 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Boehmeria_nivea_Blanco2.385-cropped.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Cillas |
Translate this page:
Summary
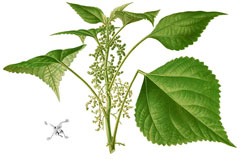
Ramie, Boehmeria nivea, is an erect, herbaceous, perennial, flowering plant up to 1 -3 m tall with thick storage roots. The leaves are heart-shaped with white, hairy underside. It is highly cultivated for its high quality fibre or as an ornamental plant. It is also used in preventing miscarriages during pregnancy. The leaves are used as treatment of fluxes and wounds while the roots are used in the treatment of threatened abortions, colic of pregnancy, haemorrhoids, leucorrhoea, impetigo, etc. The root is edible when peeled and boiled. It has a pleasant and sweet taste. The leaves are furthermore used in making cakes. Ramie is planted to prevent soil erosion. The inner bark is a source of the known longest fibre used in making paper. Other Names: China Grass, Kankura, Rami, Rhea.
Physical Characteristics

 Boehmeria nivea is an evergreen Perennial growing to 1.8 m (6ft) by 1 m (3ft 3in).
Boehmeria nivea is an evergreen Perennial growing to 1.8 m (6ft) by 1 m (3ft 3in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 7 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from September to October. The species is monoecious (individual flowers are either male or female, but both sexes can be found on the same plant) and is pollinated by Wind.
Suitable for: light (sandy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers dry or moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
B. tenacissima. Gaud.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Leaves Root
Edible Uses:
Edible portion: Root, Leaves, Seeds – oil. Root - peeled and boiled. A pleasant, sweet taste[ 179 ]. We can detect very little flavour, but the root has a very strange mucilaginous texture that does not appeal to most people who have tried it[ K ]. Once in the mouth, it takes a lot of chewing before it is ready to be swallowed[ K ]. The leaves are used for making cakes[ 283 ]. This report could refer to the plants use as a poultice[ K ]. They are also used as a dye to make black rice cake.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antiphlogistic Astringent Demulcent Diuretic Febrifuge Haemostatic Poultice Resolvent
Vulnerary Women's complaints
Antiphlogistic, demulcent, diuretic, febrifuge, haemostatic and vulnerary. Used to prevent miscarriages and promote the drainage of pus[ 147 , 178 ]. The leaves are astringent and resolvent[ 218 , 240 ]. They are used in the treatment of fluxes and wounds[ 218 ]. The root contains the flavonoid rutin[ 283 ]. It is antiabortifacient, antibacterial, cooling, demulcent, diuretic, resolvent and uterosedative[ 218 , 283 ]. It is used in the treatment of threatened abortions, colic of pregnancy, haemorrhoids, leucorrhoea, impetigo etc[ 283 ]. The fresh root is pounded into a mush and used as a poultice[ 283 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Fibre Fodder Paper
Agroforestry Uses: Planted to prevent erosion in gullies[ 331 ]. Other Uses A fibre is obtained from the inner bark of the stem - of excellent quality, it is highly water-resistant and has a greater tensile strength than cotton[ 418 ]. It is used for textiles, linen etc and is said to be moth-proof[ 1 , 46 , 57 , 61 , 74 , 171 ]. It is best harvested as the female flowers open[ 169 ]. The outer bark is removed and then the fibrous inner bark is taken off and boiled before being woven into thread[ 178 ]. The fibres are the longest known in the plant realm.[ 61 , 171 ] The tensile strength is 7 times that of silk and 8 times that of cotton, this is improved on wetting the fibre[ 61 ]. The fibre is also used for making paper[ 189 ]. The leaves are removed from the stems, the stems are steamed and the fibres stripped off. The fibres are cooked for 2 hours with lye, fresh material might require longer cooking, and they are then beaten in a Hollander beater[ 189 ] before being made into paper.
Special Uses
Carbon Farming
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Fodder: Bank Industrial Crop: Fiber Management: Fodder Management: Hay Minor Global Crop Staple Crop: Protein
A plant of the sub-tropics to the tropics, also succeeding in warm temperate areas. The plant can be grown between latitudes 6 - 45°N and 9 - 38°S. It is adapted to a relative air humidity about 80%. Both excessive rainfall and drought affects the quality of the fibre. Relatively flat areas, not subject to flooding as well as gentle sloping lands, not subject to erosion are suitable for ramie production. It is found at elevations up to 1,300 metres. It grows best in areas where annual daytime temperatures are within the range 17 - 27°c, but can tolerate 10 - 34°c[ 418 ]. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 1,500 - 2,500mm, but tolerates 1,000 - 4,000mm[ 418 ]. Requires a rich warm sandy soil that is very well drained[ 1 , 57 , 123 , 200 ]. Succeeds in a wide range of soils so long as they are fertile[ 418 ]. Intolerant of wet soils[ 200 ]. This is a very greedy plant that can soon impoverish a soil, it requires a lot of feeding if it is to perform well[ 123 ]. All plant remains, after the fibre has been removed, should be returned to the soil[ 123 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5.4 - 6.5, tolerating 4.8 - 7.5[ 418 ]. Boehmeria nivea is an extremely variable species that is widespread over large areas of subtropical and tropical Asia. Its complex species includes several infraspecific taxa, four varieties of which are found in China[ 266 ]. The sub-species B. Nivea tenacissima. (Gaud.)Miquel., which produces the fibre 'Rhea' is a native of Malaysia and is not hardy in Britain[ 200 ]. Yields are from 375 to 900 kilos of fibre (per acre?)[ 123 ]. Two to four harvests per year are possible depending upon the climate, it is harvested as the stems turn brown[ 123 ]. Yields of green plants may in temperate regions vary between 15 - 20 tonnes/ha and in tropical areas 8 - 10 tonnes/ha. Yields of about 1400 kg fibre/ha have been reported[ 418 ]. There are an increase in yields in the 2nd and 3rd year[ 418 ]. Stems can be harvested 2 - 3 times per year in temperate areas, 4 - 5 times in subtropical areas and in the tropics up to 6 crops can be produced annually[ 418 ]. The crop is normally replanted after 7 - 10 years, but may persist for 20 years[ 418 ]. The plant tends to take up whatever minerals are present in the soil. This could cause problems for example high uptake of molybdenum can lead to conditioned copper deficiency[ 289 ]. Found In: Africa, Asia, Australia, Bangladesh, Brazil, China*, East Africa, Fiji, Haiti, Hawaii, India, Indochina, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Mozambique, Norfolk Island, Pacific, Philippines, Rwanda, SE Asia, South America, Taiwan, USA, Vietnam.
Carbon Farming
-
Fodder: Bank
Fodder banks are plantings of high-quality fodder species. Their goal is to maintain healthy productive animals. They can be utilized all year, but are designed to bridge the forage scarcity of annual dry seasons. Fodder bank plants are usually trees or shrubs, and often legumes. The relatively deep roots of these woody perennials allow them to reach soil nutrients and moisture not available to grasses and herbaceous plants.
-
Industrial Crop: Fiber
Clothing, rugs, sheets, blankets etc. Currently, almost none of our fiber are produced from perennial crops but could be!
-
Management: Fodder
Non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Management: Hay
Cut to the ground and harvested annually. Non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Minor Global Crop
These crops are already grown or traded around the world, but on a smaller scale than the global perennial staple and industrial crops, The annual value of a minor global crop is under $1 billion US. Examples include shea, carob, Brazil nuts and fibers such as ramie and sisal.
-
Staple Crop: Protein
(16+ percent protein, 0-15 percent oil). Annuals include beans, chickpeas, lentils, cowpeas, and pigeon peas. Perennials include perennial beans, nuts, leaf protein concentrates, and edible milks.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow in pots and only just cover the seed. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and plant them out when at least 20cm tall. Division. Very easy, larger divisions can be planted straight into their permanent positions whilst smaller clumps are best planted in a nursery until they are growing away well. Layering. Basal cuttings. Harvest new shoots when they are about 10 - 15cm long with plenty of underground stem. Pot them up into individual pots and keep them in light shade until they are rooting well.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: China (Anhui Sheng (south), Fujian Sheng, Gansu Sheng, Guangdong Sheng, Guangxi Zhuangzu Zizhiqu, Guizhou Sheng, Hainan Sheng, Hubei Sheng, Hunan Sheng, Jiangxi Sheng, Shaanxi Sheng (south), Sichuan Sheng, Yunnan Sheng, Zhejiang Sheng), Korea, Japan, Taiwan TROPICAL ASIA: Bhutan, India, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed.

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(L.)Gaudich.
Botanical References
109200266
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment