 |
|
https://edibleplants.org/ |
 |
| https://edibleplants.org/ |
Translate this page:
Summary
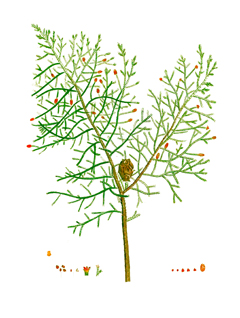
Mexican Cypress (Cupressus lusitanica) is an evergreen tree commonly found in Central America. It has a dense, cone-shaped crown and it can grow up to 40 m in height. The leaves are scale-like and dark green to yellow-green in colour. The seed cones are globose to oblong and brown in coloured when matured. Mexican cypress is fast growing and tolerant to drought. It is widely cultivated for its timber and as an ornamental tree. It can also be used as windbreaks. Medicinally, the leaves are used in the treatment of headache, catarrh, cancer, flu, and skin diseases. Essential oil from the leaves is used in the treatment of rheumatism and cough. It is also used in perfume, soaps, deodorant, and other toiletries. The wood is used for construction, poles, furniture, and posts. It also makes a good fuel. Naturalisation in parts of southern Asia. Commercial production at high altitudes in Colombia (3300 m), Bolivia and South Africa, and near sea level in New Zealand. Succeeds in Portugal, Argentina; Austin, Texas and the British Isles. Also known as: Cedro blanco; teotlate, white cedar, Mexican white cedar, cedar-of-Goa
Physical Characteristics

 Cupressus lusitanica is an evergreen Tree growing to 35 m (114ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a fast rate.
Cupressus lusitanica is an evergreen Tree growing to 35 m (114ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10 and is not frost tender. The flowers are pollinated by Wind.
Suitable for: medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very acid soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Cupressus benthami Endl. Cupressus glauca Lam. Cupressus lindleyi Lind. ex Parl.
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Antifungal Antirheumatic Antitussive Astringent Cancer Deodorant Skin Styptic
The bark is astringent[ 46 , 299 ]. The leaves are used to treat catarrh and headache, and are sometimes used in the treatment of cancer[ 299 ]. The vapour from a leaf decoction is inhaled several times a day for treatment of flu[ 299 ]. The leaf sap is applied topically to treat skin diseases[ 299 ]. The essential oil from the leaves is used in the treatment of rheumatism, whooping cough and as a styptic[ 299 ]. The essential oil from the leaves and hexane leaf extracts has shown antifungal activity against skin pathogens, which supports the use against skin diseases[ 299 ]. A crude ethanol extract of the leaves has shown cytoxicity in a range of cancer cell lines, with cell death being due to apoptosis[ 332 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Cosmetic Deodorant Essential Fencing Fuel Furniture Hedge Insecticide Shelterbelt Soap making Soil stabilization Wood
Agroforestry Uses: Trees are suitable as windbreaks[ 303 ]. They are grown as a live fence[ 303 ]. The plant makes an excellent hedge, and is much planted for this purpose in Guatemala[ 331 ]. The hedges may be trimmed to any height and become very dense by continued pruning[331. Very amenable to trimming, it is sometimes used in topiary[ 331 ]. Mexican cypress gives only limited protection against soil erosion[ 303 ]. Pure stands on slopes or erosion-prone sites should be underplanted with other suitable species[ 303 ]. Other Uses An essential oil obtained from the leaves, twigs and branches of the tree is used as an adjuvant and perfume in soaps, room sprays, deodorants and other products[ 299 ]. Distillation of the leaves, twigs, fruits or flowers yields 0.05 - 3% essential oil; the reported compositions vary widely[ 299 ]. The leaves are used to protect stored grain from insects[ 299 ]. The heartwood is yellowish, pale brown, or pinkish, sometimes streaked or variegated; it is usually sharply demarcated from the 30 - 75mm wide band of white sapwood. The wood is of very fine and uniform texture; straight or irregular-grained; of rather high lustre, fragrant. It is light in weight; soft to hard; heavy; and of high durability[ 299 , 331 ]. It saws well and is easy to work with hand and machine tools; it finishes well and has good nail-holding properties, but boring a clean hole is difficult; it stains and polishes well[ 299 ]. It is highly esteemed for construction purposes and is used to make the sounding boards of guitars and mandolins, furniture, poles and posts[ 299 , 303 , 316 , 331 ]. The wood makes a good fuel[ 303 ]. An ornamental tree.
Special Uses
Hedge
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
The tree is found at elevations of 1,000 - 4,000 metres in tropical and subtropical areas[ 303 ]. It grows in seasonally moist to permanently moist climates, with annual precipitation typically between 1,000 and 1,500 mm and a dry season lasting not more than 2 - 3 months[ 303 ]. It also occurs in very moist climates with annual precipitation up to 4,000mm[ 303 ]. It prefers areas where the mean annual temperature is in the range 12 - 30°c, and is not generally damaged by occasional snow or brief periods of frost, though there are significant differences in this among provenances[ 303 ] Prefers a sunny position, tolerating light shade[ 418 ]. Flourishes in deep, moist, well-drained, fertile loams of neutral to slightly acidic reaction[ 303 ]. Plants cannot withstand waterlogging[ 303 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5.5 - 6.5, tolerating 5 - 7[ 418 ]. The tree has escaped from cultivation and become invasive in Malawi[ 299 ]. Trees commence producing seed around the age of 6 - 9 years, or later on unfavourable sites[ 303 ]. Flowering takes place at the driest time of the year, with male and female flowers arising at different points on the crown (monosexual). Cones develop within 6 months after wind pollination and take 2 years to mature[ 303 ]. Weeding is an absolute must during the 1st years. Pruning is practised so that trees yield high-quality, knot-free sawlogs. Pruning should be done when trees are 3 years old, with 3 further prunings at 6, 9 and 13 years of age in a 25-30 year rotation. Trees grown for high-quality timber should be pruned to 30% of their stem height every 3 years without diminishing volume growth. Thinning is prescribed before each pruning. In early years, individual trees should show an annual height increment of 120 - 150cm (200cm in exceptional cases). Trees produce poles after 10 years and general-purpose timber after 20 years. They need to be protected from fire and rodent attack[ 303 ]. Annual wood production potential is 15 - 40 m3/ha[ 418 ]. Natural regeneration is good on burnt areas and natural clearings, if competition from ground flora does not become intensive[ 303 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - pre-sowing treatment is not necessary, but for rapid and uniform germination, stratification in damp sand for 30 days is recommended[ 303 ]. Direct sowing by placing seeds in bamboo sleeves has been used with some success, but sowing in a nursery bed is more common. Germination takes place in 20 - 30 days, the expected germination rate is 30 - 45% from mature, healthy seed lots[ 303 ]. Seedlings grown in raised beds are 5 - 7 cm tall in about a week, when they should be transferred into containers that have been prepared 3 - 4 weeks beforehand by sieving the soil to remove large particles and then allowing the soil to form a crumb structure, which promotes good drainage[ 303 ]. Plants 20 - 30 cm tall are transferred to a nursery before being planted out[ 303 ]. After extraction, the seeds are dried in the sun to 6-10% mc before they are stored. Long-term seed storage behaviour is orthodox. Germination rate for seeds in hermitic storage for 21 years at 5 deg. C with less than 10% mc is 10%; viability can be maintained in hermitic storage at 3 deg. C with 6-10% mc. With normal dry storage, 75% germination can be maintained for 1 year and for several years if seeds are refrigerated at 4 deg. C[ 303 ].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Mexican Cypress (Cupressus lusitanica). Also known as: Cedro blanco; teotlate, white cedar, Mexican white cedar, cedar-of-Goa
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: Mexico (Chihuahua, Zacatecas, Chiapas, Ciudad de México, Guerrero, Hidalgo, México, Michoacán de Ocampo, Puebla, Tlaxcala, Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave) SOUTHERN AMERICA: Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, El Salvador
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
The tree has escaped from cultivation and become invasive in Malawi[ 299 ].
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : Cupressus lusitanica (Mexican Cypress): Status: Least Concern

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Mill.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Cupressus lusitanica
|
|
|
|