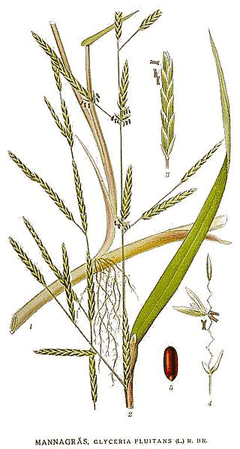
 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:450_Glyceria_fluitans.jpg |
 |
| http://www.commanster.eu/commanster.html |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

 Glyceria fluitans is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.5 m (1ft 8in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in).
Glyceria fluitans is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.5 m (1ft 8in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 5 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from May to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Wind.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid and very alkaline soils.
It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers wet soil and can grow in water.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Panicularia fluitans
Plant Habitats
Pond; Bog Garden;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Seed
Edible Uses:
Seed - raw or cooked[43, 57, 100]. A sweetish taste, the seed was considered a delicacy in some parts of Europe and was an article of commerce until well into the 20th century[183]. A flour from the seed is said to make a bread little inferior to wheat bread, the flour can also be used as a thickener in soups etc when it imparts a sweet delicate flavour[183]. Unfortunately, the seed is very small and therefore the plant is relatively unproductive[K].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Historic Staple Management: Standard Staple Crop: Balanced carb
Succeeds in most soils, so long as they are wet, and in shallow water[115]. Dislikes shade. This plant is occasionally cultivated for its edible seed[115], it is not very large and is somewhat fiddly to harvest but is considered to be an epicure's food[183].
Carbon Farming
-
Historic Staple
These crops were once cultivated but have been abandoned. The reasons for abandonment may include colonization, genocide, market pressures, the arrival of superior crops from elsewhere, and so forth.
-
Management: Standard
Plants grow to their standard height. Harvest fruit, seeds, or other products. Non-Destructive management systems.
-
Staple Crop: Balanced carb
(0-15 percent protein, 0-15 percent oil, with at least one over 5 percent). The carbohydrates are from either starch or sugar. Annuals include maize, wheat, rice, and potato. Perennials include chestnuts, carob, perennial fruits, nuts, cereals, pseudocereals, woody pods, and acorns.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow spring in a greenhouse in a pot standing in 3 - 5cm of water. Surface sow the seed, or only just cover it. Germination should take place within 3 weeks. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and plant them out in early summer. If you have sufficient seed then it can be sown outdoors in situ in mid to late spring. Division in spring. Very easy, larger clumps can be replanted direct into their permanent positions, though it is best to pot up smaller clumps and grow them on in a cold frame until they are rooting well. Plant them out in the spring.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Turkey (north), Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia (Ciscaucasia), Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia EUROPE: Denmark, Finland, United Kingdom, Ireland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, Russian Federation (European part), Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Moldova, Russian Federation (Saratov, Volgogradskaja oblast), Ukraine, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Croatia, Italy (incl. Sardinia, Sicily), Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France (incl. Corsica), Portugal AFRICA: Algeria (north), Morocco, Tunisia
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(L.)R.Br.
Botanical References
17
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
© 2010, Plants For A Future. Plants For A Future is a charitable company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales. Charity No. 1057719, Company No. 3204567.