 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:151_Ledum_palustre.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Fabelfroh |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

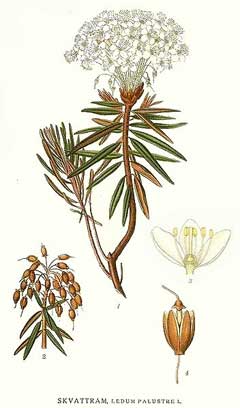
 Ledum palustre is an evergreen Shrub growing to 1 m (3ft 3in).
Ledum palustre is an evergreen Shrub growing to 1 m (3ft 3in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 2. It is in leaf all year, in flower from April to June. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist or wet soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Dappled Shade; Shady Edge; not Deep Shade; Bog Garden;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts:
Edible Uses: Condiment Tea
A tea is made from the aromatic leaves[172, 183]. Considered by some to be a better tea than that made from L. groenlandicum[183]. Some caution is advised, see the notes above on toxicity. It would be better to brew the tea in cold water by leaving it in a sunny place, or to make sure that it is brewed for a short time only in an open container. The leaves are used as a flavouring, they are a bayleaf substitute[172]. The plant has been used as a hop substitute in making beer, though this has caused an unpleasant kind of drunkenness which is accompanied by a headache and dizziness[232].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Astringent Diaphoretic Diuretic Homeopathy Laxative Narcotic Stomachic
The leaves and young flowering shoots are astringent, diaphoretic, disinfectant, diuretic, laxative, pectoral, stomachic and tonic[4, 172, 222, 257]. The plant is more strongly narcotic than L. groenlandicum[4] and should not be used without expert supervision[9]. A tea is taken internally in the treatment of asthma, coughs, colds, stomach aches, kidney ailments etc[4, 222, 257]. Externally, it is used as a wash for burns, ulcers, stings, infections etc[222, 257]. A homeopathic remedy is made from the whole, dried and powdered, plant[232]. This is used in the treatment of stings, injuries and joint pains[232]. It is also used in the treatment of various chest complaint, asthma, menstrual pain etc[9].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Insecticide Repellent Tannin
The leaves are hung up in the clothes cupboard in order to repel insects[4, 172]. The branches are also placed among grain in order to keep mice away[4, 172]. A strong decoction of the leaves is used to kill lice and insects[4, 232]. The leaves contain tannin[4].
Special Uses
Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Requires a lime-free loam or peaty soil[1, 11]. Prefers a moist humus-rich acid soil in shade or semi-shade[200]. Plants flower more freely when grown in a sunny position. Plants grow better if they have certain fungal associations in the soil. The best way of providing this is to incorporate some soil from around well-growing established plants into the soil for the new plant[200]. Hardy to at least -15°c[200]. The leaves are very aromatic[182]. When crushed, they smell strongly of hops[232]. Plants benefit from removing the dead flowers before they set seed[188]. This prevents them putting too much energy into seed production at the expense of more flowers and leaves. A good bee plant[4]. The flowers contain an oil that smells strongly of antiseptic[232].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - surface sow in a shady part of the greenhouse in February or March[78, 113]. Another report says that the seed is best sown in the autumn as soon as it is ripe[188]. Germination is variable and can be quite slow. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots as soon as they are large enough to handle and grow the pots on in a shady frame for 18 months before planting them out into their permanent positions[78]. Cuttings of half-ripe wood, 5 - 8cm with a heel, July/August in a frame. Plant out in spring. Fair percentage[78]. Cuttings of mature wood, November/December in a frame[113]. Layering in the autumn. Takes 12 months[78]. Division.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Russian Federation-Western Siberia (Western Siberia), Russian Federation-Eastern Siberia (Eastern Siberia), Russian Federation (Yakutia-Sakha, Krasnoyarsk, Irkutsk), Russian Federation (Habarovskij kraj, Amur, Kamcatskij kraj, Magadanskaja oblast, Sakhalin), Japan (Hokkaidô), Korea, North EUROPE: Finland, Norway, Sweden, Austria, Germany, Poland, Russian Federation-European part (European part (north)), Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Ukraine
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
1117200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
© 2010, Plants For A Future. Plants For A Future is a charitable company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales. Charity No. 1057719, Company No. 3204567.