 |
|
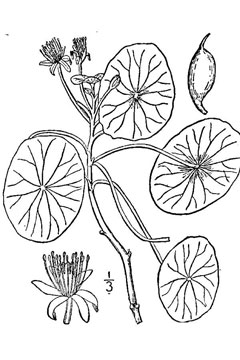
Robert H. Mohlenbrock @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / USDA NRCS. 1995. Northeast wetland flora: Field office guide to plant species. Northeast National Technical Center, Chester. |
 |
| USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913. An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. Vol. 2: 76. |
Translate this page:
Summary
Water Shield is an aquatic plant with slender, branching stems. The Leaves are entire, floating, oval to elliptic in shape, green above, often purple beneath, long-stemmed, and have the stalk or petiole attached to the lower surface instead of the base or edge. The small, purple flowers have sepals and petals that are similar to each other.
Physical Characteristics

 Brasenia schreberi is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.1 m (0ft 4in) by 2 m (6ft). It is in flower from July to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Beetles, wind.
Brasenia schreberi is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.1 m (0ft 4in) by 2 m (6ft). It is in flower from July to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Beetles, wind.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid and neutral soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It can grow in water.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
B. peltata.
Plant Habitats
Pond;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Leaves Root
Edible Uses:
The young curled leaf tips, which are coated with a thick transparent mucilage, are eaten as a salad with vinegar, sake and soy sauce, or they added to soups as a thickener[106, 159, 183]. Considered a great delicacy in Japan where they are often bottled and sold in local markets[183]. They are mainly used in the spring[46]. A nutritional analysis is available[218]. Root - cooked[2, 106, 177]. Peeled then boiled and eaten, they can also be dried and stored for later use or ground into a powder[183].
References More on Edible Uses
| Composition
|
| Figures in grams (g) or miligrams (mg) per 100g of food.
|
|
|
Leaves (Dry weight)
|
|
- 135 Calories per 100g
- Water : 0%
- Protein: 9.5g; Fat: 2.7g; Carbohydrate: 24.3g; Fibre: 1.4g; Ash: 63.5g;
- Minerals - Calcium: 122mg; Phosphorus: 311mg; Iron: 27mg; Magnesium: 0mg; Sodium: 0mg; Potassium: 0mg; Zinc: 0mg;
- Vitamins - A: 135mg; Thiamine (B1): 0.41mg; Riboflavin (B2): 0mg; Niacin: 0.05mg; B6: 0mg; C: 0mg;
- Reference: [ 218]
- Notes: The figure for ash is remarkably high and needs to be verified.
|
|
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anthelmintic Antidote Astringent Cancer Dysentery Vulnerary
The leaves are astringent[240]. They are crushed and applied to abscesses and boils[218], and are also used in the treatment of phthisis and dysentery[240]. A decoction of the seed is antidotal[218]. It is also used in the treatment of dysentery and to relieve thirst[218]. The plant is anthelmintic and vulnerary[152, 178, 218]. It is used in the treatment of cancer[218].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Herbicide
The plant has phytotoxic properties that allow it to inhibit the growth of other plants nearby and therefore allow it to become dominant. This gives it a potential for the natural control of invasive water weeds[274].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
A floating plant producing stems up to 2 metres long[266], it should be grown in still lime-free water up to 1.8 metres deep[200]. Prefers a rich soil[200]. A good plant for the water's edge but it is difficult to establish[1]. The submerged parts of the plant are conspicuously covered in a mucilaginous jelly[274]. Plants are not fully hardy in Britain[56]. According to another report this species requires a minimum winter temperature of 18°c and can only be grown in aquaria and ponds in heated greenhouses[200].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - no details have been found for this species. Seeds of many water plants have a short viability if allowed to dry out so it is probably best to sow the seed as soon as it is ripe in a warm greenhouse or to store it in water until the spring and to sow then. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on in the greenhouse for at least their first winter. Just cover the pots with water and then increase the depth as the plants grow. Plant them out into their permanent positions in late spring or early summer, after the last expected frosts. Division in spring[200].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Russian Federation (Primorye, Amur), China (Anhui Sheng, Hunan Sheng, Jiangsu Sheng, Jiangxi Sheng, Sichuan Sheng, Yunnan Sheng, Zhejiang Sheng), Korea, Japan (Hokkaidô, Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku), Taiwan TROPICAL ASIA: India (Meghalaya) NORTHERN AMERICA: United States (Alaska, Connecticut, Indiana, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Oklahoma, Wisconsin, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington, Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Texas, California), Canada (New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Ontario, Québec, Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba), Mexico (Chihuahua, San Luis Potosí, Chiapas, Jalisco, Michoacán de Ocampo, Tabasco) SOUTHERN AMERICA: Cuba, Dominican Republic, Jamaica (rare), Belize, Guatemala, Guyana (extirpated?), Venezuela (Mérida, Zulia, Táchira, Trujillo) AFRICA: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo (east), Angola, Zambia, Botswana, South Africa (Mpumalanga)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
J.F.Gmel.
Botanical References
43200235
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment