 |
|
USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database |
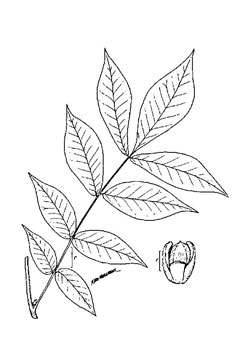 |
| USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / USDA NRCS. Wetland flora: Field office illustrated guide to plant species. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. |
Translate this page:
Summary
Carya species,
Pecans and hickory trees. Pecans are more likely to succeed in Mediterranean regions, especially in areas with hot summers and adequate water. Hickory trees struggle with the mild winters of the Mediterranean unless grown in higher elevations or cooler parts of the region. In both cases, sufficient irrigation during the dry summer months is crucial for successful cultivation.
Due to their adaptability and hardiness, Carya species are highly recommended for long-term, low-maintenance nut production. Grafted trees can yield a valuable nut crop within 3 – 4 years of planting and grow to a height of 12m (40ft). Several species have excellent edible nuts, rich in oils and B vitamins, and are native to North America. They have a lovely autumn colour. Most species in this genus have a wide distribution range, and seeds from the most appropriate provenances should be sought to find trees more suited to your growing conditions. Pecan (C. illinoinensis) is a fast-growing, large tree with sweet and delicious nuts. Eat the nuts raw or cooked; they make an excellent dessert, are added to ice cream, and are used in cakes and bread. Milk is made from nuts and thickens soups, season corn cakes, and hominy. Harvest in late autumn; eat immediately or store in a cool place in the shell for up to six months. Nut oil is edible and a staple crop. They cast a heavy shade in leaf, but because they are late coming into leaf (usually late spring) and lose their leaves early in the autumn, they are eminently suitable for mixed woodland planting with shrubs and other trees beneath them. Hickories are smaller trees with tinier nuts and prefer more humid conditions. Shellbark Hickory (C. laciniosa) and Shagbark Hickory (C. ovata) both have excellent nuts and grow to about 30m (100ft). Mockernut (C. tomentosa), another US native, is found mainly along ridges, dry hills and hillsides. Use the nuts in a similar way to pecans. Several North American hybrids produce delicious nuts, especially the Hicans, hybrids between C. illinoinensis and other Carya species.
Hicans have large and tasty nuts but are less productive than pecans.
Bloom Color: Yellow.
Main Bloom Time: Early spring, Late spring, Mid spring. Form: Oval, Rounded.
Physical Characteristics

 Carya laciniosa is a deciduous Tree growing to 30 m (98ft 5in) at a slow rate.
Carya laciniosa is a deciduous Tree growing to 30 m (98ft 5in) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6. It is in leaf from June to October, in flower from April to May, and the seeds ripen from September to October. The species is monoecious (individual flowers are either male or female, but both sexes can be found on the same plant) and is pollinated by Wind. The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
C. sulcata. Juglans laciniosa.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Canopy;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Sap Seed
Edible Uses: Sweetener
Seed - raw or cooked in pies, cakes etc[183]. Sweet, with a very fine flavour[183], it has the largest seeds of the hickories[227], up to 5cm long[229]. Probably the finest flavoured hickory[117]. The shell is hard and thick[101, 117] and the cracking quality is poor compared to C. ovata[183]. The seed ripens in late autumn and, when stored in its shell in a cool place, will keep for at least 6 months[K]. Sap - a sweet flavour[62]. Tapped in spring, it can be boiled down to a syrup or sugar and be used in similar ways to maple syrup[101, 183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Astringent Detergent
The inner bark is astringent and detergent[257]. It has been used as a dressing for cuts and has been chewed to treat sore mouths[257].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Fuel Wood
Wood - close-grained, tough, hard, heavy, elastic, very flexible. It weighs 50 lb. per cubic foot. An excellent wood, it is used for tool handles, baskets, fuel etc[46, 61, 63, 82, 226, 227]. A dynamic accumulator gathering minerals or nutrients from the soil and storing them in a more bioavailable form - used as fertilizer or to improve mulch.
Special Uses
Carbon Farming Dynamic accumulator Food Forest
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Management: Standard Regional Crop Staple Crop: Oil
Landscape Uses:Pest tolerant, Aggressive surface roots possible. Prefers a deep moisture-retentive loam in a sunny sheltered position, requiring a good summer for best development[1, 63, 137, 200]. A very ornamental but slow growing tree[1], it is sometimes cultivated for its edible seed, and is also sold in local markets in N. America[82]. There are some named varieties[183] though some of these are likely to be hybrids. 'Fayette' is a thin shelled form[200]. 'Henry' has a very large nut[200]. Trees have been planted on an experimental scale in Germany for their wood[50]. Hybridizes in the wild with C. ovata[227]. Trees take up to 15 years from seed to bear fruit[117]. Plants are strongly tap-rooted and should be planted in their permanent positions as soon as possible[1, 137]. Sowing in situ would be the best method so long as the seed could be protected from mice[1, 200]. Trees are late coming into leaf (usually late May to June) and lose their leaves early in the autumn (usually in October)[137]. During this time they cast a heavy shade. These factors combine to make the trees eminently suitable for a mixed woodland planting with shrubs and other trees beneath them[137]. Plants in this genus are notably resistant to honey fungus[200]. Most species in this genus have quite a wide range of distribution and, in order to find trees more suited to this country, seed from the most appropriate provenances should be sought[137]. Most trees growing in Britain at present tend to only produce good seed after hot summers[137]. Trees are self-fertile but larger crops of better quality seeds are produced if cross-pollination takes place[229]. Special Features:North American native, Wetlands plant, Inconspicuous flowers or blooms. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 9 through 4. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is a standard with a non-suckering single trunk [1-2]. The root pattern is a tap root similar to a carrot going directly down [1-2].
Carbon Farming
-
Management: Standard
Plants grow to their standard height. Harvest fruit, seeds, or other products. Non-Destructive management systems.
-
Regional Crop
These crops have been domesticated and cultivated regionally but have not been adopted elsewhere and are typically not traded globally, Examples in this broad category include perennial cottons and many nuts and staple fruits.
-
Staple Crop: Oil
(0-15 percent protein, 16+ percent oil). Some of these are consumed whole while others are exclusively pressed for oil. Annuals include canola, poppyseed, maize, cottonseed, sunflower, peanut. Perennials include high-oil fruits, seeds, and nuts, such as olive, coconut, avocado, oil palm, shea, pecan, and macadamia. Some perennial oil crops are consumed whole as fruits and nuts, while others are exclusively pressed for oil (and some are used fresh and for oil).
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - requires a period of cold stratification. It is best sown in a cold frame as soon as it is ripe[78]. Stored seed should be kept moist (but not wet) prior to sowing and should be sown in a cold frame as soon as possible[78]. Where possible, sow 1 or 2 seeds only in each deep pot and thin to the best seedling. If you need to transplant the seedlings, then do this as soon as they are large enough to handle, once more using deep pots to accommodate the tap root. Put the plants into their permanent positions as soon as possible, preferably in their first summer, and give them some protection from the cold for at least the first winter[78, K]. Seed can also be sown in situ so long as protection is given from mice etc and the seed is given some protection from cold[200] (a plastic bottle with the top and bottom removed and a wire mesh top fitted to keep the mice out is ideal)
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: Canada, Ontario (south), Indiana, Michigan (south), New York (west), Ohio, Pennsylvania (south), West Virginia, United States, Illinois, Iowa (southeast), Kansas (east), Missouri, Oklahoma, Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware (north), Georgia (north), Kentucky, Maryland (west), Mississippi, North Carolina (north-central), Tennessee, Virginia (west), Texas (Hardin Co.),
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(F.Michx.)Loudon.
Botanical References
1143200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Carya laciniosa
|
|
|
|