 |
|
(c) 2010 Ken Fern & Plants For A Future |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cornus_mas_Sturm40.jpg |
Translate this page:
Summary
Bloom Color: Yellow.
Main Bloom Time: Early spring, Early winter, Late winter, Mid spring, Mid winter. Form: Rounded.
Physical Characteristics

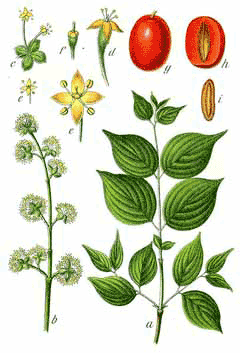
 Cornus mas is a deciduous Shrub growing to 5 m (16ft) by 5 m (16ft) at a medium rate.
Cornus mas is a deciduous Shrub growing to 5 m (16ft) by 5 m (16ft) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 5 and is not frost tender. It is in flower from February to March, and the seeds ripen in September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees.
It is noted for attracting wildlife.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and can grow in heavy clay soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils and can grow in very alkaline soils.
It can grow in semi-shade (light woodland) or no shade. It prefers moist soil. The plant can tolerates strong winds but not maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
C. mascula.
Plant Habitats
Woodland Garden Sunny Edge; Dappled Shade; Hedge;
Edible Uses
Edible Parts: Fruit Oil Oil
Edible Uses: Coffee Oil Oil
Fruit - raw, dried or used in preserves[2, 3, 7, 9, 13, 183]. Juicy, with a nice acid flavour[11]. The fully ripe fruit has a somewhat plum-like flavour and texture and is very nice eating, but the unripe fruit is rather astringent[K]. It is rather low in pectin and so needs to be used with other fruit when making jam[9]. At one time the fruit was kept in brine and used like olives[183]. The fruit is a reasonable size, up to 15mm long, with a single large seed[K]. A small amount of edible oil can be extracted from the seeds[7]. Seeds are roasted, ground into a powder and used as a coffee substitute[183].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
Astringent Cholera Febrifuge Nutritive
The bark and the fruit are astringent, febrifuge and nutritive[7]. The astringent fruit is a good treatment for bowel complaints and fevers, whilst it is also used in the treatment of cholera[4, 254]. The flowers are used in the treatment of diarrhoea[4].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Dye Hedge Hedge Oil Oil Tannin Wood
An oil is obtained from the seed[7]. A dye is obtained from the bark[3, 7]. No more details are given. Another report says that a red dye is obtained from the plant, but does not say which part of the plant[4]. The leaves are a good source of tannin[7]. Wood - very hard, it is highly valued by turners[7]. The wood is heavier than water and does not float[7]. It is used for tools, machine parts, etc[7, 11, 13, 61].
Special Uses
Attracts Wildlife Food Forest Hedge Hedge
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Border, Firewood, Pest tolerant, Hedge, Screen, Specimen, Woodland garden. An easily grown plant, it succeeds in any soil of good or moderate fertility[1], ranging from acid to shallow chalk[200]. Grows well in heavy clay soils. Prefers a moist soil[108] and a sunny position[15] but also succeeds in light shade[188]. Plants are fairly wind resistant[K]. Plants grow and crop well in pots. A very hardy plant, tolerating temperatures down to about -25°c[184]. At one time the cornelian cherry was frequently cultivated for its edible fruit, though it has fallen into virtual disuse as a fruit crop in most areas[3]. It is still being cultivated in parts of C. Europe and there are some named varieties[183]. 'Macrocarpa' has larger fruits than the type[182]. 'Nana' is a dwarf form, derived from a yellow-fruited clone[182]. 'Variegata' has been seen on a number of occasions with very large crops of fruit, even in years when the type species has not fruited well[K]. 'Jolico' has well-flavoured fruits 3 times larger than the species. There are also a number of cultivars with yellow, white and purplish fruit. Seedlings can take up to 20 years to come into fruit. Plants produced from cuttings come into fruit when much younger, though they do not live as long as the seedlings. A very ornamental plant[1] it flowers quite early in the year and is a valuable early food for bees[13, 108]. Plants in this genus are notably resistant to honey fungus[200].Special Features:Attracts birds, Not North American native, Attractive flowers or blooms. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 8 through 5. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is a standard with a non-suckering single trunk [1-2]. In garden design, as well as the above-ground architecture of a plant, root structure considerations help in choosing plants that work together for their optimal soil requirements including nutrients and water. The root pattern is branching: a heart root, dividing from the crown into several primary roots going down and out [2-1].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame or in an outdoors seedbed if there is sufficient seed[80, 113]. The seed must be separated from the fruit flesh since this contains germination inhibitors[80, 164]. Stored seed should be cold stratified for 3 - 4 months and sown as early as possible in the year[164]. Scarification may also help as may a period of warm stratification before the cold stratification[80, 164]. Germination, especially of stored seed, can be very slow, taking 18 months or more[164]. Prick out the seedlings of cold-frame sown seeds into individual pots as soon as they are large enough to handle and grow the plants on for their first winter in a greenhouse, planting out in the spring after the last expected frosts. Cuttings of half-ripe side shoots, July/August in a frame[188]. Cuttings of mature wood of the current year's growth, taken with a heel if possible, autumn in a cold frame. High percentage[78]. Layering of new growth in June/July. Takes 9 months[78].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Ciscaucasia, Dagestan, Georgia, Russian Federation, Russian Federation-Ciscaucasia,Turkey. EUROPE: Czechoslovakia (Czech Republic and Slovakia), Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Ukraine (incl. Krym), Former Yugoslavia, Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Romania, France,
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it's worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

| Related Plants
|
| Latin Name | Common Name | Habit | Height | Hardiness | Growth | Soil | Shade | Moisture | Edible | Medicinal | Other |
| Cornus alba | Tartarian Dogwood | Shrub | 3.0 |
3-7
| F | LMH | SN | Mwe | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Cornus alternifolia | Green Osier, Alternateleaf dogwood, Alternate Leaf Dogwood, Golden Shadows Pagoda Dogwood, Green Osi | Shrub | 6.0 |
3-8
| F | LMH | N | DM | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Cornus amomum | Silky Dogwood | Shrub | 3.0 |
4-8
| M | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Cornus asperifolia drummondii | Roughleaf Dogwood | Shrub | 4.0 |
5-9
| F | LMH | N | M | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Cornus australis | | Shrub | 4.0 |
6-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Cornus canadensis | Creeping Dogwood, Bunchberry dogwood, Bunchberry | Perennial | 0.3 |
2-7
| F | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Cornus capitata | Bentham's Cornel | Tree | 12.0 |
7-10
| M | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Cornus chinensis | | Tree | 10.0 |
7-10
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 3 | |
| Cornus controversa | Giant Dogwood, Wedding Cake Tree, | Tree | 15.0 |
5-8
| F | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Cornus coreana | | Tree | 20.0 |
5-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cornus elliptica | | Tree | 10.0 |
7-10
| M | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Cornus florida | Flowering Dogwood | Shrub | 6.0 |
5-9
| M | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Cornus hemsleyi | | Shrub | 4.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cornus hongkongensis | | Shrub | 15.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Cornus iberica | | Shrub | 4.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Cornus kousa | Japanese Dogwood, Kousa dogwood, Chinese Dogwood, | Tree | 10.0 |
5-8
| S | LMH | SN | M | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| Cornus kousa chinensis | Japanese Dogwood | Tree | 10.0 |
5-8
| | LMH | SN | M | 5 | 0 | 2 |
| Cornus macrophylla | Large-Leaf Dogwood | Tree | 15.0 |
5-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Cornus monbeigii | | Shrub | 5.0 |
6-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Cornus multinervosa | | Tree | 8.0 |
-
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Cornus nuttallii | Mountain Dogwood, Pacific dogwood, Western Dogwood | Tree | 10.0 |
6-8
| M | LMH | SN | DM | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Cornus oblonga | Oblong-Petal Dogwood | Tree | 6.0 |
8-11
| | LMH | SN | M | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| Cornus occidentalis | Western Dogwood | Shrub | 6.0 |
5-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 1 | |
| Cornus officinalis | Shan Zhu Yu, Asiatic dogwood, Japanese Cornel Dogwood | Shrub | 10.0 |
5-8
| M | LMH | SN | M | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Cornus poliophylla | | Shrub | 4.0 |
6-9
| | LMH | SN | M | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Cornus quinquenervis | | Shrub | 3.0 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 0 | |
| Cornus rugosa | Round-Leaved Dogwood | Shrub | 3.0 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | DM | 0 | 1 | |
| Cornus sanguinea | Dogwood, Bloodtwig dogwood | Shrub | 3.0 |
4-8
| | LMH | SN | M | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Cornus sericea | Red Osier Dogwood, Western dogwood | Shrub | 2.5 |
2-7
| F | LMH | SN | MWe | 2 | 2 | 4 |
|
|
Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Now available:
Food Forest Plants for Mediterranean Conditions
350+ Perennial Plants For Mediterranean and Drier Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens.
[Paperback and eBook]
This is the third in Plants For A Future's series of plant guides for food forests tailored to
specific climate zones. Following volumes on temperate and tropical ecosystems, this book focuses
on species suited to Mediterranean conditions—regions with hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters,
often facing the added challenge of climate change.
Read More
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
11200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment