 |
|
http://www.hear.org/starr/ |
 |
| http://plants.usda.gov/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

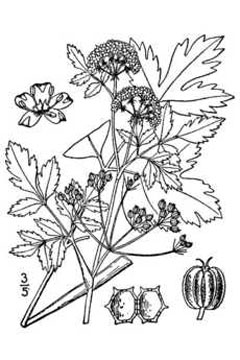
 Apium graveolens dulce is a BIENNIAL growing to 0.6 m (2ft).
Apium graveolens dulce is a BIENNIAL growing to 0.6 m (2ft).
It is not frost tender. It is in flower from June to August, and the seeds ripen from August to September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Flies. The plant is self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid and very alkaline soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Leaves Root Seed
Edible Uses: Condiment
Leaf stems - raw or cooked[1, 2, 16, 21]. A fairly common salad ingredient, celery stems are also used to make soups, stews etc. The winter varieties can be bitter if they are not blanched by excluding light from the stems for at least a few weeks prior to harvesting. Many people find the raw stalks are somewhat indigestible[113]. Leaves - raw or cooked. They are often used as a flavouring in soups etc[9, 21, 46]. They can also be eaten raw but have a very strong flavour and are probably best as a minor ingredient in a mixed salad. Seed - used as a flavouring for sauces, soups, pickles etc[171, 183]. An essential oil from the seed is also used as a flavouring[183]. Root - cooked. There is not much of it but it can be cut up and added to soups[K].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antiarthritic Aperient Carminative Diuretic Emmenagogue Galactogogue Nervine Stimulant
Tonic
Although not as medicinally active as wild celery, the cultivated forms of celery also have the same medicinal properties and, when used as an item of the diet, will have a similar effect upon the body. These medicinal uses are as follows:- Wild celery is an aromatic bitter tonic herb that reduces blood pressure, relieves indigestion, stimulates the uterus and is anti-inflammatory[238]. The ripe seeds, herb and root are aperient, carminative, diuretic, emmenagogue, galactogogue, nervine, stimulant and tonic[4, 7, 21, 165]. Wild celery is said to be useful in cases of hysteria, promoting restfulness and sleep and diffusing through the system a mild sustaining influence[4]. The herb should not be prescribed for pregnant women[238]. Seeds purchased for cultivation purposes are often dressed with a fungicide, they should not be used for medicinal purposes[238]. The root is harvested in the autumn and can be used fresh or dried[238]. The whole plant is harvested when fruiting and is usually liquidized to extract the juice[238]. The seeds are harvested as they ripen and are dried for later use[238]. An essential oil obtained from the plant has a calming effect on the central nervous system. Some of its constituents have antispasmodic, sedative and anticonvulsant actions. It has been shown to be of value in treating high blood pressure[254]. A homeopathic remedy is made from the herb[9]. It is used in treating rheumatism and kidney complaints[9].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Repellent
The growing plant is an insect repellent, it repels the cabbage white butterfly so is a good companion for brassicas[20].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a rich light moist soil with some shade in summer[1, 16, 27, 37]. Prefers a sunny position and a pH between 6.6 and 6.8[200]. Tolerates a pH in the range 4.2 to 8.3. Plants grow best in a climate with a mean temperature in the range 16 - 21°c, leaf growth is poor at higher temperatures, low temperatures can induce the plant to run to seed prematurely. Plants with 5 or more true leaves will flower following exposure to temperatures between 5 - 10°c for 10 days or more[200]. Celery is commonly cultivated in many regions of the world, mainly for its edible leaf stalks. There are many named varieties and these can supply fresh stalks from late summer to spring[46, 183]. There are two basic types of celery. Those grown for summer and autumn harvesting are called 'self-blanching' - the stems do not need to be blanched in order to be eaten, though they are usually grown quite closely together which tends to exclude quite a bit of light. Those cultivars harvested in the winter and spring tend to have bitter-tasting stems unless these are blanched by excluding light. A good companion for leeks, tomatoes, French beans and brassicas[18, 201].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - germination can be erratic and the seed is best surface sow February in a greenhouse. The maincrop can be sown as late as mid-April. Outdoor sown seed rarely germinates satisfactorily[200]. Germinates in 2 - 3 weeks at 15°c. Plant out in May. The seed can harbour certain diseases of celery, it is usually treated by seed companies before being sold but if you save your own seed you should make sure that only seed from healthy plants is used[1].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
Coming Soon
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(Mill.)Pers.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
© 2010, Plants For A Future. Plants For A Future is a charitable company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales. Charity No. 1057719, Company No. 3204567.