 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dictamnus_albus_Sturm16.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Franz_Xaver |
Translate this page:
Summary
Bloom Color: Blue, Pink, Red, White. Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Late spring, Mid summer. Form: Rounded.
Physical Characteristics

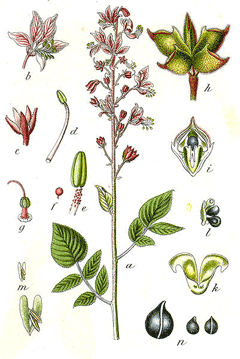
 Dictamnus albus is a PERENNIAL growing to 1 m (3ft 3in) by 0.6 m (2ft) at a slow rate.
Dictamnus albus is a PERENNIAL growing to 1 m (3ft 3in) by 0.6 m (2ft) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 3. It is in flower from June to July. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy) and medium (loamy) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry or moist soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
D. fraxinella.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts:
Edible Uses: Tea
A lemon-scented tea is made from the dried leaves[21, 46, 61]. Refreshing and aromatic[183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Abortifacient Anthelmintic Antibacterial Anticonvulsant Antirheumatic Antispasmodic Aromatic Digestive
Diuretic Eczema Emmenagogue Expectorant Febrifuge Galactogogue Homeopathy
Stimulant Tonic
The burning bush has been used in Chinese herbal medicine for at least 1,500 years[238]. The root bark is a bitter, strong-smelling herb that lowers fevers and controls bacterial and fungal infections[238]. The plant has an effect similar to rue (Ruta graveolens) in that it strongly stimulates the muscles of the uterus, inducing menstruation and sometimes causing abortion[254]. By contrast, its effect upon the gastro-intestinal tract is antispasmodic and it acts as a mild tonic on the stomach[254]. Both the flowering stems and the root-bark are used medicinally[7]. They are abortifacient, anthelmintic, antispasmodic, aromatic, digestive, diuretic, emmenagogue, expectorant, febrifuge, galactogogue, stimulant and tonic[7, 9, 19, 21, 46, 178, 211]. The plant is used both internally and externally in the treatment of skin diseases (especially scabies and eczema), German measles, arthritic pain and jaundice[238]. It is little used in Western herbalism nowadays, though it has been recommended for use in nervous complaints, intermittent fevers, scrofulous and scorbutic diseases[4]. Use with caution, in large doses it is poisonous[9, 21]. The root bark is harvested in the autumn and dried for later use[238]. An infusion of the leaves is used as a tea substitute and is a good digestive[7]. A homeopathic remedy is made from the fresh leaves[9]. It is used in the treatment of female complaints and constipation[9].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Essential
The plant contains an essential oil[211]. Yields from the fresh flowering plant are around 3% on a dry weight basis[240]. This oil is used as a cosmetic[4].
Special Uses
Attracts Wildlife Scented Plants
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Border, Foundation, Massing, Rock garden, Specimen, Woodland garden. An easily grown plant, succeeding in ordinary garden soil[1]. It prefers a dry sunny position with some lime[1, 108] and is not suitable for heavy or damp soils[111]. Established plants are drought tolerant[190]. A very ornamental plant[1], it should be planted into its permanent position as soon as possible because it dislikes root disturbance[1, 175]. The whole plant contains a very aromatic essential oil, giving out a scent somewhat like lemon peel[4]. When the plant is bruised, this smell becomes more like fine balsam[4]. This essential oil is emitted from the plant in hot weather and, on a still day, can be ignited and will burn for a second or two without harming the plant, thus giving the plant its common name[1, 4, 13, 187]. Slugs are strongly attracted to this plant and can destroy it by eating all the young growth in spring[K]. There are at least 2 named varieties, 'Pink' produces a tea with a less lemony flavour but with an added taste of almonds and vanilla, 'White' has a lemony fragrance and taste[183]. The flowers are very attractive to bees[108]. Special Features:
Attractive foliage, Edible, Fragrant foliage, Not North American native, All or parts of this plant are poisonous, Suitable for cut flowers, Suitable for dried flowers, Fragrant flowers.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown in a cold frame as soon as it is ripe[175]. Cold stratify stored seed for 6 weeks and sow in the spring in a cold frame[175]. The seed usually germinates in 1 - 6 months at 15°c[175]. As soon as they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on in the greenhouse for at least their first winter. Plant them out into their permanent positions in late spring or early summer, after the last expected frosts. Division in spring[1]. Take care since the plant resents root disturbance[1]. The plant can also be divided in autumn[200]. We have found it best to tease out divisions from the side of the clump to avoid the need to dig up the main clump. Try to get divisions that already have formed roots. Pot them up in a greenhouse and grow them on for a year to make sure they are well established before planting them out. Root cuttings in November/December.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Iran (northwest), Syria, Turkey, Russian Federation-Eastern Siberia (Eastern Siberia), Russian Federation (Altay), Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Mongolia, Russian Federation (Habarovskij kraj, Primorye, Amur), Korea TROPICAL ASIA: India (Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttar Pradesh), Pakistan (north) EUROPE: Czechoslovakia, Austria, Switzerland, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Russian Federation-European part (European part (south)), Ukraine (incl. Krym), Former Yugoslavia, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Romania, Spain
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment