 |
|
https://edibleplants.org/ |
 |
| https://edibleplants.org/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
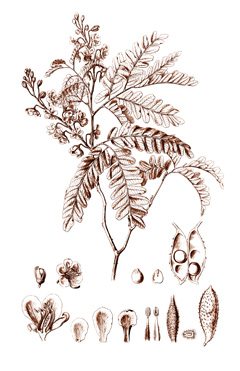
Pau Brasil, Caesalpinia echinata, is a slow-growing small tree up to 12 m high found in South America. It has a large rounded crown and the branches, leaves, and fruits are thorned. When fully established, it is drought-tolerant. Bark is powdered and used as treatment for diarrhoea in children. Pods and wood are sources of black dye and red dye (brazilin), respectively. The wood is heavy, tough, hard, and durable and is used for turnery, building ship and making musical instruments like bows for violins. Other common names include Brazil Wood and Pernambuco tree. Common names: Brazilwood, Pernambuco tree. Portuguese: Pau-Brasil, Pau de Pernambuco; Tupi Ibirapitanga.
Physical Characteristics

 Caesalpinia echinata is an evergreen Tree growing to 12 m (39ft) by 12 m (39ft) at a medium rate.
Caesalpinia echinata is an evergreen Tree growing to 12 m (39ft) by 12 m (39ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10 and is frost tender. The flowers are pollinated by Bees.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very alkaline and saline soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil and can tolerate drought. The plant can tolerates strong winds but not maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Guilandina echinata (Lam.) Spreng.
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antidiarrhoeal Odontalgic Tonic
A charcoal made from the powdered bark is infused and used to treat diarrhoea in children[ 307 ]. The wood is odontalgic and tonic[ 739 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Charcoal Dye Hedge Wood
Other uses rating: High (4/5). Seaside, Small flowering Tree, Accent, Screening, Barrier, Large planter, Xerophytic. Agroforestry Uses: Plants can be trimmed to keep them small and dense[ 307 ]. This gives them potential for use as barrier plants[ 307 ]. Other Uses An infusion of the pods, mixed with iron sulphate, yields a permanent black dye[ 307 ]. A red dye is obtained from the wood[ 46 ]. It becomes purplish when mixed with alkalis and yellow if mixed with acids[ 46 ]. A fiery red colour, the dye was a very important item of trade until virtually replaced with synthetic dyes[ 349 ]. The heartwood is red-brown to dark brown; it is clearly differentiated from the thin layer of sapwood. The wood is fine-grained, very tough, hard, heavy and very durable[ 46 , 307 , 419 ]. Very dense, it sinks in water, is easy to split and to polish[ 46 ]. Of high value, the wood is used for turnery, ship building and making musical instruments[ 46 , 307 ]. It is particularly valued for making bows for violins[ 349 ].
Special Uses
Hedge Nitrogen Fixer
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a well-drained, alkaline soil and a position in full sun[ 307 ]. Established plants are very drought tolerant[ 307 ]. Plants are fairly tolerant of salt-laden winds[ 307 ]. A moderately fast-growing tree, reaching a height of up to 2 metres within 2 years from seed[ 419 ]. Plants begin to flower when around 3 - 4 years of age[ 349 ]. The development of heartwood in plantation trees is considerably faster than in the wild; the DBH of a 17 year old plantation tree compares with a 70 year old tree in the wild[ 349 ]. The quality of wood from plantations is, apparently, not suitable for making violin bows and consequently there is a lack of interest in growing the species in plantation[ 349 ]. The flowers are very attractive to bees[ 307 ]. Trees in the wild are frequently covered with orchids and other epiphytes[ 349 ]. Plants in this genus are notably resistant to honey fungus[ 200 ]. This species has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria, these bacteria form nodules on the roots and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Some of this nitrogen is utilized by the growing plant but some can also be used by other plants growing nearby[ 200 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - pre-soak for 12 - 24 hours in warm water prior to sowing. Sow the seed in a partially shaded position in individual containers. A germination rate in excess of 60% can be expected, with the seed sprouting within 8 - 15 days[ 419 ]. When the seedlings are 4 - 6cm tall, pot them up into individual containers and they should be ready to plant out 4 - 5 months later[ 419 ]. Seeds must be sown fresh, they fail to germinate after storage for 30 days[ 349 ]. Softwood cuttings in sand in a frame[ 200 ]. This plant may be considered a protected species; check before digging or gathering seeds.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Pau Brasil, Caesalpinia echinata. Other common names include Brazil Wood and Pernambuco tree. Common names: Brazilwood, Pernambuco tree. Portuguese: Pau-Brasil, Pau de Pernambuco; Tupi Ibirapitanga.
Native Range
SOUTHERN AMERICA: Brazil (Alagoas, Bahia, Espírito Santo, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande do Norte, Santa Catarina)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : Status: Endangered A1acd.

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Lam.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Caesalpinia echinata
|
|
|
|