 |
|
commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Pethan |
 |
| commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Trifolium_spp_Sturm34.jpg |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

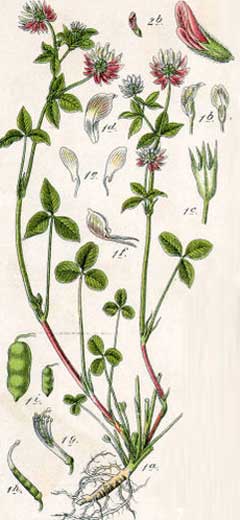
 Trifolium hybridum is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.6 m (2ft). It is in flower from June to September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
Trifolium hybridum is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.6 m (2ft). It is in flower from June to September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Trifolium elegans. Trifolium hybridum elegans
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Flowers Leaves
Edible Uses: Tea
Leaves and flower heads - raw or cooked. Boiled, or after soaking for several hours in salty water[183]. A delightful and healthful tea is made from the dried flower heads[183]. They are usually mixed with other teas[183]. The dried flower heads and seeds can be ground into a nutritious flour[183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Galactogogue
A cold infusion of the plant has been used as a wash on the breasts of a nursing mother in order to increase the milk flow[257].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Agroforestry Services: Nitrogen Agroforestry Services: Understory legume Fodder: Pasture Management: Fodder Management: Hay Minor Global Crop
Succeeds in a moist, well-drained circum-neutral soil in full sun[200]. Succeeds in poor soils. Closely related to T. repens[60]. It grows well in an apple orchard, the trees will produce tastier fruit that stores better[201]. It should not be grown with camellias or gooseberries because it harbours a mite that can cause fruit drop in the gooseberries and premature budding in the camellias[201]. This species has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria, these bacteria form nodules on the roots and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Some of this nitrogen is utilized by the growing plant but some can also be used by other plants growing nearby[200]. Buttercups growing nearby depress the growth of the nitrogen bacteria by means of a root exudate[201].
Carbon Farming
-
Agroforestry Services: Nitrogen
Plants that contribute to nitrogen fixation include the legume family – Fabaceae.
-
Agroforestry Services: Understory legume
Legume vegetation, especially the trees and shrubs growing between the forest canopy and the forest floor.
-
Fodder: Pasture
Enclosed tracts of farmland mainly of grasses, with an interspersion of legumes and other forbs (non-grass herbaceous plants).
-
Management: Fodder
Non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Management: Hay
Cut to the ground and harvested annually. Non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Minor Global Crop
These crops are already grown or traded around the world, but on a smaller scale than the global perennial staple and industrial crops, The annual value of a minor global crop is under $1 billion US. Examples include shea, carob, Brazil nuts and fibers such as ramie and sisal.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Pre-soak the seed for 12 hours in warm water and then sow in spring in situ. If the seed is in short supply it might be better to sow it in pots in a cold frame. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and plant them out after the last expected frosts. Division in spring.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russian Federation (Checheno-Ingushetia, Dagestan, Kabardino-Balkaria, Karacaevo-Cerkesskaja Respublika, Krasnodar, Stavropol) EUROPE: Czechoslovakia, Austria, Switzerland, Hungary, Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Moldova, Russian Federation (Baškortostan, Respublika, Cuvašskaja Respublika, Kalmykija, Respublika, Karelia, Komi, Marij Èl, Respublika, Mordovija, Respublika, Tatarstan, Udmurtia, Arkhangelsk, Neneckij avtonomnyj okrug, Astrakhan, Belgorod, Bryansk, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Kalužskaja oblast, Kirov, Kostroma, Kursk, Leningradskaja oblast, Lipeckaja oblast, Moscow, Murmansk, Novgorod, Orel, Orenburg, Penza, Perm, Komi-Permyak, Pskovskaja oblast, Rostov, Ryazan, Saratov, Smolensk, Tambov, Tula, Ulyanovsk, Vladimir, Volgogradskaja oblast, Vologda, Voronezh, Yaroslavl), Ukraine (incl. Krym), Former Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Greece (incl. Crete), Italy, Romania, Spain, France AFRICA: Morocco
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Trifolium bifidum | Piñole Clover, Notchleaf clover | Annual | 0.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Trifolium ciliatum | Foothill Clover | Annual | 0.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Trifolium cyathiferum | Cup Clover | Annual | 0.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium dichotomum | Branched Indian Clover | Annual | 0.6 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium dubium | Suckling Clover | Annual | 0.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Trifolium fimbriatum | Springbank Clover, Cows clover | Perennial | 1.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium fucatum | Sour Clover, Bull clover | Annual | 0.6 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium fucatum virescens | | Annual | 0.6 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium gracilentum | Pin-Point Clover, Palmer's clover | Annual | 0.6 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium incarnatum | Crimson Clover | Annual | 0.5 |
3-9
| M | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Trifolium lupinaster | Lupine clover | Perennial | 0.5 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium macrocephalum | Bighead Clover, Largehead clover | Perennial | 0.3 |
4-8
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Trifolium microcephalum | Smallhead Clover | Annual | 0.6 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Trifolium obtusiflorum | Clammy Clover | Annual | 1.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium ornithopodioides | Birdsfoot Fenugreek, Bird clover | Annual/Perennial | 0.2 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | MWe | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Trifolium pratense | Red Clover | Perennial | 0.6 |
5-9
| M | LMH | N | M | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Trifolium repens | White Clover, Dutch Clover, Purple Dutch Clover, Shamrock, White Clover | Perennial | 0.1 |
4-8
| M | LMH | N | M | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| Trifolium subterraneum | Subterranean Clover | Annual | 0.2 |
7-10
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Trifolium tridentatum | Tomcat Clover | Annual | 0.6 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Trifolium variegatum | Whitetip Clover | Annual | 1.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Trifolium wormskioldii | Cow clover | Perennial | 1.0 |
5-9
| | LMH | N | MWe | 3 | 0 | 0 |
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
17
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Trifolium hybridum
|
|
|
|