 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tagetes_erecta_Blanco2.404b-cropped.jpg |
 |
| http://www.hear.org/starr/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
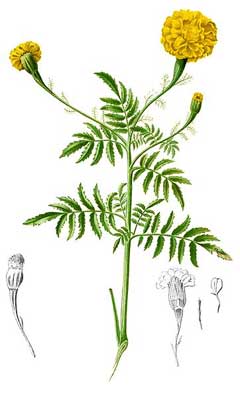
Bloom Color: Orange, Yellow. Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Early fall, Late summer, Late spring, Mid summer. Form: Upright or erect.
Physical Characteristics

 Tagetes erecta is a ANNUAL growing to 1 m (3ft 3in) by 0.4 m (1ft 4in) at a fast rate.
Tagetes erecta is a ANNUAL growing to 1 m (3ft 3in) by 0.4 m (1ft 4in) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 3 and is frost tender. It is in flower in July. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects. The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in heavy clay soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry or moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Tagetes major Gaertn.
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Flowers
Edible Uses: Colouring Condiment
The petals of the flowers of some varieties can be eaten[183]. The fresh receptacle is eaten by children[272]. A yellow dye obtained from the flowers can be used as a saffron substitute for colouring and flavouring foods[183]. The plant is used as a condiment[177]. (This probably refers to the use of the flowers as an edible dye)
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anthelmintic Aromatic Carminative Digestive Diuretic Dysentery Eczema Emmenagogue
Laxative Ophthalmic Sedative Skin Stomachic
The whole herb is anthelmintic, aromatic, digestive, diuretic, emmenagogue, sedative and stomachic[61, 238]. It is used internally in the treatment of indigestion, colic, severe constipation[238], coughs and dysentery[218]. Externally, it is used to treat sores, ulcers, eczema. sore eyes and rheumatism[218, 238, 257, 272]. The leaves are harvested as required for immediate use during the growing season, whilst the flowering plant can be dried and stored for later use[238]. A paste of the leavs is applied externally to treat boils, carbuncles and earaches[272]. The flowers are carminitive, diuretic and vermifuge[272]. A decoction is used to treat colds, and mumps[218]. It is applied externally to trea skin diseases, conjunctivitis and sore eyes[218, 272]. The root is laxative[272].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Companion Dye Insecticide Repellent
Landscape Uses:Border, Container, Foundation, Massing, Seashore, Specimen. Secretions from the roots of growing plants have an insecticidal effect on the soil, effective against nematodes and to some extent against keeled slugs. These secretions are produced about 3 - 4 months after sowing[200]. The flower petals also have nematacidal properties[218]. The growing plant is also said to repel insects and can be grown amongst crops such as potatoes and tomatoes. A yellow dye is obtained from the flowers[169, 257]. Dynamic accumulator.
Special Uses
Dynamic accumulator Food Forest Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Requires a well-drained moderately fertile soil in a sunny position[200]. Grows well in heavy clay soils and in sandy soils[188]. Although not very frost resistant, it can be grown as a tender annual in Britain, sowing the seed in a greenhouse in the spring and planting out after the last expected frosts. The flowers are often sold in local markets in Nepal and used as an offering to the Gods[272]. A number of named forms have been developed for their ornamental value[183]. The cultivar 'Yellow Climax' has mild flavoured edible flowers that can be used as colourful garnishes[183]. All parts of the plant emit an unpleasant smell similar to that of stale urine when they are bruised[245]. Removing dead flowers before the seed is formed will extend the flowering season[188]. Plants are prone to attacks by slugs, snails and botrytis[188]. Special Features:
North American native, Fragrant foliage, Suitable for cut flowers, Suitable for dried flowers.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow March in a greenhouse. Only just cover the seed. Germination usually takes place within 2 weeks. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and plant them out after the last expected frosts.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: Mexico (Durango, San Luis Potosí, Sinaloa, Sonora, Tamaulipas, Chiapas, Guerrero, Hidalgo, Jalisco, México, Michoacán de Ocampo, Morelos, Nayarit, Oaxaca, Puebla, Querétaro, Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, Yucatán) SOUTHERN AMERICA: Guatemala, Peru (Ucayali)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment