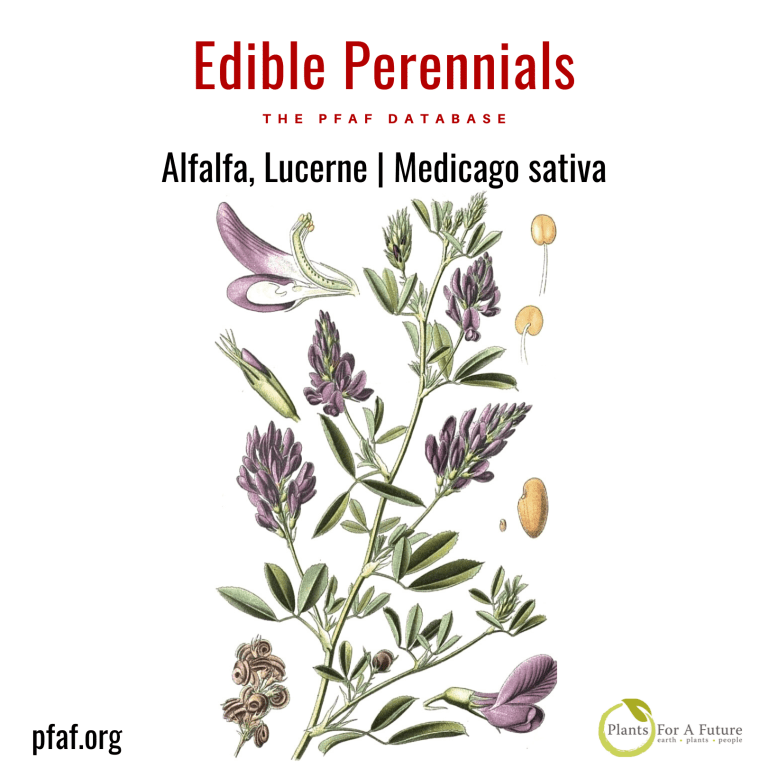
Alfalfa, also called lucerne, is a medium-sized nitrogen-fixing perennial in the legume family cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries. Ancient Greeks and Romans produced Alfalfa as livestock fodder. It is excellent green manure and a cover crop.
Is Alfalfa edible?
The seed is commonly sprouted and added to salads, used in sandwiches or cooked in soups. Alfalfa sprouts are a common ingredient in dishes made in South Indian cuisine. They are high in vitamin K and are a moderate vitamin C source, B vitamins, phosphorus and zinc. Sprouted seed is ready in about 4-6 days. The dry seeds are ground into a powder and used as a mush or mixed with cereal flours for making nutritionally improved bread.
Leaves and young shoots are eaten raw, cooked or dried for later use. They are a good source of protein and rich in vitamin A, B and C. The leaves are a rich source of vitamin K. A very nutritious food in moderation.
Alfalfa has a deep taproot (to 6m/20ft) and, once established, tolerates drought, nutritionally poor soils and arid conditions. The root brings up nutrients deep in the ground, making them available for other plants with shallower root systems. The roots fix large quantities of atmospheric nitrogen, making Alfalfa one of the best green manures. It does not tolerate waterlogging or very acidic soils. Alfalfa is an excellent companion plant for fruit trees and grapevines. Heat zones 8 through 5.
Propagation
Seed.
Other Uses of Alfalfa
• Self-fertile • Nitrogen Fixer • Dynamic Accumulator • Nectary • Wildlife
• Invertebrate Shelter • Hedge • Green manure
Medicago sativa
Family Leguminosae
Known Hazards The plant contains saponin-like substances 9see the database).
Habitats Waste ground, avoiding acid soils.
Edibility Rating 4
Other Uses 4
Weed Potential Yes
Medicinal Rating 3
More information on Alfalfa, Lucerne Medicago sativa is available in the database.