 |
|
https://edibleplants.org/ |
 |
| wikimedia.org User:Hariadhi |
Translate this page:
Summary
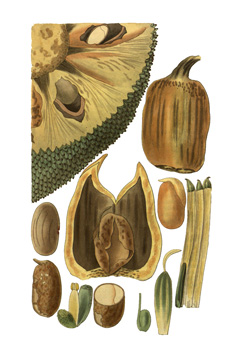
Champedak or Artocarpus integer is a fast-growing, tropical tree that reaches up to 35 meters tall and 55 cm trunk diameter when fully matured. It has a dense, rounded crown. Its bark is dark grey or red-brown in colour. The leaves are oval and leathery. The fruit is a compound fruit, sweet, spiky and yellow to brown in colour. It is eaten fresh, fried with flour, or made into a type of pudding. When unripe, it can be cooked as vegetable or added into soups. Ripe seeds can be roasted or boiled. Young leaves are cooked and consumed as vegetable. The bark yields a fibre that is used in making ropes. A resin can also be obtained from the tree and it is used as a varnishing material. The tree is a good fuel source and is often used as a construction material. Other Names: Bangkong, Banturung manuk, Baroh, Beluno, Bukoh, Campedek, Champada, Chubadak, Kakan, Mangkahai, Nakan, Nangka berit, Nangka tjomedak, Pulutan, Sempedak, Sonekadot, Temedak, Tibadak, Tibudak [1b].
Physical Characteristics

 Artocarpus integer is an evergreen Tree growing to 20 m (65ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a slow rate.
Artocarpus integer is an evergreen Tree growing to 20 m (65ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10. The flowers are pollinated by Insects, wind.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid and neutral soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Artocarpus champeden (Lour.) Stokes. Artocarpus integrifolia L.f. Artocarpus polyphema Persoon. Poly
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Fruit Leaves Seed
Edible Uses:
Edible portion: Fruit, Seeds, Leaves. Fruit - raw or cooked. The pulp of the ripe fruit is golden-yellow, it is rather slimy and strongly odoriferous, almost like that of the durian[ 301 ]. The flavour is sweet, resembling durian and mango[ 306 ]. It is eaten fresh, fried with flour, or made into a type of pudding[ 301 ]. The unripe fruit is used as a cooked vegetable or is added to soups[ 301 ]. The fruit is up to 9cm long[ 200 ]. The almost globose fruit is 20 - 35cm long x 10 - 15cm wide[ 303 ]. Each fruit can weigh from 600 - 3,500g[ 418 ]. Ripe seeds - roasted or boiled and eaten as a delicacy[ 301 ]. Rich in starch, they have a nutty flavour[ 303 , 306 ]. Young leaves - cooked and used as a vegetable[ 301 , 320 ].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Dye Fibre Fuel String Tannin Varnish Wood
Other uses rating: Medium (3/5). Agroforestry Uses: The tree is well suited for reforestation projects in association with other species[ 303 ]. Other Uses A fibre obtained from the bark can be used to make rope[ 303 , 306 , 320 ]. A resin obtained from the tree is used as a varnishing material[ 303 ]. The latex obtained from the plant has no value[ 303 ]. It can be used for making lime[ 320 ]. The bark contains tannin. With alum, the extract of heartwood provides a yellow dye that is moderately fast on silk. This dye is used in colouring the saffron-coloured robes of Buddhists[ 303 ]. The dark yellow to brown wood is strong and durable and is used for building construction, furniture and boats[ 306 ]. Sold under the trade name jack, is as strong as teak (Tectona grandis), takes a good polish, saws and works easily, and is durable under water[ 303 ]. It is generally not attacked by fungi and termites[ 303 ]. The tree is a good fuel wood; the calorific value of moisture-free heartwood is 5369 kcal/kg of wood[ 303 ].
Special Uses
Carbon Farming Food Forest
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Industrial Crop: Hydrocarbon Management: Standard Regional Crop Staple Crop: Balanced carb Staple Crop: Basic Starch
A plant of the lowland humid tropics, growing best at an altitude below 1,200 metres [ 200 , 303 ], in its native range it is always restricted to regions without a distinct dry season[ 303 , 306 ]. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 22 - 38c, but can tolerate 16 - 47c[ 418 ]. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 2,200 - 3,500mm, but tolerates 1,250 - 4,500mm[ 418 ]. Prefers a deep, well-drained fertile soil[ 200 , 306 ]. Young plants need some shade, but need increasing light levels as they mature [ 200 ]. Prefers a fairly high water table[ 306 ], it can survive periodic flooding even with acid swamp water[ 306 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 4.5 - 6, tolerating 4 - 6.5[ 418 ]. The tree usually fruits prolifically and is capable of very high yields [ 306 ]. Seedlings start bearing fruit after 3 - 6 years; clonal trees bear after 2 - 4 years. Flowers may be found at any time of year, but bloom is concentrated around one period of the year[ 303 ]. Female flower heads are found only on cauliflorous shoots; most male heads are formed on shoots in the periphery of the canopy. This may facilitate pollination by wind, although the pollen is sticky. Insects visit the scented male inflorescence, not the female ones, which lack nectar [ 303 ].
Carbon Farming
-
Industrial Crop: Hydrocarbon
Materials, chemicals and energy include bioplastics, rubber, biomass products gasoline, jet fuel, diesel, butane, propane, biogas. Plants are usually resprouting plants and saps.
-
Management: Standard
Plants grow to their standard height. Harvest fruit, seeds, or other products. Non-Destructive management systems.
-
Regional Crop
These crops have been domesticated and cultivated regionally but have not been adopted elsewhere and are typically not traded globally, Examples in this broad category include perennial cottons and many nuts and staple fruits.
-
Staple Crop: Balanced carb
(0-15 percent protein, 0-15 percent oil, with at least one over 5 percent). The carbohydrates are from either starch or sugar. Annuals include maize, wheat, rice, and potato. Perennials include chestnuts, carob, perennial fruits, nuts, cereals, pseudocereals, woody pods, and acorns.
-
Staple Crop: Basic Starch
The Carbon Farming Solution. Eric Toensmeier.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe[ 200 ]. The seed germinates best at a temperature of 24 - 27c[ 200 ]. It can be raised by direct sowing or planting nursery-raised container seedlings[ 303 ]. Fresh seeds record germination rates of about 75%[ 303 ]. Root cuttings. Air layering.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Champedak or Artocarpus integer. Other Names: Bangkong, Banturung manuk, Baroh, Beluno, Bukoh, Campedek, Champada, Chubadak, Kakan, Mangkahai, Nakan, Nangka berit, Nangka tjomedak, Pulutan, Sempedak, Sonekadot, Temedak, Tibadak, Tibudak.
Native Range
TROPICAL ASIA: New Guinea, Indonesia, Papua, Thailand, Borneo, Brunei Darussalam, Indonesia, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Jawa, Maluku, Sumatera, Malaysia, Singapore,
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed.

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(Thunb.) Merr.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Artocarpus integer
|
|
|
|