 |
|
|
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Rasbak |
Translate this page:
Summary
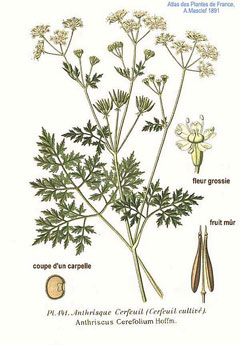
Physical Characteristics

 Anthriscus cerefolium is a BIENNIAL growing to 0.5 m (1ft 8in) by 0.3 m (1ft).
Anthriscus cerefolium is a BIENNIAL growing to 0.5 m (1ft 8in) by 0.3 m (1ft).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 7 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from May to June, and the seeds ripen from June to July. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects. The plant is self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Chaerophylum sativum.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Shady Edge; Hedgerow; Cultivated Beds;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Leaves Root
Edible Uses: Condiment
Edible leaves - raw in salads or used as a flavouring in cooked foods such as soups and stews[2, 14, 21, 27, 46, 61, 100, 244]. A mild aromatic flavour[183] that is suggestive of aniseed[238]. The leaves are often used as a flavouring, they form the basis of the seasoning 'fines herbes'[200] and are an essential ingredient of 'bouquet garni'[244]. The leaves should always be used fresh because the delicate flavour does not withstand drying or prolonged cooking[238, 244]. The leaves are ready for harvesting in about 8 weeks from sowing, the plant responds well to cut and come again harvesting[200]. The flowers are used as a seasoning[183]. The root is said to be edible[177, 183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Digestive Diuretic Expectorant Ophthalmic Poultice Stimulant
Chervil is not widely used as a medicinal herb, though it is sometimes employed as a 'spring tonic' for cleansing the liver and kidneys, is a good remedy for settling the digestion and is said to be of value in treating poor memory and mental depression[238, 244, 254]. The fresh plant, harvested just before flowering, is digestive, diuretic, expectorant, poultice and stimulant[9, 21, 201]. The juice is used in the treatment of dropsy, arthritis and chronic skin ailments[9]. The bruised leaves are used as a poultice for slow-healing wounds[9] and a warm poultice is applied to painful joints[268]. An infusion of the fresh leaves is also used as an eyewash to treat sore or inflamed eyes[244].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a well-drained moisture retentive soil[200]. Plants dislike hot dry summers[200], it is best to give summer crops a cool shady position but winter crops require a sunny position[14, 18, 37, 52]. Tolerates a pH in the range 5.8 to 7.6. Plants are hardy to about -10°c[200]. Chervil is occasionally cultivated as a salad plant, especially in France[268]. There are some named varieties[183]. It can supply fresh leaves all year round from successional sowings, especially if given some protection in winter[238]. Although a biennial, it is usually cultivated as an annual[238]. It often self-sows when grown in a suitable position[18, 200]. Be careful if harvesting this plant from the wild because it is superficially similar to some poisonous species such as young plants of hemlock, Conium maculatum[244]. Chervil is an aromatic plant with pleasantly scented leaves[245]. It is said to be a good companion plant for growing with carrots and radishes[18, 201], the radishes becoming hotter and crisper[201]. It also grows well with dill and coriander[201]. When grown with lettuces it is said to protect them from aphids and ants, the plant is also said to repel slugs[238].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - sow in situ in succession from February to October. The seed usually germinates in 2 - 3 weeks[200]. The February, September and October sowings should be made in a very sheltered warm and sunny position outdoors or under some protection such as a frame. Other sowings can be made in a position that has at least some shade from the midday sun since the plant runs to seed quickly if it gets too hot or the soil is dry[238]. The seed only remains viable for about a year[238].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Cyprus, Iran, Iraq (north), Turkey, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan EUROPE: Austria, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany (south), Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, Belarus, Estonia, Moldova, Russian Federation (Astrakhan, Rostov), Ukraine (incl. Krym), Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece, Croatia, Italy (incl. Sardinia), North Macedonia, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, France (southeast)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
(L.)Hoffm.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment