 |
|
Ted Bodner @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Miller, J.H. and K.V. Miller. 2005. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. University of Georgia Press, Athens. |
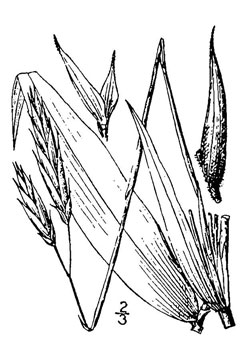 |
| USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913. An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. Vol. 1: 295. |
Translate this page:
Summary
Canebrake bamboo - Young shoots are edible and cooked. They are used as a pot-herb. The seed is also cooked and used as a wheat substitute. The extensive growth of the plant provides streambank stabilization, sediment retention, and bioaccumulation of nutrients and toxins.So long as it can be restrained, the plant makes an excellent, dense hedge or screen. Arundinaria gigantea tecta is a smaller subspecies commonly called dwarf canebrake and grows to about 1.5m. Conditions for dwarf canebrake are similar to the larger version.
Physical Characteristics

 Arundinaria gigantea is an evergreen Bamboo growing to 9 m (29ft 6in).
Arundinaria gigantea is an evergreen Bamboo growing to 9 m (29ft 6in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6. It is in leaf all year. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Wind.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
A. macrosperma. Arundo gigantea. Bambusa newmanii.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Shady Edge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Seed Shoots Stem
Edible Uses:
Young shoots - cooked[11, 22, 46, 105, 183]. Used as a pot-herb[236]. Seed - cooked[46, 61, 161]. It can be used as a wheat substitute[2, 105], for which it is not much inferior[213], but it is rather small and difficult to collect in quantity[159]. The plants only flower at irregular intervals of several years.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Cathartic
The root is cathartic. A decoction has been used to stimulate the kidneys and 'renew strength'[257].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Basketry Fodder Hedge Musical Soil stabilization Weaving
Agroforestry Uses: With its extensive running root system, the plant is ideal for helping to control soil erosion, especially along the sides of rivers[352]. The extensive growth of the plant provides streambank stabilization, sediment retention, and bioaccumulation of nutrients and toxins[1050].So long as it can be restrained, the plant makes an excellent, dense hedge or screen[352]. The canes are used as pipe-stems, are woven into baskets and mats plus a variety of other purposes[169, 236]. The hollow stems can be made into flutes[257]. Carbon Farming Solutions - Industrial Crop: biomass (Crops grown for non-food uses. Industrial crops provide resources in three main categories: materials, chemicals, and energy. Traditional materials include lumber and thatch, paper and cardboard, and textiles) [1-1]. Fodder: bank.
Special Uses
Carbon Farming Food Forest Hedge
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Fodder: Bank Management: Managed Multistem Wild Crop
Prefers an open loam of fair quality and a position sheltered from cold drying winds[1, 11, 25]. Succeeds on peaty soils. Requires abundant moisture and plenty of organic matter in the soil. Plants are intolerant of drought[1]. Succeeds in full sun or dappled shade in warm, humid, damp conditions[200]. Some reports say that this plant is only hardy in S.W. England[1, 11, 25] though another report says that the roots are hardy to about -30°c if they are heavily mulched[169]. This plant used to form very extensive stands in much of south-eastern N. America, but it provides a nutritious forage and is very easily destroyed by the continuous grazing of cattle or the rooting of pigs and so has been greatly reduced in the wild[236]. This species is notably resistant to honey fungus[200]. Plants only flower at intervals of many years. When they do come into flower most of the plants energies are directed into producing seed and consequently the plant is severely weakened. They sometimes die after flowering, but if left alone they will usually recover though they will look very poorly for a few years. If fed with artificial NPK fertilizers at this time the plants are more likely to die[122]. The rootstock is running, forming new shoots from late May[25]. Carbon Farming Solutions - Managed bamboo forest sequester more carbon than wild bamboo and the same as fast-growing tropical trees like eucalyptus. Cultivation: minor global crop. Management: managed multistem (Describes the non-destructive management systems that are used in cultivation) [1-1]. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 9 through 5. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. An evergreen. The plant growth habit is a runner spreading indefinitely by rhizomes or stolons [1-2]. The root pattern is rhizomatous with underground stems sending roots and shoots along their length [1-2].
Carbon Farming
-
Fodder: Bank
Fodder banks are plantings of high-quality fodder species. Their goal is to maintain healthy productive animals. They can be utilized all year, but are designed to bridge the forage scarcity of annual dry seasons. Fodder bank plants are usually trees or shrubs, and often legumes. The relatively deep roots of these woody perennials allow them to reach soil nutrients and moisture not available to grasses and herbaceous plants.
-
Management: Managed Multistem
Regularly removing some multiple stems. A non-A non-destructive management systems maintaining the soil organic carbon.
-
Wild Crop
Some wild plants have strong historical or contemporary use. Although they are not cultivated crops, they may be wild-managed.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - surface sow as soon as it is ripe in a greenhouse at about 20°c. Do not allow the compost to dry out. Germination usually takes place fairly quickly so long as the seed is of good quality, though it can take 3 - 6 months. When large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on in a lightly shaded place in the greenhouse until large enough to plant out. Bamboos only flower at intervals of several years and so seed is rarely available. Division in late spring as new growth commences. Take divisions with at least three canes in the clump, trying to cause as little root disturbance to the main plant as possible. Grow them on in light shade in a greenhouse in pots of a high fertility sandy medium. Mist the foliage regularly until plants are established. Plant them out into their permanent positions when a good root system has developed, which can take a year or more[200]. Rhizome cuttings. Basal cane cuttings.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Canebrake bamboo, Cane reed, Giant cane, Giant cane bamboo.
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: United States, Indiana (south), Ohio (south), West Virginia, Illinois (south), Missouri (south), Oklahoma, Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland (southeast), Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Texas,
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(Walter.)Muhl.
Botanical References
1143200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
© 2010, Plants For A Future. Plants For A Future is a charitable company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales. Charity No. 1057719, Company No. 3204567.