 |
|
|
 |
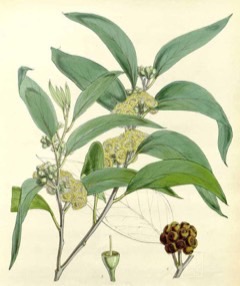
| Ian Brooker and David Kleinig wikimedia.org |
Translate this page:
Summary
Physical Characteristics

 Eucalyptus delegatensis is an evergreen Tree growing to 40 m (131ft) by 25 m (82ft) at a fast rate.
Eucalyptus delegatensis is an evergreen Tree growing to 40 m (131ft) by 25 m (82ft) at a fast rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 7. The flowers are pollinated by Bees, Insects.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil. It cannot tolerate atmospheric pollution.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
E. delegatensis R.T.Baker subsp. delegatensis. E. delegatensis subsp. tasmaniensis. E. delegatensis subsp. tasmaniensis
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Eucalyptus leaves are a traditional Aboriginal herbal remedy. The essential oil found in the leaves is a powerful antiseptic and is used all over the world for relieving coughs and colds, sore throats and other infections[254]. The essential oil is a common ingredient in many over-the-counter cold remedies[254]. The plant is an aromatic, astringent, tonic herb that sticks to the teeth and turns the saliva red[238]. The report says that the leaves, essential oil and oleo-resin are used[238], but does not specify which properties apply to the different parts of the plant[K]. The leaves and the oil will have very similar properties, the oil being much stronger in its effect since it is distilled from the leaves[K]. Detailed below is how the oleo-resin and oil are commonly used in other species[K]. The essential oil obtained from various species of eucalyptus is a very powerful antiseptic, especially when it is old, because ozone is formed in it on exposure to air. It has a decided disinfectant action, destroying the lower forms of life[4]. The oil can be used externally, applied to cuts, skin infections etc, it can also be inhaled for treating blocked nasal passages, it can be gargled for sore throat and can also be taken internally for a wide range of complaints[4]. Some caution is advised, however, because like all essential oils, it can have a deleterious effect on the body in larger doses[4]. An oleo- resin is exuded from the tree[238]. It can also be obtained from the tree by making incisions in the trunk[4, 152]. This resin contains tannin and is powerfully astringent, it is used internally in the treatment of diarrhoea and bladder inflammation[4, 152, 238], externally it is applied to cuts etc[4, 152]. Treats throat ailments[156].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
An essential oil is obtained from the leaves. Total quantity of the oil, and its composition, can vary widely from plant to plant, but we have reports that the fresh leaves contain around 1.8 - 3.9% (2.5 - 5.6% dry weight) essential oil. The main components include phellandrene, cymene, pperitone, methyl cinnamate and eudesmol[1659 ]. The heartwood is pale brown, straw-coloured or pinkish; the 30mm thick band of sapwood is almost white. The wood is open-textured, straight-grained, with conspicuous growth rings. It bends fairly well, is easily worked and polishes well. An excellent timber, it is widely in construction, for purposes such as building framing, flooring, plywood and veneers, furniture, panelling, turnery, handles and pulp for hardboard and paper[1097 , 1658 ]. Eucalypts are culturally important to the Indigenous Australians for a great variety of uses and meanings (Neyland, M. 2010. Eucalyptus delegatensis Forests).
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Eucalyptus delegatensis is native to the temperate climate of southeastern Australia, where it is found at elevations up to 1,500 metres. Summers are warm and can be dry, with most rainfall occurring in the winter months and a dry season that can be up to 3 months long. Mean annual rainfall is within the range 2,500 - 3,700mm, sometimes as snow; mean maximum of the hottest month is 21c; mean minimum of the coldest month is 0c, and there are generally around 70 - 100 frosts a year[1658 ]. When dormant, the plant can survive temperatures down to about -12c, but young growth is more tender and can be severely damaged at -1c[418 ]. Requires a sunny position, succeeding in a wide range of well-drained soils of high to moderate fertility[418 ]. The soils of the better forests in which it grows are moist but well-drained loams, especially those derived from granites or dolerites, but the mother rock may be a variety of sedimentary deposits in some places[1658 ]. Prefers a pH in the range 5.5 - 6.5, tolerating 5 - 7[418 ]. A quick-growing tree that is easy to regenerate[1658 ]. It responds well to coppicing[1212 ]. Eucalyptus delegatensis occurs at a higher elevation than any other important timber species in Australia. The natural occurrences of the species are likely to have snow on the ground for several weeks each year[1658 ]. Annual wood production potential is 10 - 25 cubic metres per hectare[418 ]. Eucalyptus species have not adopted a deciduous habit and continue to grow until it is too cold for them to do so. This makes them more susceptible to damage from sudden cold snaps. If temperature fluctuations are more gradual, as in a woodland for example, the plants have the opportunity to stop growing and become dormant, thus making them more cold resistant. A deep mulch around the roots to prevent the soil from freezing also helps the trees to survive cold conditions[200 ]. Many members of this genus are remarkably adaptable however, and there can be a dramatic increase in the hardiness of subsequent generations from the seed of survivors growing in temperate zones[200 ]. The tree has good prospects for planting in cool areas with a fairly high winter rainfall. It is one of the eucalypts resistant to frosts at least as severe as 9c at the time of planting[1658 ]. It has beens introduced into South Africa in Zones E and G on a relatively small scale and showed good height and diameter growth, but did not become a preferred species. Several countries have good specimens but the main commercial plantations are in New Zealand. In New Zealand it is planted both in containers and as bare-rooted planting stock. With adequate root-pruning good seedlings are prepared and planted either by hand or by machine The trees grow vigorously but the leading shoot is attacked each autumn by the fungus Mycosphaerella nubilosa, which results in multiple leaders. One of these becomes the main stem early in the next growing season, but successive attacks of the fungus cause a series of large branches to develop on the trunk. This is not of great significance if the crop is being grown for pulpwood, but is more serious in the case of sawtimber[1658 ].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - surface sow late winter/early spring in a sunny position in a greenhouse[11 , 78 , 134 ]. Species that come from high altitudes appreciate 6 - 8 weeks cold stratification at 2c[200 ]. Pot up the seedlings into individual pots as soon as the second set of seed leaves has developed, if left longer than this they might not move well. Plant out into their permanent positions in early summer and give them some protection from the cold in their first winter. The seed can also be sown in early summer, the young trees being planted in their final positions in late spring of the following year. The seed has a long viability[200 ].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Alpine ash, Gum-topped stringybark. White-top, Tasmanian Oak
Native Range
AUSTRALASIA: Australia (Tasmania, New South Wales (south), Victoria, Australian Capital Territory)
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
None Known
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status : Least Concern ver 3.1

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Corymbia citriodora | Lemon-Scented Gum, blue spotted gum, lemon eucalyptus, eucalyptus citriodora. | Tree | 45.0 |
10-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus brassiana | Cape York red gum | Tree | 20.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus caesia | Gungurru | Tree | 10.0 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 2 | 0 | |
| Eucalyptus camaldulensis | Red River Gum, Murray Red Gum, River Red Eucalyptus | Tree | 30.0 |
8-12
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus citriodora | Lemon-Scented Gum, Lemon Scented Eucalyptus | Tree | 45.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus coccifera | Mt. Wellington Peppermint | Tree | 15.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus dumosa | Water Mallee | Tree | 7.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus globulus | Tasmanian Blue Gum, Eurabbie, Blue Gum, Blue Eucalyptus | Tree | 55.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus gomphocephala | Tuart. Tuart Gum | Tree | 40.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DM | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus grandis | Flooded Gum, Gum, Rose Eucalyptus | Tree | 50.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | SN | DM | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus gummifera | Red Bloodwood | Tree | 15.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus gunnii | Cider Gum | Tree | 30.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus johnstonii | Yellow Gum, Johnston's gum | Tree | 60.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus largiflorens | Black Box | Tree | 18.0 |
9-11
| S | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus leucoxylon | Yellow Gum, White ironbark, White Eucalyptus | Tree | 15.0 |
10-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus macrorhyncha | Red Stringybark | Tree | 45.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus melliodora | Yellow Box | Tree | 30.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus microcorys | Tallow Wood, Australian tallowwood | Tree | 45.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus microtheca | Coolabah, Coolibah, Flooded Box, Coolibah | Tree | 15.0 |
9-12
| F | LMH | N | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus obliqua | Messmate | Tree | 60.0 |
8-12
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Eucalyptus pauciflora | Cabbage Gum, Snow gum | Tree | 12.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus pauciflora niphophila | Snow Gum | Tree | 6.0 |
6-9
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus perriniana | Spinning Gum | Tree | 6.0 |
7-10
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Eucalyptus piperita | Sydney Peppermint | Tree | 18.0 |
9-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus polybractea | Blue Mallee | Tree | 6.0 |
-
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus punctata | Grey Gum | Tree | 30.0 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 1 | 0 | |
| Eucalyptus racemosa | Snappy Gum | Tree | 0.0 |
-
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 3 | |
| Eucalyptus regnans | Mountain Ash | Tree | 75.0 |
8-11
| F | LMH | N | DMWe | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Eucalyptus robusta | Swamp Mahogany, Eucalyptus Gum | Tree | 30.0 |
8-12
| F | LMH | SN | DM | 0 | 3 | 4 |
|
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
F.Muell. ex R.T.Baker
Botanical References
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
A special thanks to Ken Fern for some of the information used on this page.
Readers comment
| Add a comment |
|
If you have important information about this plant that may help other users please add a comment or link below. Only comments or links that are felt to be directly relevant to a plant will be included. If you think a comment/link or information contained on this page is inaccurate or misleading we would welcome your feedback at [email protected]. If you have questions about a plant please use the Forum on this website as we do not have the resources to answer questions ourselves.
* Please note: the comments by website users are not necessarily those held by PFAF and may give misleading or inaccurate information.
To leave a comment please Register or login here All comments need to be approved so will not appear immediately.
|
Subject : Eucalyptus delegatensis
|
|
|
|