 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Euonymus_europaeus_Sturm20.jpg |
 |
| http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:MPF |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

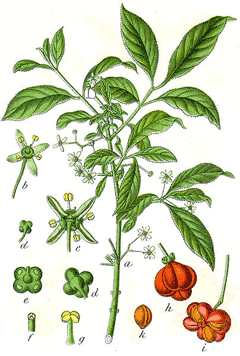
 Euonymus europaeus is a deciduous Shrub growing to 6 m (19ft 8in).
Euonymus europaeus is a deciduous Shrub growing to 6 m (19ft 8in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 3. It is in flower from May to June, and the seeds ripen from September to November. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very alkaline soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers dry or moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Shady Edge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Manna Oil
Edible Uses: Colouring Oil
An edible yellow dye is obtained from the fruit and seed[46, 61, 103, 183]. Pink from the fruit case, orange from the seed[141]. These reports should be treated with some caution since many members of this genus are poisonous. One report suggests that the plant is a source of a manna[183], there are no further details.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Alterative Cholagogue Hepatic Laxative Parasiticide Purgative Stimulant Tonic
The bark is alterative, cholagogue, hepatic, laxative, stimulant and tonic[4, 7]. The root bark is the part normally used, though bark from the stems is sometimes employed as a substitute[4]. In small doses it stimulates the appetite, in larger doses it irritates the intestines[4]. The bark is especially useful in the treatment of liver disorders which follow or accompany fevers[4]. The seeds are strongly emetic and purgative[4]. The fresh leaves, and the dried fruit and seeds, are used externally to treat scabies, lice (head, body or pubic), ticks and other skin parasites[268].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Charcoal Dye Insecticide Latex Oil Parasiticide Wood
The whole plant yields a volatile oil that is used in soap making[13, 46]. Other reports say that the oil is obtained from the seed[46, 61, 103, 115]. It is possible that there are two oils, an essential oil from the plant and an oil from the seed[K]. A good yellow dye is obtained from the fleshy coating around the seeds[4]. This becomes green with the addition of alum, but unfortunately both colours are rather fugitive[4]. The baked and powdered berries are used to remove lice from the hair[6, 19, 66], they are also used as an insecticide[15]. The leaves are used[115]. Roots yield up to 4% gutta-percha, a non elastic rubber used as an electrical insulation and for making plastics[74]. Wood - very hard, easily split, fine-grained, not durable[4, 6, 13, 46]. Used for spindles, skewers, knitting needles, toothpicks, carving etc[6, 100, 103]. A high quality charcoal is obtained from the wood, it is used by artists[46, 74, 103, 115].
Special Uses
Food Forest
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
An easily grown plant, it thrives in almost any soil, including chalk, and is particularly suited to dry shaded areas[200]. Prefers a well-drained loamy soil[1]. If cultivated for its latex it is best grown in a dry open position[74]. A very cold-hardy plant, tolerating temperatures down to about -25°c[184]. A very ornamental plant, there are many named varieties[11]. This species is often damaged by caterpillars during the flowering season[11]. It is a favoured home for blackfly, so should not be grown near broad beans[121]. In garden design, as well as the above-ground architecture of a plant, root structure considerations help in choosing plants that work together for their optimal soil requirements including nutrients and water. The root pattern is branching: a heart root, dividing from the crown into several primary roots going down and out [2-1].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame. Stored seed requires 8 - 12 weeks warm followed by 8 - 16 weeks cold stratification and can then be sown in a cold frame[98]. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on in the greenhouse for at least their first winter. Plant them out into their permanent positions in late spring or early summer, after the last expected frosts. One report says that the seed can be sown in an outdoors seedbed in early spring with good results[78]. Grow the seedlings on for two years in the seedbed before planting them out into their permanent positions. Cuttings of half-ripe wood, 5 - 8cm long taken at a node or with a heel, July/August in a frame. Very easy[78]. Cuttings of mature wood, November in a frame[113]. Layering in July/August. Takes 14 months[78].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Turkey, Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia (Ciscaucasia), Azerbaijan, Georgia, Russian Federation (Dagestan) EUROPE: Denmark, United Kingdom, Ireland, Norway (south), Sweden (south), Czechoslovakia, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Russian Federation-European part (European part (south)), Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Moldova, Ukraine (incl. Krym), Former Yugoslavia, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy (incl. Sardinia, Sicily), Romania, Spain, France (incl. Corsica), Portugal
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
1117200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment