 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Illustration_Solanum_dulcamara0.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Llez |
Translate this page:
Summary
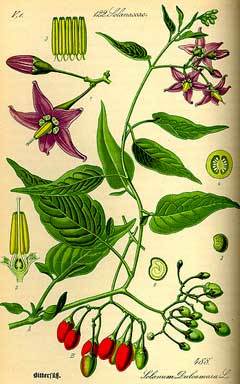
Bloom Color: Blue, Lavender, Red. Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Early fall, Late summer, Late spring, Mid summer. Form: Upright or erect.
Physical Characteristics

 Solanum dulcamara is a PERENNIAL CLIMBER growing to 2.5 m (8ft) by 2.5 m (8ft) at a medium rate.
Solanum dulcamara is a PERENNIAL CLIMBER growing to 2.5 m (8ft) by 2.5 m (8ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 4. It is in flower from June to September, and the seeds ripen from August to October. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil. The plant can tolerates strong winds but not maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Shady Edge; Hedgerow;
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Alterative Anodyne Cancer Depurative Diuretic Eczema Emetic Expectorant
Hepatic Homeopathy Narcotic Purgative
Bittersweet is a poisonous plant that has a long history of use in the treatment of skin diseases, warts, tumours, felons etc[238]. It should be used with caution and only under the supervision of a qualified practitioner, this is a poisonous plant that, in excess, paralyzes the central nervous system, slows the heart and respiration, and lowers temperature, causing vertigo, delirium, convulsions and death[21, 238]. See also the notes above on toxicity. All parts of the plant are alterative, anodyne, depurative, mildly diuretic, emetic, expectorant, hepatic, mildly narcotic and purgative[4, 7, 9, 13, 21, 165]. The dried stem, usually collected in the autumn and preferably from the ends of branches 2 - 3 years old, is the part that is most valued medicinally, though the leaves are also used[4]. The plant is chiefly used as an alterative when taken internally in the treatment of a range of skin diseases, it is also used in the treatment of arthritis, rheumatism, bronchial congestion, heart ailments, ulcerative colitis and jaundice[4, 218, 238]. Externally, the plant is used to treat skin eruptions, ulcers, rheumatism and cellulite[238]. Two to three year old stems are harvested in the spring, or after the leaves have fallen in the autumn, and dried for later use[238]. The fruits are marinated in vinegar and applied to cancerous sores and other swellings[218]. A decoction of the root is used in the treatment of cancer and swellings[218]. The root is harvested in the autumn and dried for later use[238]. A homeopathic remedy is made from the fresh, green, still pliant stems and leaves, harvested as the plant begins to flower[232]. This is used in treating a variety of complaints including backaches, cough, diarrhoea, eye inflammations and joint pains[232]. The German Commission E Monographs, a therapeutic guide to herbal medicine, approve Solanum dulcamara for eczema, furuncles (boils), acne, warts (see [302] for critics of commission E).
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
An easily grown plant, it succeeds in most soils[1, 202]. Prefers a damp shady position and a neutral to alkaline soil[10, 238]. Succeeds in full sun to light shade[202]. If being grown for its medicinal uses, the plant is best placed in a dry and exposed position[4]. Hardy to at least -15°c[202]. Special Features:Attractive foliage, Not North American native, Invasive, Naturalizing, All or parts of this plant are poisonous.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow spring in a cold frame. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and plant them out into their permanent positions in the summer. If you have sufficient seed then it can be sown outdoors in situ in the spring. Division in spring.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Afghanistan, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia (Ciscaucasia), Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russian Federation (Dagestan), Russian Federation-Western Siberia (Western Siberia), Turkmenistan, Mongolia, China (Hebei Sheng, Heilongjiang Sheng, Jilin Sheng, Liaoning Sheng, Nei Mongol Zizhiqu, Qinghai Sheng, Sichuan Sheng (southwest), Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu, Yunnan Sheng (northwest)) TROPICAL ASIA: India (north), Nepal, Pakistan EUROPE: Denmark, Finland, United Kingdom, Ireland, Norway, Sweden, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Russian Federation (European part), Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Moldova, Ukraine (incl. Krym), Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Croatia, Italy, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France, Portugal AFRICA: Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Solanum aethiopicum | Mock Tomato, Ethiopian nightshade | Shrub | 2.5 |
10-12
| | LMH | N | M | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Solanum ajanhuiri | Ajanhuiri | Perennial | 0.0 |
9-11
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum americanum | American Nightshade, American black nightshade | Annual | 1.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Solanum andigenum | Andigena | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum aviculare | Kangaroo Apple, New Zealand nightshade | Shrub | 1.8 |
8-11
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Solanum boreale | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum boyacense | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum cari | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum carolinense | Horse Nettle, Carolina horsenettle | Perennial | 1.0 |
3-7
| | LMH | SN | M | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Solanum chaucha | Chaucha | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum curtilobum | Rucki | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum fendleri | Wild Potato, Fendler's horsenettle, Texan horsenettle | Perennial | 0.0 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | M | 3 | 2 | |
| Solanum jamesii | Colorado Wild Potato, Wild potato | Perennial | 0.2 |
8-11
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum juzepczukii | Rucki | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum kurzii | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum laciniatum | Kangaroo Apple | Shrub | 3.0 |
8-11
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Solanum linearifolium | Mountain Kangaroo Apple | Shrub | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum liximitante | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum luteum | | Annual | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | |
| Solanum lycopersicum | Tomato, Garden Tomato | Annual | 2.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Solanum lyratum | | Perennial Climber | 2.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 1 | 2 | |
| Solanum maglia | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum melongena | Aubergine, Eggplant | Perennial | 1.0 |
8-11
| | LMH | N | M | 3 | 2 | |
| Solanum muricatum | Pepino | Shrub | 1.0 |
8-11
| | LMH | N | M | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Solanum nigrum | Black Nightshade, Common Nightshade, Poisonberry, Black Nightshade | Annual | 0.6 |
0-0
| | LMH | N | DM | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Solanum paniculatum | Jurubeba, Nightshade | Shrub | 2.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | SN | M | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Solanum phureja | Phureja, Nightshade | Perennial | 0.0 |
8-11
| | LMH | SN | M | 3 | 0 | |
| Solanum piliferum | | Perennial | 0.0 |
-
| | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Solanum pimpinellifolium | Currant Tomato | Annual/Biennial | 1.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 4 | 2 | 2 |
|
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
17200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment