 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mespilus_germanica_Sturm2.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Llez |
Translate this page:
Summary
Mespilus germanica is a synonym of Crataegus germanica. Mespilus germanica,
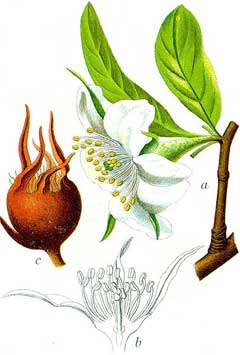
Medlar is a small, deciduous, ornamental tree valued for its unique fruit, which has an unusual ripening process called “bletting” before it becomes palatable when eaten fresh. The fruit is eaten raw or cooked. For the best flavour, the fruit is harvested in late autumn, stored, stalk upwards, and in a cool place until it softens, a process that involves waiting until it is close to decay or “bletting.” The fruit’s flesh changes from white to brown, becoming soft, sweet, and richly flavoured during this process. When properly bletted, medlar fruit tastes sweet and reminiscent of tropical fruit. The size of the fruit can vary, with wild species producing fruit up to 25mm in diameter, while cultivated varieties can reach up to 65mm or more. Medlar fruit can also be used in cooking, making jams, jellies, and desserts. The fruit may require frost exposure to improve its flavour in cooler climates. The tree is drought-tolerant once established. Medlar has attractive white blossoms.
Medlar is native to Iran, Iraq, and the Caucasus region. It has been cultivated for centuries in many parts of Europe, including France, Germany, Italy, Greece, Spain, and Great Britain. It is well-adapted to temperate climates and has been introduced into various regions, from the Mediterranean to parts of Eastern Europe and even the Pacific Northwest of the United States.
Harvesting: autumn.
Physical Characteristics

 Mespilus germanica is a deciduous Tree growing to 6 m (19ft) by 6 m (19ft) at a medium rate.
Mespilus germanica is a deciduous Tree growing to 6 m (19ft) by 6 m (19ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from May to June, and the seeds ripen in November. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees. The plant is self-fertile.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil. The plant can tolerates strong winds but not maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Crataegus germanica. Pyrus germanica.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Secondary; Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Fruit
Edible Uses:
Fruit - raw or cooked[2, 3, 5, 7, 12]. The fruit does not always ripen fully in cooler temperate zones such as Britain. However it can be harvested in late autumn (preferably after it has had some frost) whilst still hard and then needs to be bletted before it can be eaten raw. This entails storing it, stalk end upwards, in a cool place for a short while until it is on the point of (but not quite) rotting[200], a state described as incipient decay. At this stage the flesh turns from white to brown, becomes very soft and is quite sweet with an absolutely delicious flavour that somewhat resembles a luscious tropical fruit[K]. The fruit of the wild species is up to 25mm in diameter, though some cultivars can be 65mm or more in diameter[200].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Astringent Laxative
The pulp of the fruit is laxative[7]. The leaves are astringent[7]. The seed is lithontripic[7]. It is ground up for use, but caution should be employed since the seeds contain the toxin hydrocyanic acid[7]. The bark has been used as a substitute for quinine, but with uncertain results[7].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Wood
Agroforestry uses:
Medlar can be used as a small fruit tree in mixed orchards or home gardens. It also has ornamental value due to its attractive flowers and unique fruit. Wood - hard, flexible[100]. 1. Nectary - Flowers rich in nectar and pollen:
Yes – Medlar flowers produce nectar and pollen, attracting bees and other pollinators.
2. Wildlife - Food (Fruit, Seeds, Leaf litter, Shelter, Nesting, Roosting):
Yes – The fruit is consumed by birds and some mammals. The tree’s dense foliage can offer shelter and roosting opportunities for birds and small animals.
3. Invertebrate Shelter (Overwintering sites, Leaf litter, Groundcover):
Yes – The rough bark and fallen leaf litter can provide shelter for invertebrates, and the tree may create overwintering sites for beneficial insects.
4. Pest Confuser (Smell):
No – Medlar does not emit a significant scent that would confuse pests.
Special Uses
Food Forest
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Succeeds in most soils[11], preferring one that is moist and well-drained[1, 37, 200]. Prefers a sunny position[1, 3] and a fertile soil[188]. Occasionally cultivated for its edible fruit, there are some named varieties[183, 200]. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 9 through 6. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is a standard with a non-suckering single trunk [1-2]. In garden design, as well as the above-ground architecture of a plant, root structure considerations help in choosing plants that work together for their optimal soil requirements including nutrients and water. The root pattern is branching: a heart root, dividing from the crown into several primary roots going down and out [2-1]. Medlar fruits are harvested in Autumn when they have ripened.
Medlar trees flower in Spring. Mespilus germanica is generally self-fertile, meaning it can produce fruit without the need for a different variety for pollination.
Medlar trees are slow to moderate growers, reaching a height of about 4-5 meters (13-16 feet) and taking several years to mature and start bearing fruit, often around 3-4 years after planting.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in late autumn in a cold frame[78]. The seed has a very hard and impermeable seedcoat and will not usually germinate until it has gone through two winters. Commercially, such seeds are soaked for a short while in sulphuric acid to break down the seed coat and allow the seed to take up moisture, this is a very delicate procedure and difficult to do on a small scale. A home gardener could try soaking the seed for 24 hours in warm water then cold stratifying it for 2 - 3 months at 1 - 5°c before sowing it. Alternatively, if you can harvest the seed green (as soon as it is mature but before the seed coat has dried and hardened), then sow it immediately in a cold frame you might reduce the time needed for it to germinate. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and grow them on in the cold frame for their first winter. Plant them out into their permanent positions in late spring or early summer, after the last expected frosts. Cuttings of mature wood, November in a cold frame. Poor percentage. Layering in autumn or early spring. Takes 18 months[78].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Ciscaucasia, Dagestan, Georgia, Iraq (north), Russian Federation, Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia, Turkey, Turkmenistan (south),Iran (north). EUROPE: Ukraine, Krym, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy (incl. Sardinia, Sicily (but doubtfully indigenous)),
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
11200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment