 |
|
http://www.edibleplants.org |
 |
| http://www.edibleplants.org |
Translate this page:
Summary
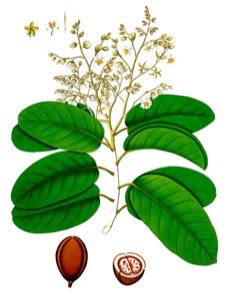
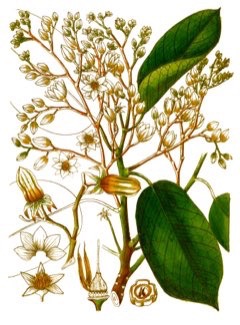
A plant endemic to India and threatened by habitat loss, White Dammar or Vateria indica is a large, slow-growing, and evergreen tree reaching a height of about 40 m. The trunk is cylinder-shaped covered with light gray, smooth bark. The leaves are oval with a short point and red when young. The flowers are white, fragrant, and hand in drooping clusters. The fruit is a large and fleshy five-valved capsule.The seeds yield solid oil known as ?piney tallow? which can be used as food flavoring and as a ghee substitute. It can also be used as a fuel for lamps and in candlemaking.The bark is used to control fermentation when making alcoholic beverages. Resin from the bark is used as an incense in India and as an Ayurvedic medicine. The resin can be mixed with coconut oil and rolled into candles. It is also used for making imitation amber beads. The fruits and bark contain tannins. The wood is tough and hard and used for making canoes, vessel masts, and coffins.
Physical Characteristics

 Vateria indica is an evergreen Tree growing to 40 m (131ft) by 30 m (98ft) at a slow rate.
Vateria indica is an evergreen Tree growing to 40 m (131ft) by 30 m (98ft) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid and neutral soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
This name is unresolved.
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Inner bark Oil Seed
Edible Uses: Condiment Oil
The seeds contain up to 50% of a solid oil known as 'piney tallow'[146 , 439 ]. This can be used for flavouring food and as a substitute or adulterant for ghee[439 ]. The bark is used to control fermentation in when making alcoholic beverages such as arrack and toddy[439 ].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antirheumatic Astringent
The resin obtained from the tree has the same uses as pine resin[46 , 439 ]. An oil obtained from the seeds is valued locally as an external application to relieve rheumatism[439 ]. The bark is astringent[439 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Beads Lighting Oil Resin Tannin Varnish Wood
Other Uses A resin is obtained from the tree by incising the trunk[46 ]. It is only slightly soluble in alcohol, but dissolves at once in turpentine and drying oils[439 ]. Like copal, it is chiefly used for making varnishes[439 ]. The resin can be mixed with coconut oil and rolled into candles (which burn with a dark, heavy smoke), and it is also used for making imitation amber beads[146 , 439 ]. The resin is said to occur in three forms compact piney, cellular piney and dark-coloured piney resin. The names sufficiently indicate their respective characters, which are said to be due to the mode of collection and the age of the tree The seeds contain a large quantity of a solid oil known as 'piney tallow'[439 ]. This can be used as a fuel for lamps and has been used to make candles[439 ]. The candles burn well, but are too soft[146 ]. The fruit contains 25% tannins[439 ]. The bark contains tannins[438 ]. The heartwood is light gray, the sapwood white with a tinge of red or grey[146 ]. The wood is tough and hard. It is not in much request, but is sometimes utilised locally for making canoes, the masts of native vessels and coffins[439 ].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
A tree of low to moderate elevations in the moist, monsoonal tropics, where it can be found at elevations up to 1,200 metres[418 ]. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 24 - 33°c, but can tolerate 17 - 38°c[418 ]. It can be killed by temperatures below 14°c[418 ]. It prefers a mean annual rainfall of 2,500 - 3,000mm, but tolerates 2,000 - 3,500mm[418 ]. Succeeds in full sun and also, especially when young, in fairly dense shade[418 ]. Prefers a light, fairly fertile, well-drained soil[418 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5 - 6, tolerating 4.5 - 6.9[418 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed -
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Piney varnish-tree, White dhup, Ajakarna, Safed damar, Kahruba, Chundrus, Guli, Telladamaru, Ral, Dhupadamaru, Vellei, Vellai-damar, Biladupa, Velleikuntricum, Pineymaram, Dhupmaram, Hoogadamara, Munda-dhupa, Saldhupa, Maddidhupa, Looguludhupa, Bilaguggala, Biladaamara, Vellakunturukkum, Payin, Peinimarum, Perumpiney, Payani, Veltha paini, Payia, Dammar, ajakar?a, chandras, dhupadamara, dupa, devdhupa, india cop tree, kungiliyam, karsya, mandadhupa, payin, raal, rala, safed damar, sandaras, sandras, saraja, sarja, sarja (exudate), sasyasumbara, sava, shakgachha, telladamaramu, tellaguggilarnu, vateria, vellai kundarakam, vellai kuntarakam, white damar tree, white dammar.
Native Range
Coming Soon TROPICAL ASIA: India
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : Status: Critically Endangered A1cd

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
|