 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koeh-050.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Llez |
Translate this page:
Summary
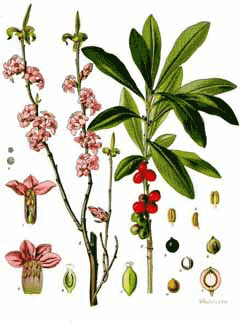
Bloom Color: Pink, White.
Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Late spring, Mid spring. Form: Rounded.
Physical Characteristics

 Daphne mezereum is a deciduous Shrub growing to 1.5 m (5ft) by 1.5 m (5ft) at a medium rate.
Daphne mezereum is a deciduous Shrub growing to 1.5 m (5ft) by 1.5 m (5ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 4 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from February to March, and the seeds ripen from June to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees, flies, Lepidoptera (Moths & Butterflies). The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and can grow in heavy clay soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland). It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Shady Edge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Oil
Edible Uses: Oil
None known
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antirheumatic Antiseborrheic Cancer Cathartic Diuretic Emetic Homeopathy Rubefacient
Stimulant Vesicant
Mezereum has been used in the past for treating rheumatism and indolent ulcers, but because of its toxic nature it is no longer considered to be safe[238]. The plant contains various toxic compounds, including daphnetoxin and mezerein, and these are currently being investigated (1995) for their anti-leukaemia effects[238, 254]. The bark is cathartic, diuretic, emetic, rubefacient, stimulant and vesicant[4, 7, 9, 21, 46]. The root bark is the most active medically, but the stem bark is also used[4]. It has been used in an ointment to induce discharge in indolent ulcers[4] and also has a beneficial effect upon rheumatic joints[254]. The bark is not usually taken internally and even when used externally this should be done with extreme caution and not applied if the skin is broken[4, 21, 254]. The bark is harvested in the autumn and dried for later use[7]. The fruits have sometimes been used as a purgative[4]. A homeopathic remedy is made from the plant[7]. It is used in the treatment of various skin complaints and inflammations[7, 9].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Dye Oil
A yellow to greenish-brown dye is obtained from the leaves, fruit and bark[13]. The seed contains up to 31% of a fatty oil[74]. No further details are given.
Special Uses
Attracts Wildlife Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Border, Foundation, Specimen. A good sandy loam suits most members of this genus[11]. Prefers a good heavy soil and some shade[31, 49]. Prefers a calcareous soil[13, 17, 19] and cool moist conditions[11, 49]. There is no evidence to suggest it requires a calcareous soil, but all members of this genus do well on acid soils[11]. A very ornamental plant[1], it is hardy to about -30°c[184]. Plants tend to be short-lived in cultivation, probably due to excessive seed bearing[11, 200]. Plants are resentful of root disturbance and should be planted into their permanent positions as soon as possible[188]. They also resent being cut and so should not be pruned unless it is essential[245]. A good bee plant, providing a source of nectar very early in the year[108]. The flowers have a delicious sweet perfume[245]. Special Features:Attractive foliage, Not North American native, Naturalizing, All or parts of this plant are poisonous, Fragrant flowers, Attractive flowers or blooms.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown in a greenhouse as soon as it is ripe with the pot sealed in a polythene bag to hold in the moisture. Remove this bag as soon as germination takes place[164]. The seed usually germinates better if it is harvested 'green' (when it has fully developed but before it dries on the plant) and sown immediately. Germination should normally take place by spring, though it sometimes takes a further year. Stored seed is more problematic. It should be warm stratified for 8 - 12 weeks at 20°c followed by 12 - 14 weeks at 3°c. Germination may still take another 12 months or more at 15°c[164]. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots as soon as they are large enough to handle. Grow the plants on in the greenhouse for their first winter and then plant out in spring after the last expected frosts. Cuttings of half-ripe wood, July/August in a frame. Layering.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Iran (north), Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia (Ciscaucasia), Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russian Federation (Dagestan), Russian Federation (Altay, Buryatia, Gorno-Altay, Irkutsk, Kemerovskaja oblast, Krasnoyarsk, Novosibirsk) EUROPE: Finland, United Kingdom, Norway, Sweden, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Russian Federation-European part (European part (incl. arctic region)), Belarus, Lithuania, Latvia, Moldova, Ukraine (incl. Krym), Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Croatia, Italy, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
1117200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Daphne mezereum
|
|
|
|