 |
|
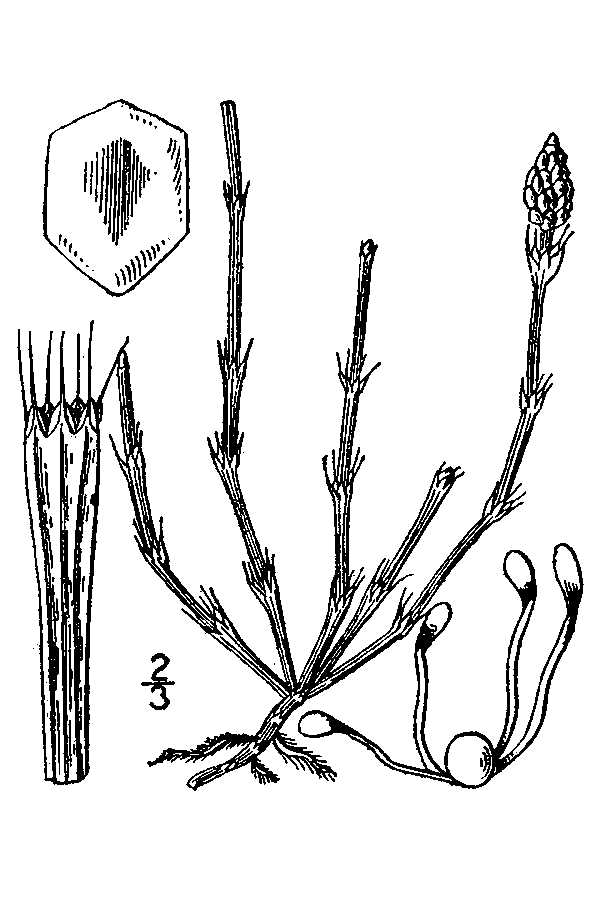
USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913. An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. Vol. 1: 42. |
 |
| http://njflora.rutgers.edu/plants/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
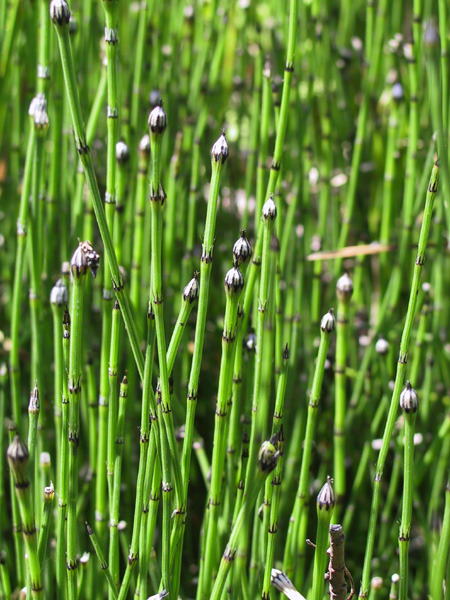
Equisetum species - horsetail family are Creeping, perenial, Branching rootstocks, rooted at the nodes. The Arial stems may be annual or Perennial, are cylindrical, fluted, simple or with whorled branches at the jointed nodes. The internodes are usually hollow. The Surfaces of the stems are covered with Silica. The Cones are terminal.
Physical Characteristics

 Equisetum variegatum is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.6 m (2ft) by 1 m (3ft 3in).
Equisetum variegatum is a PERENNIAL growing to 0.6 m (2ft) by 1 m (3ft 3in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 2. The seeds ripen from July to August.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers dry or moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Horsetails have an unusual chemistry compared to most other plants[238]. They are rich in silica, contain several alkaloids (including nicotine) and various minerals[238]. Horsetail is very astringent and makes an excellent clotting agent, staunching wounds, stopping nosebleeds and reducing the coughing up of blood[254]. It helps speed the repair of damaged connective tissue, improving its strength and elasticity[254]. The plant has been used in the treatment of sore eyes[257].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
The stems contain 10% silica and are used for scouring metal[4, 7, 20, 94, 102] and as a fine sandpaper[7, 54, 99, 257]. They can also be used as a polish for brass, hardwood etc[94]. The infused stem is an effective fungicide against mildew, mint rust and blackspot on roses[14, 18, 20, 54]. It also makes a good liquid feed[54].
Special Uses
Dynamic accumulator
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a moist but well-drained fertile soil with a pH between 6.5 and 7.5[200, 238]. A very cold-hardy species tolerating temperatures down to about -30°c[200]. Plants have a deep and penetrating root system and can be invasive. If grown in the garden they are best kept in bounds by planting them in a large container which can be sunk into the ground[200].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Spores - best collected as soon as they are ripe in the spring and surface-sown immediately on a sterile compost. Keep moist and pot up as soon as the plants are large enough to handle. Very difficult[200]. Division. The plants usually spread very freely when well sited and should not really need any assistance.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Mongolia, China (Jilin Sheng, Liaoning Sheng, Nei Mongol Zizhiqu, Sichuan Sheng, Xinjiang Uygur Zizhiqu), Japan NORTHERN AMERICA: Canada (Northwest Territories, Yukon, Québec, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Saskatchewan, Alberta, Manitoba, British Columbia), Greenland, United States (Alaska, Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Hampshire, New York, Vermont, Illinois, Minnesota, South Dakota, Wisconsin, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Wyoming, Utah) EUROPE: Denmark, Finland, Faroe Islands, United Kingdom, Ireland, Iceland, Norway, Svalbard and Jan Mayen, Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, Belarus, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Ukraine, Greece, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Schleich. ex Web.&Mohr.
Botanical References
17200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Equisetum variegatum
|
|
|
|