ripen from August to November. The species is monoecious (individual flowers are either male or female, but both sexes can be found on the same plant) and is pollinated by Bees. The plant is self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
B. cerifera.
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Flowers Fruit Leaves Seed
Edible Uses:
Fruit - raw or cooked[74, 114]. Used as a vegetable, and in pickles, curries and preserves[1, 2, 27, 61, 183]. The fruit can be eaten when it is young or old[116], it can be picked as early as one week after fertilization[206]. A juicy texture with a mild flavour, the flavour is somewhat stronger in younger fruits[206]. Because of its waxy coating, it will store for several months, sometimes as long as a year[116, 206]. Mature fruits can vary in weight from 2 - 50 kg[206]. A nutritional analysis is available[218]. Young leaves and flower buds are steamed and eaten as a vegetable, or are added as a flavouring to soups[183, 200]. Seed - cooked[74, 114, 177, 183]. Rich in oil and protein.
References More on Edible Uses
| Composition
|
| Figures in grams (g) or miligrams (mg) per 100g of food.
|
|
|
Fruit (Fresh weight)
|
|
- 13 Calories per 100g
- Water : 96.1%
- Protein: 0.4g; Fat: 0.2g; Carbohydrate: 3g; Fibre: 0.5g; Ash: 0.3g;
- Minerals - Calcium: 19mg; Phosphorus: 19mg; Iron: 0.4mg; Magnesium: 0mg; Sodium: 6mg; Potassium: 111mg; Zinc: 0mg;
- Vitamins - A: 0mg; Thiamine (B1): 4mg; Riboflavin (B2): 0.11mg; Niacin: 0.4mg; B6: 0mg; C: 13mg;
- Reference: [ 218]
- Notes:
|
|
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anthelmintic Antiperiodic Aphrodisiac Cancer Demulcent Diuretic Epilepsy Expectorant
Febrifuge Laxative Salve Tonic Urinary VD
The wax gourd has been used as a food and medicine for thousands of years in the Orient. All parts of the fruit are used medicinally. The rind of the fruit is diuretic[218, 238]. It is taken internally in the treatment of urinary dysfunction, summer fevers etc[238]. The ashes of the rind are applied to painful wounds[218]. The seed is anthelmintic, anti-inflammatory, demulcent, diuretic, expectorant, febrifuge, laxative and tonic[218, 238]. A decoction is used internally in the treatment of vaginal discharges and coughs[238, 254]. In combination with Rheum palmatum it is used to treat intestinal abscesses[254]. In Ayurvedic medicine the seed is used in the treatment of coughs, fevers, excessive thirst and to expel tapeworms[254]. The oil from the seed is also used as an anthelmintic[240]. The fruit is antiperiodic, aphrodisiac, diuretic, laxative and tonic[240]. It is used in Ayurvedic medicine in the treatment of epilepsy, lung diseases, asthma, coughs etc[238]. The fruit juice is used in the treatment of insanity, epilepsy and other nervous diseases[240]. Recent research has shown that the fruits contain anti-cancer terpenes[238]. An infusion of the root is used in the treatment of gonorrhoea[218]. Demulcent, salve. Facilitates pus drainage[147, 176, 178].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Rootstock
A wax that coats the fruit is used to make candles[2, 27, 238]. The roots have considerable resistance to soil-borne diseases and they are sometimes used as a rootstock for melons and other cucurbits[206].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Requires a warm sunny position in a rich well-drained soil and plenty of moisture in the growing season[1, 200, 238]. Established plants are reasonably drought tolerant[206]. Tolerates a pH in the range 5.8 to 6.8. This species is not very frost hardy, it is best grown in a greenhouse in Britain[86] but can succeed outdoors in good summers if started off in a greenhouse and planted out after the last expected frosts. Plants require stable temperatures in excess of 25°c if they are to do well[200]. Short daylengths and lower temperatures stimulate female flower development, higher temperatures stimulate male flower production[200]. Plants take 5 months from seed to produce a mature crop, though the fruits can be eaten when immature[206]. The wax gourd is frequently cultivated for its edible fruit in the tropics, there are many named varieties[183]. One group, sometimes classified as B. hispids chieh-gua, is known as the hairy melon or jointed gourd. This form is grown for its immature fruit in much the same way as courgettes are used[206]. Mature fruits of this form do not develop a waxy coating[206]. The fruit can be harvested about 3 months after sowing[206].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow March/April in a greenhouse. Germination should take place within 3 weeks. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on fast in a rich compost in the greenhouse. Try to maintain a minimum night temperature of at least 10°c for the seedlings first few weeks[206]. Plant out in May/June after the last expected frosts[1].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TROPICAL ASIA: Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands AUSTRALASIA: Australia (Queensland)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(Thunb.)Cogn.
Botanical References
200266
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment