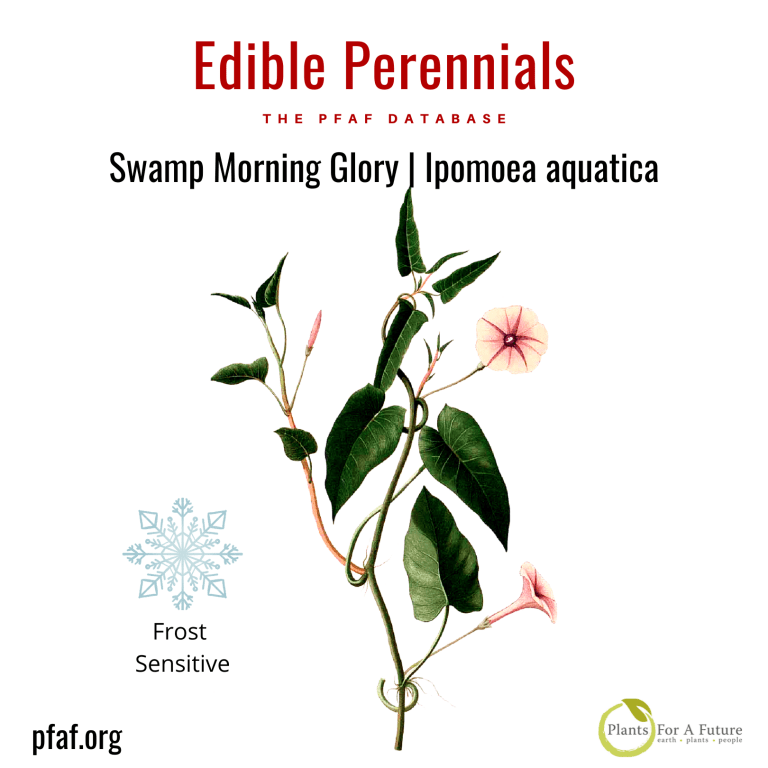
Ipomoea aquatica
Ipomoea aquatica, commonly known as the water morning glory or Kangkong, is a perennial flowering plant. It is native to moist areas of the Americas, where it grows in water or wet soils. I. aquatica can reach up to one meter in height, or the stems sprawl for 2-3 m over the ground, float in water, or twine into other plants for support.
Is Ipomoea aquatica, Water Morning Glory Edible?
The tasty leaves and young shoots are produced year-round and are eaten raw or cooked. The youngest shoot tips are added to salads; older leaves are cooked and make mild-flavoured spinach. The leaves can be stir-fried, steamed, boiled for a few minutes, lightly fried in oil, and eaten in various dishes. They are often mixed with hot peppers and garlic and prepared with a savoury dish. Very nutritious, the leaves are a good source of protein as well as providing reasonable quantities of vitamin A, iron, calcium and phosphorus. Roots – occasionally cooked and eaten.
Propagation: Seed. Cuttings -Easy.
Other Uses of Ipomoea aquatica
- Medicinal
- Water Plant
- Water and soil reclamation
- Fodder
Ipomoea aquatica
Family: Convolvulaceae
Known Hazards: Accumulates heavy metals
Habitats: Moist, marshy or inundated localities, shallow pools, ditches, rice fields, forming dense masses.
Edibility Rating: 4
Other Uses: 2
Weed Potential: Yes
Medicinal Rating: 2
More information on Ipomoea aquatica | Water Morning Glory or Kangkong is available in the database.