 |
|
Thomas G. Barnes @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database |
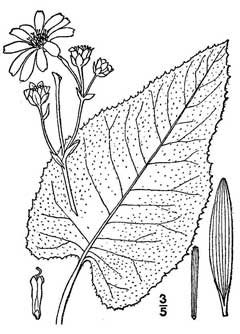 |
| USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database / Britton, N.L., and A. Brown. 1913. An illustrated flora of the northern United States, Canada and the British Possessions. 3 vols. Charles Scribner's Sons, New York. Vol. 3 |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

 Silphium terebinthinaceum is a PERENNIAL growing to 1.5 m (5ft) by 1 m (3ft 3in).
Silphium terebinthinaceum is a PERENNIAL growing to 1.5 m (5ft) by 1 m (3ft 3in).
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 4. It is in flower from July to August, and the seeds ripen in August. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts:
Edible Uses: Gum
None known
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Diuretic Emetic Expectorant Tonic Vermifuge
A tea made from the roots is vermifuge and a tonic for general debility[4, 61, 222]. A tea made from the leaves is emetic, it has been used in the treatment of coughs, lung ailments and asthma[4, 61, 222]. A resin in the plant is diuretic[4, 61, 222].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Gum
A gum or resin that is obtained from the stem can be chewed to cleanse the mouth and teeth[207].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Succeeds in any ordinary garden soil[1]. Prefers a deep moisture retentive moderately fertile soil that is not too nitrogen rich, in sun or dappled shade[200]. Succeeds in the wild or woodland garden[200]. Plants have a deep and extensive root system which makes transplanting difficult[200].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in a greenhouse[200]. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots as soon as they are large enough to handle and plant them out in the summer. Division in spring[188]. This is very difficult due to the deep and extensive root system.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
NORTHERN AMERICA: United States (Indiana, Michigan, New York, Ohio, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Kentucky, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, Mississippi, Tennessee (east))
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
Jacq.
Botanical References
200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment