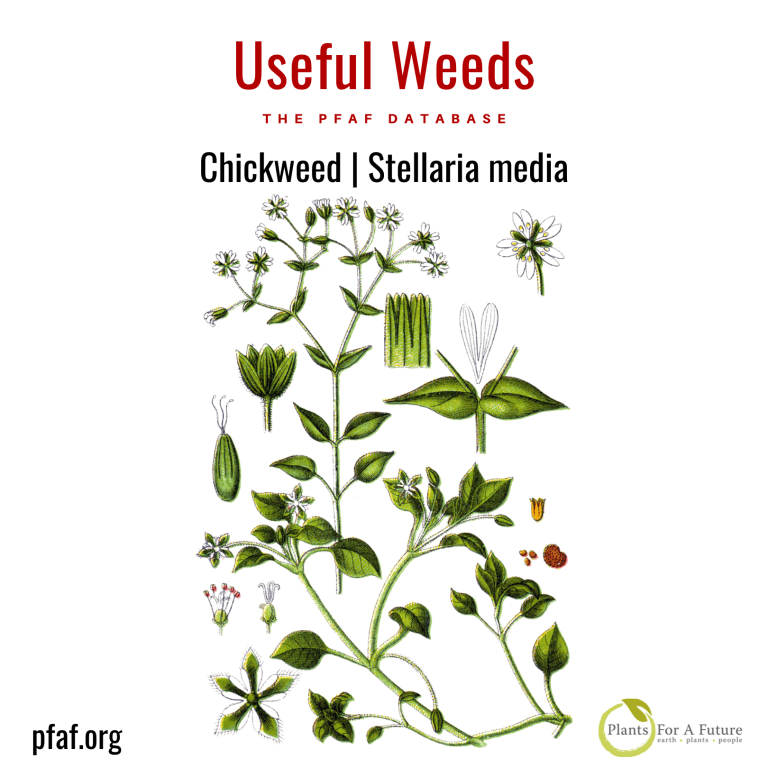
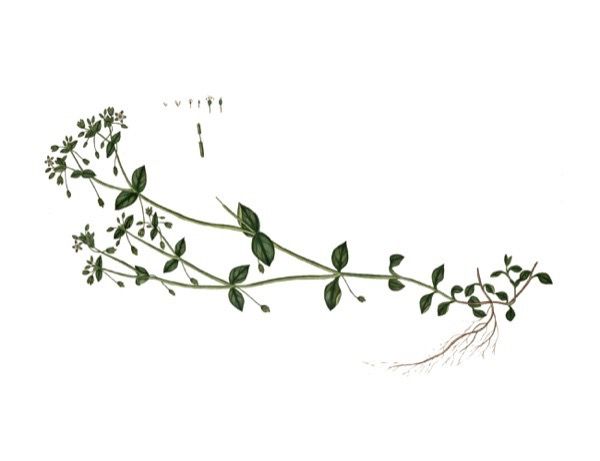
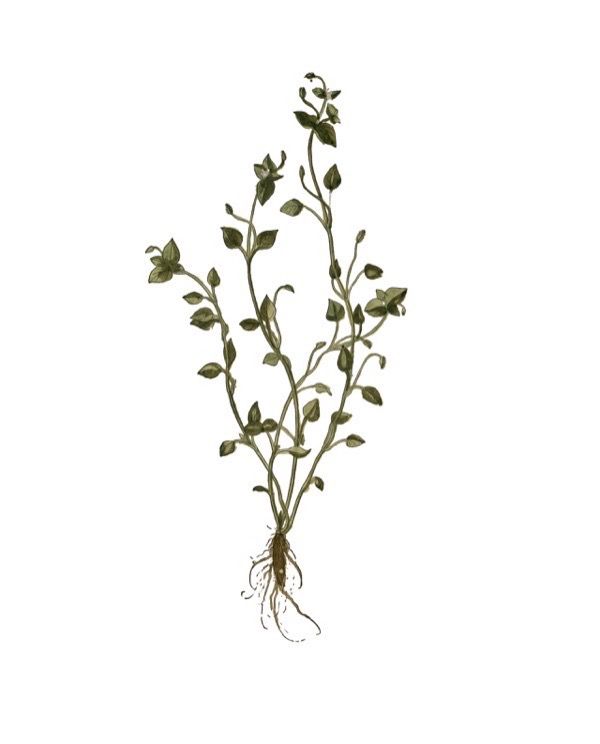
Is chickweed edible?
Chickweed is a very prolific and easy to find edible weed. Young leaves are eaten raw or cooked as a potherb. They can be available all year round if the winter is not too severe. They are very nutritious, they are added to salads whilst the cooked leaves can scarcely be distinguished from spring spinach. The leaves contain saponins, so some caution is advised; see the note on toxicity at the bottom of the page. The seed – is ground into a powder and used in making bread or to thicken soups. It would be very fiddly to harvest any quantity of this seed since it is produced in small amounts throughout most of the year and is very small. The seed contains 17.8% protein and 5.9% fat.
Medicinal uses of chickweed
Chickweed has a very long history of herbal use, being particularly beneficial in the external treatment of any itching skin condition. It has been known to soothe severe itchiness even where all other remedies have failed. In excess doses, chickweed can cause diarrhoea and vomiting. It should not be used medicinally by pregnant women. The whole plant is astringent, carminative, demulcent, diuretic, expectorant, laxative, refrigerant, and vulnerary. Taken internally, it helps treat chest complaints, and in small quantities, it also aids digestion. It can be applied as a poultice and will relieve roseola, and is effective wherever there are fragile superficial veins. An infusion of the fresh or dried herb can be added to bathwater. Its emollient property will help reduce inflammation in rheumatic joints, for example, and encourage tissue repair.
Chickweed is best harvested between May and July; it can be used fresh or be dried and stored for later use. A decoction of the whole plant is taken internally as a post-partum depurative, emmenagogue, galactagogue and circulatory tonic. It is also believed to relieve constipation and be beneficial in treating kidney complaints. The decoction is also used externally to treat rheumatic pains, wounds and ulcers. The expressed juice of the plant has been used as an eyewash.
Other uses of chickweed
Chickweed is a dynamic accumulator gathering minerals or nutrients from the soil and storing them in a more bioavailable form. It is used as fertilizer or to improve mulch. Farmers in Scandanavia encourage its growth as they believe a ground cover results in better fruit quality and yield. Chickweed is eaten by chickens, wild birds, and mountain sheep. A food plant for the caterpillars of many butterfly species. Suitable for cut flowers and dried flowers. Chickweed helps with erosion control and dune stabilization.
Growing chickweed
Chickweed is a very easily grown plant; it prefers moist soil and a position in full sun or partial shade. It can be very lush and vigorous when grown in fertile soil, but it will flower and set seed whilst still very small in infertile soils. A widespread garden weed, chickweed grows, flowers and sets seed all year round. The flowers open around 9 o’clock in the morning and remain open for about 12 hours. They do not open in dull weather. The leaves fold up at night, enfolding and protecting the tender buds of new shoots.
Seed – this species should not need any encouragement; you are much more likely to be trying to get rid of it than introducing it (eating it is one way of doing that!)
Chickweed
Stellaria media
Family Caryophyllaceae
Known Hazards The leaves contain saponins. Although toxic, these substances are very poorly absorbed by the body and so tend to pass through without causing harm. They are also broken down by thorough cooking. Saponins are found in many plants, including several that are often used for food, such as certain beans. It is advisable not to eat large quantities of food that contain saponins. Saponins are much more toxic to some creatures, such as fish, and hunting tribes have traditionally put large quantities of them in streams, lakes etc in order to stupefy or kill the fish. Report of paralysis attributed to excessive intake. Should not be used during pregnancy or during breastfeeding.
Habitats Growing almost anywhere, it is a common garden weed.
Range A cosmopolitan plant, found in most regions of the world, including Britain.
Edibility Rating 3
Other Uses 2
Weed Potential Yes
Medicinal Rating 3


Database entry
http://www.pfaf.org/user/plant.aspx?LatinName=Stellaria+media