 |
|
https://edibleplants.org/ |
 |
| https://edibleplants.org/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
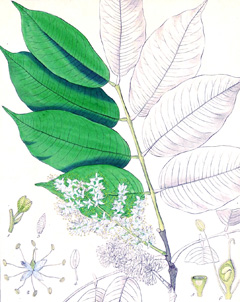
Found in Northern South America, Copaifera guyanensis is an evergreen tree that grows up to 40 m in height. The trunk has a thick base. The resin obtained from the trunk is used as food additive and as flavouring agent in food and beverages. It is also used widely medicinally for its antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, disinfectant, diuretic, and astringent properties. The resin may be taken internally against respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems conditions or applied externally for various skin ailments. It can also be gargled to cure sore throat and tonsillitis. The resin is also used in perfumery, varnishes and lacquers, and as substitute for diesel oil. The wood is used in light carpentry, interior panelling and joinery, flooring, boxes and crates, furniture, veneer, and fibre boards. Found In: South America - Brazil.
Physical Characteristics

 Copaifera guyanensis is an evergreen Tree growing to 30 m (98ft) by 30 m (98ft) at a slow rate.
Copaifera guyanensis is an evergreen Tree growing to 30 m (98ft) by 30 m (98ft) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Copaiba guianensis Kuntze Copaifera beyrichii Hayne ex Baker Copaifera bijuga Hayne Copaiva guianens
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Edible Parts:
Edible Uses: Condiment
The resin has been approved officially in the U.S. as a food additive and is used in small amounts as a flavouring agent in foods and beverages[ 318 ].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anodyne Antacid Antibacterial Antifungal Antiinflammatory Antiseptic Antitumor Aromatic
Astringent Cytostatic Demulcent Digestive Disinfectant Diuretic Eczema
Expectorant Kidney Laxative Skin Stimulant Urinary Vermifuge
Copaiba-balsam, an oily oleo-resin obtained from the trunk of the tree, has a very long history of use medicinally. It was widely used by the native peoples prior to the Europeans reaching S. America and these uses were soon taken up by the Europeans[ 317 ]. The resin is especially valued for its ability to counter mucous in the chest and genito-urinary system[ 254 ]. The resin is an aromatic, stimulant herb with a bitter, burning taste[ 238 ]. Both it and the bark are anodyne, antacid, antibacterial, antifungal, antiinflammatory, antimicrobial, astringent, cytostatic, demulcent, digestive, disinfectant, diuretic, expectorant, mildly laxative, vermifuge and vulnerary[ 318 ]. The resin obtained from the trunk contains a number of medically active constituents including 30 - 90% essential oils and unusual condensed tannins[ 238 ]. The essential oil contains alpha- and beta-caryophyllene, sesquiterpenes, resins and terpenic acids[ 254 ]. It improves the digestion, has diuretic and expectorant effects, and controls bacterial infections[ 238 ]. Much of the clinical research performed to date has verified the traditional uses of copaiba. It has, for instance, been shown to be highly effective as a topical wound healer and anti-inflammatory agent[ 318 ]. The anti-inflammatory effect is mainly due to the sesquiterpenes, particularly caryophyllene which has also demonstrated effective pain-relieving properties, antifungal properties against nail fungus and gastroprotective properties[ 318 ]. The resin as a whole (and, particularly, two of its diterpenes - copalic acid and kaurenic acid) has demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity against gram-positive bacteria. One of copaiba?s other chemicals, kaurenoic acid, has also demonstrated selective antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria in other recent studies[318. Other constituents of the resin have demonstrated significant antitumor activity[ 318 ]. The resin is taken internally in the treatment of a range of respiratory problems such as tuberculosis, bronchitis and sinusitis; urinary tract and reproductive system conditions such as cystitis, kidney and bladder infections, vaginal discharge and gonorrhoea[ 238 , 254 ]. Stomach ulcers, tetanus, herpes, pleurisy and haemorrhages are just some of the other conditions treated with the resin[ 318 ]. Externally, it is used in the treatment of a range of skin problems including insect bites, eczema, chilblains, sores and psoriasis[ 238 , 254. It is also used to treat wounds and stop bleeding[ 318 ]. As an antiseptic gargle, it is used to treat sore throats and tonsillitis[ 318 ]. The resin should be used with care, see notes above on toxicity[ 238 ]. The resin is tapped at intervals from the tree and the holes filled in afterwards[ 238 ]. It is used in infusions or distilled for its essential oil[ 238 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Containers Disinfectant Essential Fuel Furniture Lacquer Resin Tannin Varnish Wood
Other Uses: An oleoresin is obtained from the tree[ 46 ]. It is used in varnishes and lacquers; for photographic paper; removing varnish from old oil paintings etc[ 46 ]. The resin can be used, direct from the tree, as a substitute for diesel oil[ 238 ]. The heartwood is pink to red-brown with copper-coloured veins; it is clearly demarcated from the 2 - 3cm wide band of sapwood. The texture is medium; the grain straight or interlocked, sometimes wavy. The wood is light to very light in weight, soft to moderately hard; somewhat durable being resistant to dry wood borers but susceptible to fungi and termites. It seasons quickly with very little risk of checking or distortion; once dry it is moderately stable to stable in service. It can be worked with normal tools, though they need to be kept sharp to avoid fuzzy surfaces; nailing and screwing are often poor; gluing is correct[ 848 ]. An excellent timber[ 461 ], the wood has a wide range of uses, including for light carpentry, interior panelling and joinery, flooring, boxes and crates, furniture, veneer and fibre boards[ 848 ].
Special Uses
Nitrogen Fixer
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
A tropical tree. Copaifera is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family. Producing economically important resins and essential oils. Also important for production of biodiesel and wood. The scientific name means "copal-bearer?.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Copaifera guyanensis, Hoepel, Guyanense Copaiba
Native Range
SOUTHERN AMERICA: French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, Brazil (north)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Desf.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Copaifera guyanensis
|
|
|
|