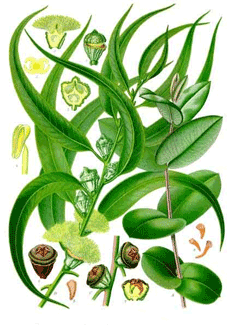
 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Koeh-147.jpg |
 |
| http://www.hear.org/starr/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
Bloom Color: White. Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Early spring, Late summer, Late spring, Mid summer, Mid spring. Form: Oval, Upright or erect.
Physical Characteristics

 Eucalyptus globulus is an evergreen Tree growing to 55 m (180ft) by 15 m (49ft) at a fast rate.
Eucalyptus globulus is an evergreen Tree growing to 55 m (180ft) by 15 m (49ft) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 9. It is in leaf all year, in flower from July to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry moist or wet soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Eucalyptus maidenii subsp. globulus (Labill.) J.B.Kirkp
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Bog Garden;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts:
Edible Uses: Condiment
An essential oil from the fresh or dried leaves is used as a flavouring in sweets, baked goods, ice cream etc[177, 183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antibacterial Antiperiodic Antirheumatic Antiseptic Antispasmodic Appetizer Aromatherapy Aromatic
Deodorant Expectorant Febrifuge Hypoglycaemic Stimulant
Eucalyptus leaves are a traditional Aboriginal herbal remedy. The essential oil found in the leaves is a powerful antiseptic and is used all over the world for relieving coughs and colds, sore throats and other infections[254]. The essential oil is a common ingredient in many over-the-counter cold remedies[254]. The adult leaves, without their petioles, are antiperiodic, antiseptic, aromatic, deodorant, expectorant, febrifuge, hypoglycaemic and stimulant[4, 7, 21, 46]. The leaves, and the essential oil they contain, are antiseptic, antispasmodic, expectorant, febrifuge and stimulant[218]. Extracts of the leaves have antibacterial activity[218]. The essential oil obtained from various species of eucalyptus is a very powerful antiseptic, especially when it is old, because ozone is formed in it on exposure to air. It has a decided disinfectant action, destroying the lower forms of life[4]. The oil can be used externally, applied to cuts, skin infections etc, it can also be inhaled for treating blocked nasal passages, it can be gargled for sore throat and can also be taken internally for a wide range of complaints[4]. Some caution is advised, however, because like all essential oils, it can have a deleterious effect on the body in larger doses[4]. The oil from this species has a somewhat disagreeable odour and so it is no longer used so frequently for medicinal purposes, other members of the genus being used instead[4]. An oleo- resin is exuded from the tree[238]. It can also be obtained from the tree by making incisions in the trunk[4, 152]. This resin contains tannin and is powerfully astringent, it is used internally in the treatment of diarrhoea and bladder inflammation[4, 152, 238], externally it is applied to cuts etc[4, 152]. The essential oil is used in aromatherapy. Its keyword is 'Respiratory system'[210].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Cleanser Deodorant Dye Essential Fuel Repellent Wood
The leaves and the essential oil in them are used as an insect repellent[14, 152, 174, 240]. The trees can also be planted in wet areas where mosquitoes abound. The ground will be dried out by the trees, making it unsuitable for the mosquitoes to breed[238]. A decoction of the leaves is used for repelling insects and vermin[269]. Africans use finely powdered bark as an insect dust[269]. An essential oil is obtained from the leaves[46, 61, 156]. It is used in perfumery and in medicines[100]. The yield is about 0.9% by steam distillation[154]. The essential oil is also in spot removers for cleaning off oil and grease[238]. Yields of 40 to 45 kilos of oil per hectare have been reported[269]. A yellow/brown dye is obtained from the young leaves. It does not require a mordant[168]. Grey and green dyes are obtained from the young shoots[168]. A dark green dye is obtained from the young bark[168]. Wood - heavy[46, 61], (or light according to another report[167]), durable, fire resistant[155]. An important timber species, it is used for various purposes such as carpentry, construction, fences, piles, platforms, plywood, poles, sheds, tool handles and veneer[238, 269]. The oil-rich wood is resistant to termites[269]. This is one of the best eucalypts for pulp production for making paper[152, 269].
Special Uses
Carbon Farming Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Industrial Crop: Hydrocarbon Industrial Crop: Medicinal Management: Coppice Management: Standard Minor Global Crop Other Systems: SRC
Landscape Uses:Aggressive surface roots possible, Specimen. Prefers a sunny position in a moderately fertile well-drained moisture retentive circum-neutral soil[200]. Succeeds in most soils[167], tolerating poor and dry soils, especially those low in mineral elements[200]. Established plants are drought tolerant[200]. Plants should not be grown in frost pockets or windy sites[107]. Requires a sheltered position, disliking cold, dry or desiccating winds[154]. Plants are reported to tolerate an annual precipitation of 80 to 160cm and an annual temperature range of ca 16 to 20°C[269]. This species is not very hardy in Britain, tolerating temperatures down to about -5°c[200] and often succumbing to heavy frosts[11, 107, 155]. There is a tree 35 metres tall on the Isle of Man, there are several taller trees in S. Ireland and a tree on the Isle of Wight was 20 metres tall when it was 9 years old from seed[11]. Eucalyptus species have not adopted a deciduous habit and continue to grow until it is too cold for them to do so. This makes them more susceptible to damage from sudden cold snaps. If temperature fluctuations are more gradual, as in a woodland for example, the plants have the opportunity to stop growing and become dormant, thus making them more cold resistant. A deep mulch around the roots to prevent the soil from freezing also helps the trees to survive cold conditions[200]. The members of this genus are remarkably adaptable however, there can be a dramatic increase in the hardiness of subsequent generations from the seed of survivors growing in temperate zones[200]. The Tasmanian blue gum is the most extensively planted eucalypt species in the world with a total of 800,000 ha in dozens of countries[269]. This species is commonly planted in S. Europe, especially in Italy, Spain and Portugal, for timber, soil stabilization and the essential oil in its leaves[50, 61]. Trees have also been planted in marshy areas where they have the ability to reduce the wetness of the land (because they transpire so much water) thus getting rid of mosquitoes that were breeding there[4]. Eucalyptus monocultures are an environmental disaster, they are voracious, allelopathic and encourage the worst possible attitudes to land use and conservation[200]. A very fast growing tree, new growth can be up to 2.5 metres per year[11, 49, 107]. Trees are gross feeders and can severely stunt the growth of nearby plants[14]. Trees are very amenable to coppicing[49]. Plants are shallow-rooting and, especially in windy areas, should be planted out into their permanent positions when small to ensure that they do not suffer from wind-rock[245]. They strongly resent root disturbance and should be container grown before planting out into their permanent position[11]. The flowers are rich in nectar and are a good bee crop[168, 200]. The bruised leaves emit a powerful balsamic smell[245]. This species is the national emblem of Tasmania[156, 167]. Special Features:Fragrant foliage, Not North American native, Invasive, Inconspicuous flowers or blooms.
Carbon Farming
-
Industrial Crop: Hydrocarbon
Materials, chemicals and energy include bioplastics, rubber, biomass products gasoline, jet fuel, diesel, butane, propane, biogas. Plants are usually resprouting plants and saps.
-
Industrial Crop: Medicinal
Most pharmaceuticals are synthesized from petroleum but 25% of modern medicines are based on plants.
-
Management: Coppice
Cut to the ground repeatedly - resprouting vigorously. Non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Management: Standard
Plants grow to their standard height. Harvest fruit, seeds, or other products. Non-Destructive management systems.
-
Minor Global Crop
These crops are already grown or traded around the world, but on a smaller scale than the global perennial staple and industrial crops, The annual value of a minor global crop is under $1 billion US. Examples include shea, carob, Brazil nuts and fibers such as ramie and sisal.
-
Other Systems: SRC
Short-rotation coppice.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - surface sow February/March in a sunny position in a greenhouse[11, 78, 134]. Species that come from high altitudes appreciate 6 - 8 weeks cold stratification at 2°c[200]. Pot up the seedlings into individual pots as soon as the second set of seed leaves has developed, if left longer than this they might not move well. Plant out into their permanent positions in early summer and give them some protection from the cold in their first winter. The seed can also be sown in June, the young trees being planted in their final positions in late spring of the following year. The seed has a long viability[200].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
AUSTRALASIA: Australia (Tasmania, New South Wales (east), Victoria)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Corymbia citriodora | Lemon-Scented Gum, blue spotted gum, lemon eucalyptus, eucalyptus citriodora. | Tree | 45.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus brassiana | Cape York red gum | Tree | 20.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus caesia | Gungurru | Tree | 10.0 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 2 | 0 | |
| Eucalyptus camaldulensis | Red River Gum, Murray Red Gum, River Red Eucalyptus | Tree | 30.0 |
8-12
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus citriodora | Lemon-Scented Gum, Lemon Scented Eucalyptus | Tree | 45.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus coccifera | Mt. Wellington Peppermint | Tree | 15.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus delegatensis | Alpine ash | Tree | 40.0 |
7-11
| F | LMH | N | M | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus dumosa | Water Mallee | Tree | 7.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus gomphocephala | Tuart. Tuart Gum | Tree | 40.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus grandis | Flooded Gum, Gum, Rose Eucalyptus | Tree | 50.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | SN | DM | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus gummifera | Red Bloodwood | Tree | 15.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus gunnii | Cider Gum | Tree | 30.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus johnstonii | Yellow Gum, Johnston's gum | Tree | 60.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus largiflorens | Black Box | Tree | 18.0 |
9-11
| S | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus leucoxylon | Yellow Gum, White ironbark, White Eucalyptus | Tree | 15.0 |
10-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus macrorhyncha | Red Stringybark | Tree | 45.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus melliodora | Yellow Box | Tree | 30.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus microcorys | Tallow Wood, Australian tallowwood | Tree | 45.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus microtheca | Coolabah, Coolibah, Flooded Box, Coolibah | Tree | 15.0 |
9-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus obliqua | Messmate | Tree | 60.0 |
8-12
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus pauciflora | Cabbage Gum, Snow gum | Tree | 12.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus pauciflora niphophila | Snow Gum | Tree | 6.0 |
6-9
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus perriniana | Spinning Gum | Tree | 6.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus piperita | Sydney Peppermint | Tree | 18.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus polybractea | Blue Mallee | Tree | 6.0 |
-
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus punctata | Grey Gum | Tree | 30.0 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | |
| Eucalyptus racemosa | Snappy Gum | Tree | 0.0 |
-
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 3 | |
| Eucalyptus regnans | Mountain Ash | Tree | 75.0 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus robusta | Swamp Mahogany, Eucalyptus Gum | Tree | 30.0 |
8-12
| F | LMH | SN | DM | 0 | 3 | 4 |
|
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Labill.
Botanical References
11200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment