 |
|
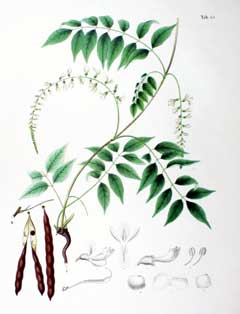
commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Millettia_japonica_SZ43.png |
 |
| commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:S_Sepp |
Translate this page:
Summary
UPDATE 12/09/2011: Wisteria japonica Siebold & Zucc. is a synonym of Millettia japonica (Siebold & Zucc.) A.Gray
Physical Characteristics
![]()
![]() Wisteria japonica is a deciduous Climber.
Wisteria japonica is a deciduous Climber.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 8. It is in flower from July to August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
It can fix Nitrogen.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid and neutral soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Milletia japonica. Sieb.&Zucc.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Shady Edge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Leaves Seed
Edible Uses:
Seed - cooked[105]. A famine food, used when all else fails[177]. Some caution is advised, see the notes on toxicity at the top of the page. Young leaves - cooked[105]. A famine food, they are only used when all else fails[177].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a good loamy soil in a sunny south or south-west facing position, sheltered from cold winds and from early morning sun on frosty mornings[11, 200]. Plants can become chlorotic on alkaline soils[200]. A soil that is too rich results in excessive foliage at the expense of flowering[200]. This species is not hardy in the colder areas of the country[200]. There is some confusion over the correct name of this species, many authorities referring it to a separate genus as Millettia japonica (Sieb.&Zucc.)A.Gray.[249]. Plants can take a few years to settle down after planting out[219]. Too much shade or too rich a soil are normally the culprits, some form of root restriction can be beneficial[219]. A climbing plant, attaching itself to branches or whatever by twining in a clockwise direction[249]. Plants in this genus are notably susceptible to honey fungus[200]. This species has a symbiotic relationship with certain soil bacteria, these bacteria form nodules on the roots and fix atmospheric nitrogen. Some of this nitrogen is utilized by the growing plant but some can also be used by other plants growing nearby[200]. The plants also form a symbiotic relationship with a mycorrhizal fungus which makes more water, phosphorus and other minerals available to the plants[249].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
The seed does not exhibit any dormancy habits. It can be sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame and should germinate in the spring. Pre-soak stored seed for 24 hours in warm water and then sow in a greenhouse in early spring. The seed can also be sown in an outdoor seedbed in late spring[126]. Germination should take place in the first spring, though it can sometimes be delayed for another 12 months. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when they are large enough to handle and grow them on in a cold frame for their first winter. Plant them out in late spring or early summer. Plants are very slow from seed and can take up to 20 years to come into flower[200]. Basal cuttings of side-shoots in early to mid summer in a frame[200]. Take the cuttings as soon as the new growth has hardened sufficiently, each cutting should have 2 - 3 leaves[249]. It can also help to remove a shallow slice of bark from the bottom 15mm of the cutting to expose extra cambium, since this will encourage more callusing and better rooting[249]. When kept in a mist frame with a bottom heat of 27 - 30°c, they will root within 4 weeks and produce well-established plants by the autumn[249]. Layering in spring. Simply lay any convenient long shoot along the ground and cover it with a shallow layer of soil. The shoot will readily produce roots at intervals along the stem. When these are well formed, the shoot can be divided up into a number of plants. These should be potted up and kept in a lightly shaded position in a greenhouse until well established and can then be planted out as required.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Korea, Japan (Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Siebold.&Zucc.
Botanical References
1158200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
© 2010, Plants For A Future. Plants For A Future is a charitable company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales. Charity No. 1057719, Company No. 3204567.