 |
|
|
 |
| http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Gerhard_Elsner |
Translate this page:
Summary
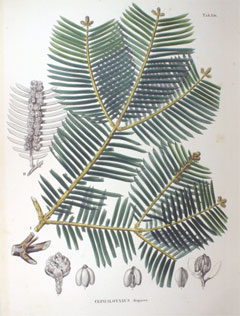
Physical Characteristics

 Cephalotaxus_harringtonia is an evergreen Shrub growing to 5 m (16ft) by 3 m (9ft) at a slow rate.
Cephalotaxus_harringtonia is an evergreen Shrub growing to 5 m (16ft) by 3 m (9ft) at a slow rate.
See above for USDA hardiness. It is hardy to UK zone 7 and is not frost tender. It is in leaf all year, in flower from April to May, and the seeds ripen from October to November. The species is dioecious (individual flowers are either male or female, but only one sex is to be found on any one plant so both male and female plants must be grown if seed is required). and is pollinated by Wind. The plant is not self-fertile.
Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils. Suitable pH: mildly acid, neutral and basic (mildly alkaline) soils. It can grow in full shade (deep woodland) or semi-shade (light woodland). It prefers moist soil.
UK Hardiness Map
US Hardiness Map
Synonyms
Taxus harringtonia.
Plant Habitats
Edible Uses
Fruit. - raw or cooked. About 2 - 3cm long[200]. The fruit of this plant is said to be astringent and inedible even when fully ripe[200]. However, several of its sub-species produce a very nice sweet fruit - see cultivation details for more information. Seed - raw or cooked[81, 105]. Oily[1] with a slightly resinous flavour[K]. The seed is up to 15mm long.
References More on Edible Uses
Medicinal Uses
Plants For A Future can not take any responsibility for any adverse effects from the use of plants. Always seek advice from a professional before using a plant medicinally.
None known
References More on Medicinal Uses
The Bookshop: Edible Plant Books
Our Latest books on Perennial Plants For Food Forests and Permaculture Gardens in paperback or digital formats.

Edible Tropical Plants
Food Forest Plants for Hotter Conditions: 250+ Plants For Tropical Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

Edible Temperate Plants
Plants for Your Food Forest: 500 Plants for Temperate Food Forests & Permaculture Gardens.
More

More Books
PFAF have eight books available in paperback and digital formats. Browse the shop for more information.
Shop Now
Other Uses
An oil obtained from the seed is used as an illuminant[105]. Very tolerant of pruning, this plant makes a very good hedge in shady positions[200].
Special Uses
References More on Other Uses
Cultivation details
Prefers a moist well-drained sandy soil but succeeds in most soils though it dislikes dry gravelly or chalky soils[1, 200]. Prefers a position in semi-shade but tolerates full shade[11, 81] and it also succeeds but does not usually thrive in full sun[200]. It grows very well in the mild wet coastal region of W. Scotland where it succeeds even in full sun[200]. Requires a humid sheltered site[200], strongly disliking very exposed positions[1]. Although the dormant plant is very cold-hardy, the young growth in spring, even on mature plants, is frost-tender and so it is best to grow the plants in a position sheltered from the early morning sun[K]. The Japanese plum yew is a very slow growing tree[185] with an excellent potential as a food crop in Britain. It generally has a large crop of fruit and seeds, these are often eaten in Japan. In addition, the seeds seem to be immune to the predations of squirrels, the seed on trees growing at Kew Botanical gardens being untouched even though virtually every other nut tree there has its crop destroyed[K]. There has been some confusion in the naming of this species. Some botanists have separated off C. drupacea as a separate species, though most nowadays include it as a subspecies of this plant as C. harringtonia drupacea. (Sieb.&Zucc.)Koidzumi., differing from the species in its shortly pedunculate male catkins[81]. In cultivation it is often known as the variety 'Fastigiata'[81]. Another subspecies, C. harringtonia nana. (Nakai.)Rehd. is a small spreading shrub to 2 metres, spreading by means of suckers[81, 200]. This form is said to have the best fruit of this genus[200], it is a very hardy plant, succeeding as far north as S. Sweden and Nova Scotia[200]. Plants are dioecious, but female plants sometimes produce fruits and infertile seeds in the absence of any male plants[11]. However, at least one male plant for every five females should be grown if you are growing the plants for fruit and seed. Plants have also been known to change sex[81]. Male cones are produced in the axils of the previous year's leaves, whilst female cones are borne at the base of branchlets[200]. The plant is heat tolerant in zones 9 through 3. (Plant Hardiness Zones show how well plants withstand cold winter temperatures.
Plant Heat Zones show when plants would start suffering from the heat.
The Plant Heat Zone map is based on the number of "heat days" experienced in a given area where the temperature climbs to over 86 degrees F (30°C).
At this temperature, many plants begin to suffer physiological damage. Heat Zones range from 1 (no heat days) to 12 (210 or more heat days).
For example Heat Zone. 11-1 indicates that the plant is heat tolerant in zones 11 through 1.) For polyculture design as well as the above-ground architecture (form - tree, shrub etc. and size shown above) information on the habit and root pattern is also useful and given here if available. The plant growth habit is multistemmed with multiple stems from the crown [1-2]. An evergreen.
References Carbon Farming Information and Carbon Sequestration Information
Temperature Converter
Type a value in the Celsius field to convert the value to Fahrenheit:
Fahrenheit:
The PFAF Bookshop
Plants For A Future have a number of books available in paperback and digital form. Book titles include Edible Plants, Edible Perennials, Edible Trees,Edible Shrubs, Woodland Gardening, and Temperate Food Forest Plants. Our new book is Food Forest Plants For Hotter Conditions (Tropical and Sub-Tropical).
Shop Now
Plant Propagation
Seed - best sown as soon as it is ripe in a cold frame[113], it should then germinate in the following spring[K]. A hard seedcoat can delay germination, especially in if the seed is not sown as soon as it is ripe[81, K]. Stored seed should be cold-stratified and sown in a cold frame in the spring[200]. Germination can take 18 months or more. Prick out the seedlings as soon as they are large enough to handle and grow them on for at least their first winter under cover. Plant out in late spring after the last expected frosts. Greenwood cuttings of terminal shoots, August/September in a humid cold frame[1, 200]. Difficult[113].
Other Names
If available other names are mentioned here
Native Range
TEMPERATE ASIA: Honshu, Japan, Kyushu, Shikoku,Korea.
Weed Potential
Right plant wrong place. We are currently updating this section.
Please note that a plant may be invasive in one area but may not in your area so it’s worth checking.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants Status :

Growth: S = slow M = medium F = fast. Soil: L = light (sandy) M = medium H = heavy (clay). pH: A = acid N = neutral B = basic (alkaline). Shade: F = full shade S = semi-shade N = no shade. Moisture: D = dry M = Moist We = wet Wa = water.
Expert comment
Author
(Knight. ex J.Forbes.)K.Koch.
Botanical References
11200275
Links / References
For a list of references used on this page please go here
Readers comment