 |
|
https://edibleplants.org/ |
 |
| Fidy Ratovoson |
Translate this page:
Summary
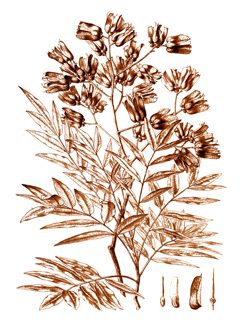
Katrafay or Cedrelopsis grevei is a deciduous bush tree endemic from Madagascar. It is usually 28 m in height. The trunk is straight with diameter of about 60cm and can be unbranched for up to 9 m. The stem bark is bitter and aromatic. It is used in local rum and as an ingredient in non-alcoholic drinks. Katrafay is considered to be one of the most important medicinal trees. The bark and leaves yield essential oil that is used in traditional medicine particularly in the treatment of malaria, fever, and muscular fatigue. A stem bark extract is used for coughs, headache, asthma, tuberculosis, rheumatism, pneumonia, etc. The wood is used as construction material and for fuel and charcoal-making. It is resistant to fungal and insect attacks. C. grevei can be grown from seed or cuttings.
Physical Characteristics

 Cedrelopsis grevei is a deciduous Tree growing to 22 m (72ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a slow rate.
Cedrelopsis grevei is a deciduous Tree growing to 22 m (72ft) by 20 m (65ft) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 10.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry or moist soil and can tolerate drought.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Katafa crassisepalum Costantin & Poiss.
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Inner bark Oil
Edible Uses: Drink Oil
The bitter and aromatic stem bark is used to aromatise local rum, and is also an ingredient of bitter, non-alcoholic drinks[ 299 ]. One of the most important medicinal trees in Madagascar, it is valued especially for the essential oil obtained from the bark (see medicinal uses below).
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Anthelmintic Antiarthritic Antiasthmatic Antidiarrhoeal Antirheumatic Antitussive Aphrodisiac Febrifuge
Hypotensive Malaria Odontalgic Parasiticide Tonic
One of the most important medicinal trees in Madagascar, it is valued especially for the essential oil obtained from the bark, but also has a wide range of other applications. There have been several studies carried out on the plant. The constituents of the essential oil can be extremely variable depending on the location of collection. The main components are ishwarane, beta-caryophyllene, alpha-copaene, beta-elemene and alpha-selinene[ 299 ]. The oils from the bark and the leaf were found to have a similar composition, but the relative percentages of some compounds notably differed[ 299 ]. Numerous coumarins have been isolated from the stem bark. One of these, cedrecoumarin A, showed agonistic activity on both alpha and beta-oestrogenic receptors as well as superoxide scavenging activity[ 299 ]. The hexane extract of the stem bark furthermore yielded triterpenoids, limonoid derivatives, pentanortriterpenoids, a hexanortriterpenoid and quassinoids[ 299 ]. The bark extract has been shown to induce a progressive decrease in blood pressure, which is partly due to the presence of coumarins[ 299 ]. A crude stem bark extract showed significant cicatrizing effect on skin ulcers, as well as antibacterial activity (e.g. against Staphylococcus albicans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and antifungal activity (against Candida albicans)[ 299 ]. The essential oil obtained from the bark is commonly used in massaging to treat general body pain, toothache, broken bones, muscular pain, arthritis and rheumatism, and a massage of the back is given to treat tiredness and fever. It is also used in baths for these purposes. Its tonic effects as well as its aphrodisiac effects are well appreciated, as it is considered to improve physical and mental fitness[ 299 ]. A stem bark extract is traditionally taken against cough, asthma, tuberculosis, pneumonia, diabetes, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, rheumatism, intestinal worms, headache, tiredness and as a post-partum tonic. It is also used as a vaginal shower after childbirth for its tonic effects, and is externally applied to wounds and skin infections[ 299 ]. Sometimes a root bark decoction is taken to treat diarrhoea or asthma[ 299 ]. A vapour bath of the leaves is taken to treat weakness of the blood vessels, headache and a sore throat[ 299 ]. The seeds are chewed as an anthelmintic and to treat stomach-ache[ 299 ].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Charcoal Fuel Furniture Oil Parasiticide Wood
Other uses rating: Medium (3/5). Other Uses: An essential oil is obtained from the bark. It is mainly used medicinally[ 299 ]. The heartwood is pale yellow to pale brown, somewhat mottled and slightly darker than the 25mm wide band of whitish sapwood. The grain is usually straight; texture fine. The wood is scented and contains resin cells. The wood is very heavy, very hard, flexible. It works fairly well with hand and machine tools, but has a marked blunting effect and stellite-tipped sawteeth are needed. Splitting on nailing and screwing is common, and pre-boring is recommended. The wood glues, polishes, waxes, varnishes and paints well. It is reputed for its resistance to wood rot and insect attack. The sapwood is susceptible to Lyctus borers. The heartwood is very resistant to impregnation. The wood has a wide range of used, being employed in heavy construction, carving, cabinet work, tool handles, interior joinery, interior trim, heavy parquet flooring, sliced veneer, plywood, ship and boat building, railway sleepers, vehicle bodies, electricity and construction poles and cattle enclosures. Because of its hardness and resistance to fungal and insect attack, it is considered imperishable and it is traditionally used for making royal Sakalava tombs[ 299 ]. The wood is used for fuel and for making charcoal[ 299 ].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Found in the wild on a wide variety of soil types, often on red or yellow sandy soils, but it grows taller in river valleys than on plateau soils[ 299 ]. The tree grows slowly, with annual increments in height of less than 50cm per year. It reaches a height of 50 - 300cm by the age of 7 years[ 299 ]. It is estimated to need over 40 years to produce a small pole[ 299 ]. This species can be either monoecious or dioecious. If dioecious, then both male and female forms need to be grown if fruit and seed are required[ 299 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - a high germination rate when sown fresh and directly into the field[ 299 ]. Cuttings.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Katrafay or Cedrelopsis grevei
Native Range
AFRICA: Madagascar
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : This taxon has not yet been assessed but is knwn to be vulnerable

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Baill.
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Cedrelopsis grevei
|
|
|
|