 |
|
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:270_Sedum_album.jpg |
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Ies |
Translate this page:
Summary
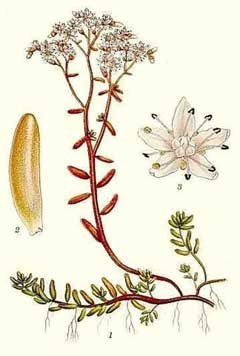
Bloom Color: White. Main Bloom Time: Early summer, Late summer, Late spring, Mid summer. Form: Spreading or horizontal.
Physical Characteristics

 Sedum_album is an evergreen Perennial growing to 0.1 m (0ft 4in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in) at a medium rate.
Sedum_album is an evergreen Perennial growing to 0.1 m (0ft 4in) by 0.5 m (1ft 8in) at a medium rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 6 and is not frost tender. It is in leaf all year, in flower from July to August, and the seeds ripen from August to September. The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Bees, flies. The plant is self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils, prefers well-drained soil and can grow in nutritionally poor soil. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers dry or moist soil and can tolerate drought. The plant can tolerate maritime exposure.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
S. athoum. S. balticum. S. turgidum.
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Leaves - raw or cooked[2, 46, 52, 100]. Usually eaten as a pickle[4], though it can also be added to salads or cooked with other leafy vegetables[244].
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
The leaves and stems are applied externally as a poultice to inflammations and are especially recommended for treating painful haemorrhoids[4, 244].
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
Agroforestry Uses:
The plant spreads aggressively and can be used for ground cover in a sunny position amongst plants tall enough not to be overrun by it. It is best planted about 45cm apart each way[208
]. Strong growing bulbs such as some lilies will grow happily through this ground cover[K
].
The plant can grow in very low moisture levels and has been used as a green covering on roofs[372
]. Green roofs are incorporated into the structure of the building, providing habitats for wildlife as well as insulating the building and helping to improve the environmen.t The subspecies minima and the cultivars 'Athorum' and 'Coral Carpet' have been specifically mentioned in this respect.
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Landscape Uses:Alpine garden, Border, Container, Ground cover, Rock garden, Specimen. A very easily grown plant, it succeeds in most soils[188] but prefers a fertile well-drained soil[200]. Established plants are drought tolerant[190, 200], they grow well in dry soils and succeed on a wall[190]. Requires a sunny position[188]. Plants spread rapidly and aggressively at the roots[190]. If clearing the plant from an area it is quite important to try and remove every part of the plant since even a leaf or a small part of the stem, if left on the ground, can form roots and develop into a new plant[200]. This species has white flowers. All members of this genus are said to have edible leaves, though those species that have yellow flowers can cause stomach upsets if they are eaten in quantity[62, 85]. Plants in this genus seem to be immune to the predations of rabbits[233]. Special Features:
Attractive foliage, Not North American native, Invasive. For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. An evergreen. The plant growth habit is a runner spreading indefinitely by rhizomes or stolons [1-2].
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - surface sow in spring in well-drained soil in a sunny position in a greenhouse. Do not allow the soil to dry out. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots when they are large enough to handle. If sufficient growth is made, it is possible to plant them out during the summer, otherwise keep them in a cold-frame or greenhouse for their first winter and plant them out in early summer of the following year[K]. Division is very easy and can be carried out at almost any time in the growing season, though is probably best done in spring or early summer. Larger divisions can be planted out direct into their permanent positions. We have found it best to pot up the smaller divisions and grow them on in a lightly shaded position in a cold frame, planting them out once they are well established in the summer.
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey,Iran (west). EUROPE: Finland (south), Norway (south), Sweden (south), Austria, Belgium, Switzerland, Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland (south), Slovakia, Estonia, Latvia, Ukraine, Krym, Albania, Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greece (incl. Crete), Croatia, Italy (incl. Sardinia, Sicily), North Macedonia, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, France (incl. Corsica), Portugal, AFRICA: Algeria, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia.
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it’s worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Expert comment
Author
L.
Botanical References
17200
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment
© 2010, Plants For A Future. Plants For A Future is a charitable company limited by guarantee, registered in England and Wales. Charity No. 1057719, Company No. 3204567.