 |
|
edibleplants.org |
 |
| Mason Brock (Masebrock) wikimedia.org |
Translate this page:
Summary
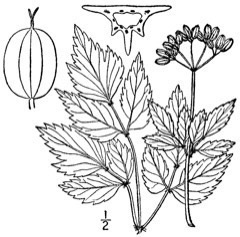
Physical Characteristics

 Thaspium barbinode is a PERENNIAL growing to 1.2 m (4ft) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in) at a medium rate.
Thaspium barbinode is a PERENNIAL growing to 1.2 m (4ft) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 5.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Ligusticum barbinode Michx. T. barbinode var. barbinode
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Invertebrates shelter: beneficial for insects and other arthropods. Nectary: provides nectar or pollen for beneficial insects [1-2]. Many kinds of insects are attracted to the flowers, especially short-tongued bees, wasps, flies, and beetles. The caterpillars of the butterfly Papilio polyxenes asterias (Black Swallowtail) feed on the foliage and flowers. This plant is not known to be toxic, and it is probably consumed occasionally by various mammalian herbivores, although information about this is limited [1-6].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers full or partial sun and mesic (environment or habitat containing a moderate amount of moisture) conditions. The soil can contain significant amounts of loam, sand, or rocky material. Light shade is tolerated, but growth will be less robust and flowering less abundant. Hairy-Jointed Meadow Parsnip develops rapidly during the spring, and is usually taller than the surrounding plants when the blooming period begins. After flowering, the condition of the plant rapidly deteriorates [1-6]. For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is a clumper with limited spread [1-2]. The root pattern is a tap root similar to a carrot going directly down [1-2].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Hairy-Jointed Meadow Parsnip, meadowparsnip, meadow-parsip.
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: Canada (Ontario), United States (Indiana, Michigan, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Oklahoma, Wisconsin, Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida (north), Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, Mississippi, Tennessee)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known. Possibly mistaken for Wild Parsnip (Pastinaca sativa), a highly invasive species found across Minnesota, is a much larger plant (often 4-5+ feet tall) with a larger flower cluster (to 8 inches across), duller, somewhat greenish-yellow flowers, once-compound leaves with up to 15 leaflets.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : Not Listed.

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(Michx.) Nutt.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Thaspium barbinode
|
|
|
|